todo
Overview 部分
-
垃圾回收机制
-
保留字
-
内存分布
-
访问权限符
-
Package
类
-
继承
-
类内类的顺序
容器
-
Vector
-
Exception
- fw
IO
Others
- regex
Java¶
约 3847 个字 587 行代码 15 张图片 预计阅读时间 27 分钟
Tip
- 用
jshell可以使用与 python 类似的交互
概念
-
SDK
-
JDK
功能齐全的 Java 开发工具包。包含JRE和Java Development Tools
-
JVM
Java 虚拟机(Java Virtual Machine, JVM)是运行 Java 字节码的虚拟机。JVM 有针对不同系统的特定实现(Windows,Linux,macOS),目的是使用相同的字节码,它们都会给出相同的结果。字节码和不同系统的 JVM 实现是 Java 语言“一次编译,随处可以运行”的关键所在。
-
JRE 是运行已编译 Java 程序所需的环境,主要包含以下两个部分:
-
JVM : 也就是我们上面提到的 Java 虚拟机。
-
Java 基础类库(Class Library):一组标准的类库,提供常用的功能和 API(如 I/O 操作、网络通信、数据结构等)。
-
overview¶
- Compiled Language
- All objects should be constructed in runtime and be stored in heap.
- 单根结构(除了C++的所有OOP语言) Every class in Java is a descendant of one class: Object
- Java 中的输入输出,Scanner 容易超时
//import java.util.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(a);
}
}
- Java 中的保留字
- Identifier
和 C++ 不同的语言特性
-
Java 中的常量使用关键字
final而不是const.final int a = 5; -
Java 中类型推导关键字为
varvar s = new StringBuffer(); -
Java 的 reference 更像是 C++中的指针,不可计算. 任何对象变量都是指针
- 对象变量的赋值
Example
将这里理解为类似指针,是操作权指向的赋予,不会像 C++ 一样做赋值
var a = new A(10);
var b = new A(20);
System.out.printf("%d %d\n", a.i, b.i);
a = b;
b.i = -20;
System.out.printf("%d %d\n", a.i, b.i);
-
Auto Memory Management -- 单根结构
-
index check
- Primitive 可以存放在栈,对象全部都放在堆(heap 只能通过
new获得)
- Primitive 可以存放在栈,对象全部都放在堆(heap 只能通过
Dynamic
- Java 中的一个文件只能含有一个
public类,其名称与文件名称相同
Java 的运行
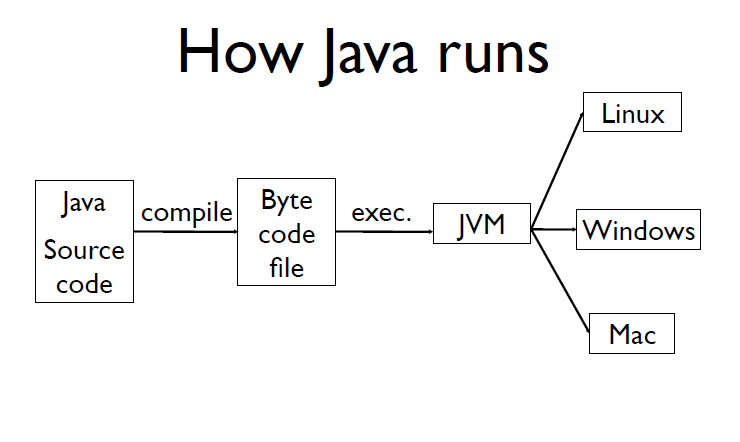
内存布局¶
Package¶
- Java 的 Package 依赖于目录
- 之后的代码属于这个 package
- 这部分代码必须放在一个名为
<Package name>的文件夹中
package <Package name>
- 设置寻找 Package 的地址
- 环境变量
- 通过
-cp指定寻找路径,java -cp java hello.Hello
Package的作用域
包在 Java 的访问控制中起着重要作用,主要涉及以下访问修饰符:
- public:公共访问,任何类都可以访问。
-
protected:受保护的访问,允许同一包内的类和不同包中的子类访问。
- 跟C++不同
-
默认(包私有):如果不指定访问修饰符,默认为包私有,只有同一包内的类可以访问。
- private:私有访问,仅在同一类内可见
Static Import¶
double r = Math.cos(Math.PI * theta);
import static java.lang.Math.PI;
import static java.lang.Math.*;
double r = cos(PI * theta);
String API¶
- 所有字符类型都是 unicode,就像下面的中文也会是一个字节
- 结尾没有
\0
String a = "hello你好"; // len = 7
String b = "hello"; // len = 5
- String 为不可变类型。
Methods¶
得到属性
- s.length ()
- s.charAt (int index)
切片
s.substring (int , int )
比较
s.compareTo ()s.equals ()s.equalsIgnoreCase ()Boolean startsWith (String str)Boolean endsWith (String str)
变换
String trim ()删除前导、后导空格String replace (char c 1, char c 2)替换public String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement)可使用正则表达式进行替换。- 正则表达式 与其他的值相互转化
String piStr = "3.14159";
Float pi = Float.ValueOf (piStr);
Float pi2 = Float.ParseFLOAT (piStr);
比较¶
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "abc"; // 指向字符串常量池
String t = "abc";
String u = new String("abc"); // new的时候一定会创建一个新的对象在heap
System.out.println(s == t); // true
System.out.println(s == u); // false
}
String str = "Person";
String str1 = new String("Person");
System.out.println(str == "Person"); // true
System.out.println(str1 == "Person"); // false
Basic¶
参数传递 - Passing value - 对象传递也是类似指针,无法阻止函数内部对对象的改变 Relation - 整型的 wrapper 在[-128,127]之间是一个固定的对象(类似于字符串常量池的概念)
Integer n1 = new Integer(47);
Integer n2 = new Integer(47);
System.out.println(n1 == n2); // false
Integer n3 = 47;
Integer n4 = 47;
System.out.println(n3 == n4); // true
Integer n1 = 147;// new Integer(47);
Integer n2 = 147;// new Integer(47);
System.out.println(n1 == n2); // false
垃圾回收 GC¶
深入理解 JVM 的垃圾回收机制 | 二哥的Java进阶之路 (javabetter.cn)
使用大端编码
Class¶
Note
-
类在内存中也是一个对象属于 Class
-
Java 会对 new 的对象的内存清空为 0
-
定义初始化,在构造函数之前,初始化顺序与在 class 中定义的顺序相关
-
一个类的定义,可以继承一个父类的同时,再实现多个接口
class MathTest extends Student implements BaseTest- 可以在
Student类中实现一部分接口的函数,在MathTest中就无需实现这部分
- 可以在
代理构造¶
Java 的代理构造和调用父类的构造函数都要放在构造函数开始的位置。
public Rectangle(int width, int length) {
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
}
public Rectangle() {
this(0, 0);
}
初始化顺序¶
Static member is to be initialized in the loading of the class
graph LR
1[Load 调用static函数] --> 2[定义初始化] --> 3[调用构造函数]
- Java的初始化会在Heap上申请内存,把这一块内存初始化为空
- 对于Primitive会赋初值如0
静态初始化
static { ... }
- 在类被装载的时候运行且只会执行一次
- 类的状态是运行时装载,所以可能一个类未被装载
定义初始化
{ ... }
- ==每次创建实例==都会调用
构造初始化
ClassName(){}
一个例子
class A {
{
System.out.println("class A : instance initializer");
}
public int i = baz();
{
System.out.println("class A : i = " + i);
}
public int baz() {
System.out.print("class A : baz\n");
return 0;
}
}
public class B extends A {
public int baz() {
System.out.print("class B baz : B\n");
return 10;
}
public int i = baz();
public static void main(String[] args) {
B b = new B();
}
}
- 输出
class A : instance initializer class B baz : B class A : i = 10 class B baz : B
函数的绑定¶
Case 2 Shape. Java
Java 默认为动态绑定,
- Static binding: call the function as the code
- Dynamic binding: call the function of the object
override¶
Final¶
Abstract & Interface¶
Abstract
- 一个抽象类中可以没有 abstract 函数,但含有 abstract 函数一定要是抽象类
Interface
- 不能拥有构造函数
- All data members in interface are public static final.
-
All methods in interface are public.
- 这里实现的时候一定要注意权限的问题,因为默认的权限是
public的,所以在实现函数的时候要加上publicinterface I { void f(); } class C { void f() { }; } interface A extends I { void f(); } class B extends C implements I { // ERROR : 正在尝试分配更低的访问权限; 以前为public,现在为default }
- 这里实现的时候一定要注意权限的问题,因为默认的权限是
-
implementsinterface可以实现多个接口
interface Instrument5 {
// Compile-time constant:
int i = 5; // static & final
// Cannot have method definitions:
void play(); // Automatically public
String what();
void adjust();
}
- 它前面的修饰符只能是
abstract / public
abstract interface BaseTest
Note
接口引入了新的方法类型:default 方法、static 方法和 private 方法。这些方法让接口的使用更加灵活。
- Java 8 引入的
default方法用于提供接口方法的默认实现,可以在实现类中被覆盖。这样就可以在不修改实现类的情况下向现有接口添加新功能,从而增强接口的扩展性和向后兼容性。
public interface MyInterface {
default void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("This is a default method.");
}
}
static方法无法在实现类中被覆盖,只能通过接口名直接调用(MyInterface.staticMethod()),类似于类中的静态方法。static方法通常用于定义一些通用的、与接口相关的工具方法,一般很少用。
public interface MyInterface {
static void staticMethod() {
System.out.println("This is a static method in the interface.");
}
}
- Java 9 允许在接口中使用
private方法。private方法可以用于在接口内部共享代码,不对外暴露。
public interface MyInterface {
// default 方法
default void defaultMethod() {
commonMethod();
}
// static 方法
static void staticMethod() {
commonMethod();
}
// 私有静态方法,可以被 static 和 default 方法调用
private static void commonMethod() {
System.out.println("This is a private method used internally.");
}
// 实例私有方法,只能被 default 方法调用。
private void instanceCommonMethod() {
System.out.println("This is a private instance method used internally.");
}
}
Enum 枚举类¶
-
也是类,相当于构建了匿名子类,不是像C一样的宏(会进行类型检查
int i = 1; i == ONE报错)-
==和equals效果相同,是比较特殊的引用类型equals会在null的时候报错enum类型的每个常量在JVM中只有一个唯一实例,所以可以直接用==比较
-
无法通过
new创建实例 Suit.values()直接遍历访问整个enum类的所有
-
public enum Rank { DEUCE, THREE, FOUR, FIVE, SIX,
SEVEN, EIGHT, NINE, TEN, JACK, QUEEN, KING, ACE }
public enum Suit { CLUBS, DIAMONDS, HEARTS, SPADES }
static {
for (Suit suit : Suit.values())
for (Rank rank : Rank.values())
protoDeck.add(new Card(rank, suit));
}
-
可以存在同名的函数与变量
-
解决
switch case的思路之一 -
枚举常量必须在字段和构造函数之前定义
public enum Planet { MERCURY(3.303e+23, 2.4397e6), VENUS(4.869e+24, 6.0518e6), EARTH(5.976e+24, 6.37814e6), MARS(6.421e+23, 3.3972e6), JUPITER(1.9e+27, 7.1492e7), SATURN(5.688e+26, 6.0268e7), URANUS(8.686e+25, 2.5559e7), NEPTUNE(1.024e+26, 2.4746e7), PLUTO(1.27e+22, 1.137e6); private final double mass; // in kilograms private final double radius; // in meters Planet(double mass, double radius) { this.mass = mass; this.radius = radius; } public double mass() { return mass; } public double radius() { return radius; } // universal gravitational constant (m3 kg-1 s-2) public static final double G = 6.67300E-11; public double surfaceGravity() { return G * mass / (radius * radius); } public double surfaceWeight(double otherMass) { return otherMass * surfaceGravity(); } public static void main(String[] args) { double earthWeight = Double.parseDouble(args[0]); double mass = earthWeight / EARTH.surfaceGravity(); for (Planet p : Planet.values()) System.out.printf("Your weight on %s is %f%n", p, p.surfaceWeight(mass)); } }
继承与多态¶
class BoardGame extends Game {
BoardGame(int i) {
super(i);
System.out.println("BoardGame constructor");
}
}
- Java 没有 name hide 的问题,子类的一个函数 override 不会覆盖父类的同名函数
- 静态初始化的顺序问题
- Upcast
内部类¶
- 装载是分开做的,只有在使用的时候才会进行装载。
- 函数中的内部类
- 会在前面加上数字编号以区分不同的函数中的类
成员内部类¶
- 成员内部类可以调用外部的变量
局部内部类¶
匿名类¶
- 构造匿名子类
- 可以访问外部的内容 but Argument must be final to use inside anonymous inner class
- 闭包 与它相关的本地变量不会被回收,(保存当时的外部环境)
- 定义初始化块可以充当它的初始化函数
// 函数中的匿名类
public Contents cont() {
return new Contents() {
private int i = 11;
public int value() {
return i;
}
}; // Semicolon required in this case
}
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
t.start();
}
}
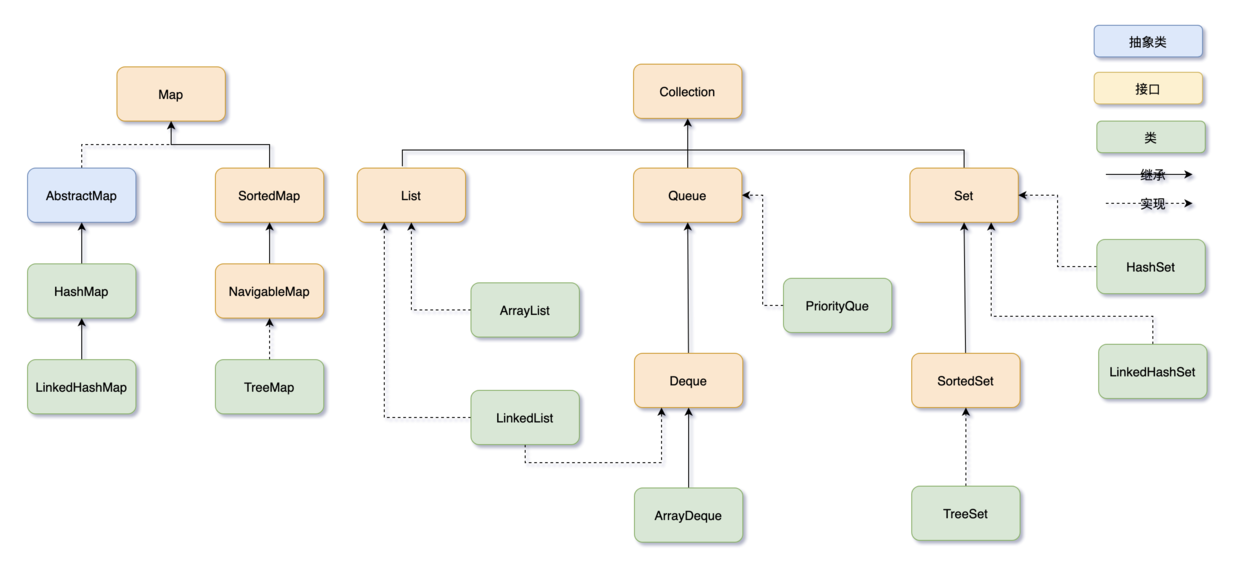
Generic Containers | 泛型容器¶
Var Args
static void f(Object[] x) {
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.println(x[i]);
}
}
f(new Object[] { new A(), new A(), new A() });
使用 Object 可以接受这种类型的数组,但是对于Array就会失效
- 与C++相同,同时使用index和iterator访问时,如果使用index删除某个元素,可能导致iterator的混乱
Iterator<A> it = v.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
ArrayList
ArrayList<Integer> a = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10));
// error
不应该使用int赋给Integer,ArrayList<Integer> a = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10));
Array¶
int [] a = new int[10];
for (var x: a){
x += 1; // 不会改变它的值,相当于使用值(尽管Array本身是指针)
}
int [] b = a; // 指针
b[0] = 16; // a[0] = 16
- 对象的数组中放的实质是指针
Value [] a = new Value[10];
for (var x: a) // 这里x为指针,通过x访问它的元素然后改变
Collection¶
- Java没有实现重载,访问某个元素只能使用
get不能使用[] - Java的泛型不支持Primitive,只能使用wrapper类
共有操作
addaddAll(Collection)toArray
Colletion
List¶
ArrayList<Content_Type> 存储方式为Array
add一个类的对象,放的还是指针
ArrayList<Value> list = new ArrayList<>;
...
Value v1 = list.get(0);
Set¶
Map¶
使用自己定义的类作为键值对
- must override both hashCode( ) and equals( ),
Generic¶
- A generic type declaration is compiled once and for all, and turned into a single class file. 这一点和C++不同
subtype

- Vector
WildCards
void printCollection(Collection<?> c) {
for (Object e : c) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
// 限定shape子类
public void drawAll(List<? extends Shape> shapes)
{ ... }
- 带边界的泛型可以是一个类或多个类的子类。例如,
<T extends A & B>表示T必须是A和B的子类。如果用户不清楚这一点,可能会误解如何使用泛型。
Exception & IO¶
System.out.println(true ? Integer.valueOf(1) : Double.valueOf(2.0));- 编程语言的格式对齐,一条表达语句的结果只能存在一种情况
- Java中
throw的对象一定是Throwable (the exception root class) object
匹配机制
- 和C++相同,父类放在最后
异常声明
- 未处理的异常必须要声明
throws ...void f() throws TooBig, TooSmall, DivZero{ } - 一个函数中存在异常
- 调用的函数抛出异常
- 自己抛出异常
类型
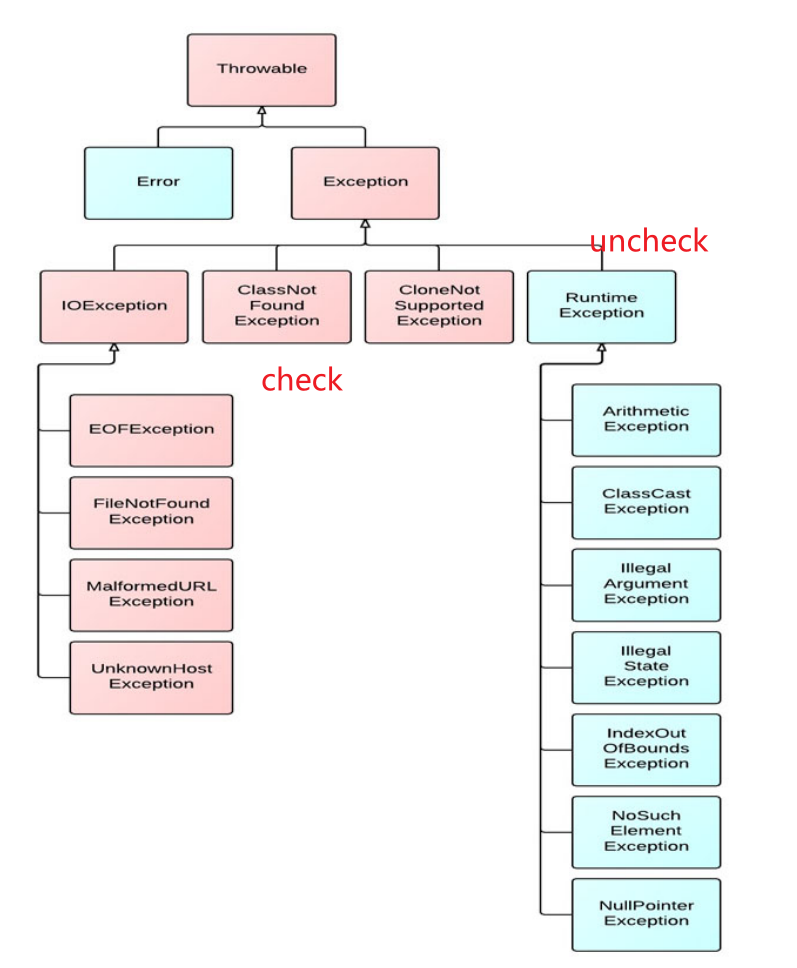
- Error 是编译时检查的错误
限制
-
When you override a method, you can throw only the exceptions that have been specified in
the base-class version of the method.
-
Classs
- 构造
- 仍然存在C++资源泄露的问题(文件)
- 非构造
- 构造
- 对于多来源的类,子类的能抛出的异常是父类的交集(可能被当做任何一种类,is-a)
Stream¶
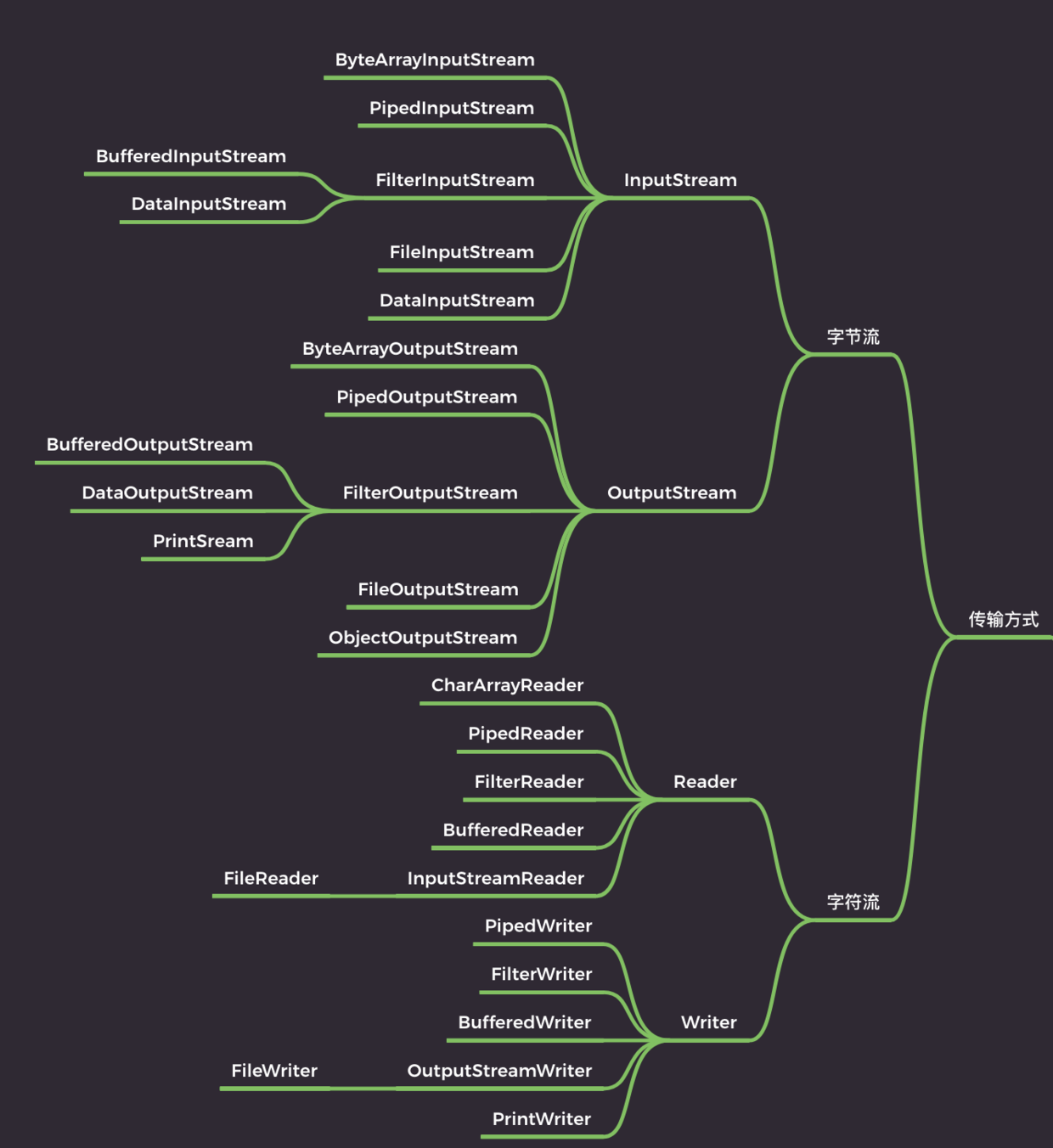
这里不同种类的IO不是相互替代的关系
version 1
-
inputStream
-
outputStream
一些需要注意的类
- media
filter Stream-
DataInputStream实现读写基本数据类型 读取xx个byte并转换¶
System.in.read 读取裸数据
Bridge
version 2
- Reader
- Writer
在binary和/R/W之间搭建桥梁
File Class¶
序列化¶
public class Employee implements Serializable {
public static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; // 用于检测是否是同一个版本,判断是否可用于反串行化
public String name;
public String address;
public transient int age; // transient瞬态修饰成员,不会被序列化
}
static和transient修饰的字段是不会被序列化的。- 读写之后的对象不是同一个对象
- 但是写进去的时候构造函数不会被调用,直接把值放进去
- 只有在父类也实现
Serializable才能保存其数据,也可以直接由父类实现,而子类不实现
transient
- 只能修饰字段,而不能修饰方法和类
自定义
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream oos) throws IOException {
oos.defaultWriteObject(); // 使用默认序列化
oos.writeObject(encrypt(password)); // 对敏感数据加密后序列化
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ois.defaultReadObject(); // 使用默认反序列化
password = decrypt((String) ois.readObject()); // 反序列化后解密
}
GUI¶
Note
MVC
MVVM
Thread¶

- RR round-robin-scheduling
- 在调用start之后,只是加入到了Ready queue中并不会马上执行
基本实现
public class MyThread extends ThreadThread t1; t1.setName(""); t1.start();
public class MyRunnable implements RunnableMyRunnable mr; Thread t1 = new Thread(mr, "name");- 好处:避免了 Java 单继承的局限性,Java 不支持多重继承,因此如果我们的类已经继承了另一个类,就不能再继承 Thread 类了。
函数
-
wait -
public final void wait() throws InterruptedException- 调用wait需要考虑后面的exception
-
进入等待队列前,会把所有线程的 key "归还"
-
回来的条件
-
被nofity
-
能够获得key
synchronized (theSender) { theSender.isValid = false; // theSender.notify(); } //
-
-
The
wait(),notify(), andnotifyAll()methods must be called in a synchronized method or a synchronized block on the calling object of these methods. -
sleep -
和wait抛出的异常相同
- 一个静态函数
Thread.sleep(<time>),针对对当前线程 -
使得休眠时间 >= 指定时间
-
yield-
放弃当前这个时间片,直接进入ready queue
-
可能导致资源被浪费:CPU 占用率居高不下
-
-
join -
等待
Group¶
- 介绍
- 每个线程属于一个group
- Tree的架构
- 优先级问题
- 默认和创建线程的线程优先级相同
synchronized | 对共享变量的访问控制¶
- 保证一个线程的变化(主要是共享数据的变化)被其他线程所看到
- zhi'neng
- 阻止同时访问某一段代码
- Synchronized Method | 不需要在函数内部使用关键字
synchronized void sync() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "in sync");
}

线程交互
自嵌套
-
java可以保证再次使用
key的正确性,不会导致死锁
DeadLock
Pipe
out - > in
Producer - Consumer¶
Explicit Lock¶
- 由 synchronized 是一个内置的同步机制(内部锁 | 隐式锁),它依赖于JVM来管理锁的获取和释放。
- 显式锁
ReentrantReadWriteLock rwLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
Lock readLock = rwLock.readLock();
Lock writeLock = rwLock.writeLock();
// 获取读锁
readLock.lock();
try {
// 执行读操作
} finally {
readLock.unlock();
}
// 获取写锁
writeLock.lock();
try {
// 执行写操作
} finally {
writeLock.unlock();
}
并行和并发¶
线程安全类¶
- ArrayList、HashSet 线程不安全¶
volatile¶
- mark 一个主存中的变量
-
不保证原子性(相邻原子操作之间不是原子)
- increment操作可能失效
- Any operation over double and long is not an atomic one, unless the variable is declared as volatile
- 对于一个
-
作为 fence (和OS中的指令作用
sfence.vma zero, zero很相似,用来刷新之前的写的值到memory/cache)- volatile object
Student Ss the pointer is volatile, not the whole object
- volatile object
Socket & JDBC¶
SQL¶
- PK 的选择
- 一般整数
- 数据字典
- {1 : "Name"}
- 数据库迁移
- 数据类型(某些特殊的)
TCP¶
- ServerSocket
- 在一个线程中一直等待连接,一旦来了一个连接就创建一个新的线程来处理(创建一个socket)
- Socket
- 具体的连接都是使用这个类
NIO¶
-
Channels: Connections to files, sockets etc that support non-blocking reads
-
Buffers: Array-like objects that can be directly read or written by Channels
- 不同的数据类型
- Selectors: Tell which of a set of Channels have IO events
- 向 selector 注册 channel
- 阻塞,
- SelectionKeys: Maintain IO event status and bindings
Lambda 表达式¶
- 没有变量必须存在
()btn.addActionListener(event -> System.out.println("OK"));
- 存在一个的情况下可以不加
() - Lambda expression needs an explicit target-type
- 从lambda 表达式引用的本地变量必须是最终变量或实际上的最终变量
- 内部新定义的值可以不是 final var
- Lambda expression's local variable i cannot redeclare another local variable defined in an enclosing scope. 表达式内部使用的值不能覆盖外部的值
- 闭包 closure
BinaryOperator<Long> add = (x,y) -> x+y;
System.out.println(add.apply(100L, 200L));
BinaryOperator<Long> addExp = (Long x,Long y) -> x+y;
System.out.println(addExp.apply(100L, 200L));
- 赋值
- 如果某个类/接口中只有一个函数,可以直接把lambda表达式赋值 | Functional Interface
interface Func {
void ff();
}
public class FuncInterface {
public void app(Func f) {
f.ff();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
FuncInterface fi = new FuncInterface();
fi.app(()->System.out.println("Hello"));
}
}
- Predicate
Predicate<Integer> atLeast5 = x-> x>5;
public inteface Predicate<T> {
boolean test(T t);
}
- Binary Operator
BinaryOperator<Integer> addInt = (x,y) -> x+y;
Stream | 流式计算¶
设计模式¶
单例模式 | Singleton¶
补充知识¶
命名规范¶
5 分钟编码,1 小时命名,笑 | 二哥的Java进阶之路 (javabetter.cn)
Java 正则表达式¶
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("your_regex_pattern"); // 创建正则表达式
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher("your_input_string"); // 创建匹配器对象
Pattern¶
Matcher类¶
Matcher 类 - Dev.java - Java 中文 (java-lang.cn)
boolean matches():整个输入字符串是否完全匹配正则表达式。
boolean find():扫描输入字符串,查找与正则表达式匹配的下一个子序列。
String group():返回上一次匹配的子序列。
int start():返回上一次匹配的起始索引。
int end():返回上一次匹配的结束索引(不包括)。
String replaceAll(String replacement):替换所有匹配的子字符串。
String replaceFirst(String replacement):替换第一个匹配的子字符串。
中文处理¶
处理输入输出¶
练习题¶
Week 1¶
Week 2¶
Question
Q 1
About access control in Java, which statement below is correct?
A. A member without any access modifier is default to private
B. A member without any access modifier is default to public
C. A member without any access modifier is default to protected
D. Classes in the same package can access members without any access modifier.
Note
Java 中的访问权限是 public、protected、default 和 private。其中 default 具有包访问权
Question
Q 2

Week 3 | Class¶
-
What will happen if you try to compile and execute B’s
main()method? ( )class A { int i; A(int i) { this.i = i * 2; } } class B extends A { public static void main(String[] args) { B b = new B(2); } B(int x) { System.out.println(x); } }D. This code will not compile
Note
class A中只有一个带参数的初始化函数,必须要显式调用!(如果删除则可以通过编译)
Week 5 容器¶
Question
Given list an object of ArrayList, which code below for //todo delete can remove an element in the list correctly and safely?
Iterator it = list.iterator();
int index = 0;
while (it.hasNext()){
Object obj = it.next();
if (needDelete(obj)) { // returns Boolean for removing or not
//todo delete
}
index ++;
}
A. list.remove(obj);
B. list.remove(index);
C. list.remove(it.next());
D. it.remove();
Question
For code below:
ArrayList<Integer> a = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ArrayList<Double> b = new ArrayList<Double>();
Which statement below is NOT correct?
A. a.getClass().equals(b.getClass()) is true
B. a.getClass() == b.getClass() is true
C. a instanceof ArrayList is true
D. a.getClass() == b.getClass() is false
Exception¶
Question
Suppose there is no file Hello.txt in the current directory. Run the program:
import java.io.*;
public class ABC {
public static void main(String argv[]) throws Exception {
ABC m=new ABC();
System.out.println(m.ff());
}
public int ff() {
try {
FileInputStream dis=new FileInputStream("Hello.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException fne) {
System.out.print("No such file found, ");
throw fne;
} finally {
System.out.print("Doing finally, ");
}
return 0;
}
}
A.
No such file found,
B.
No such file found ,0
C.
No such file found, Doing finally,
D.
No such file found, Doing finally, 0
Note
IO¶
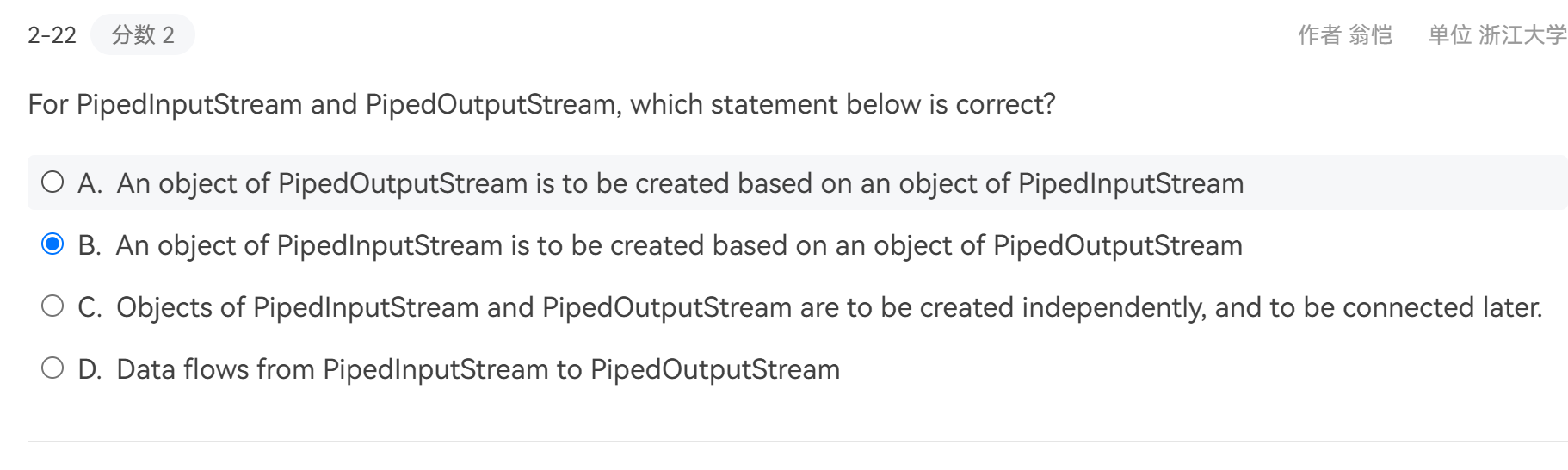
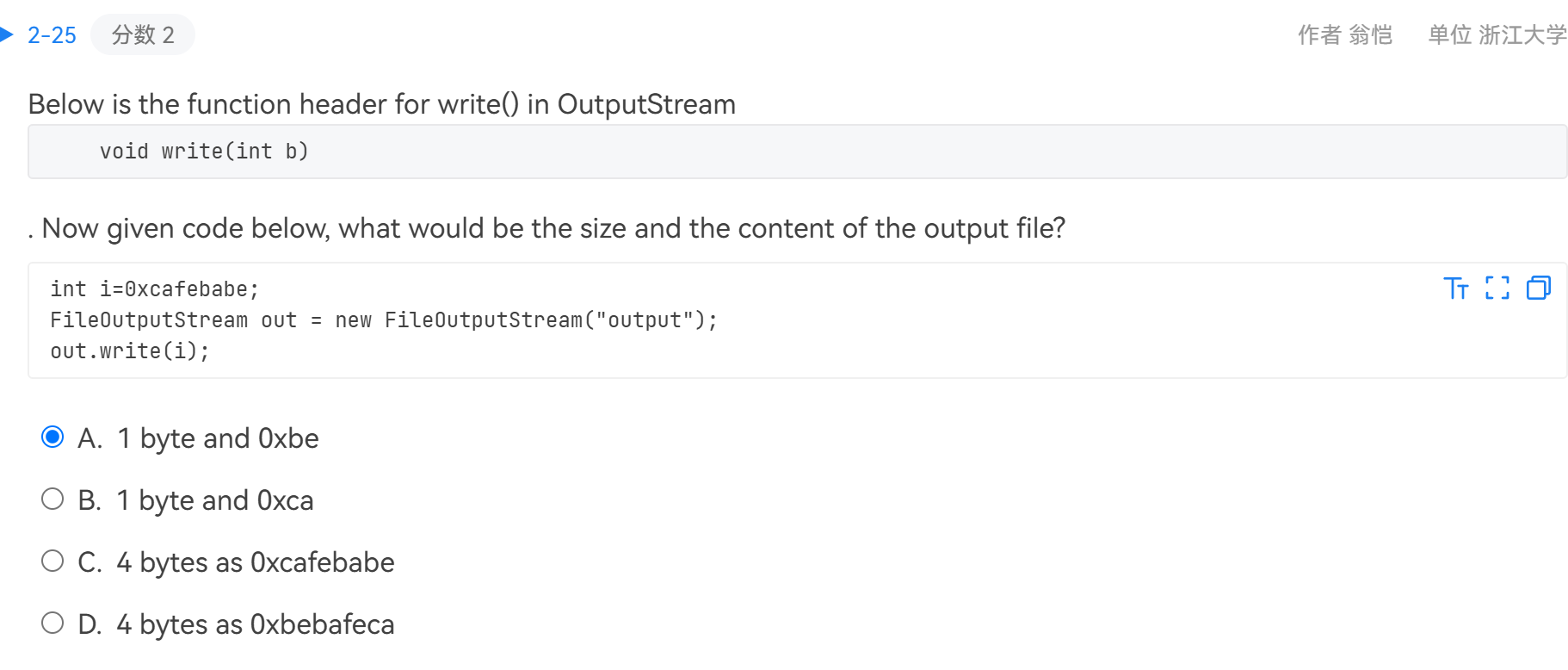

read()返回int,因为需要返回 -1 表示文件结束。
Week 10 | Thread & 同步问题¶

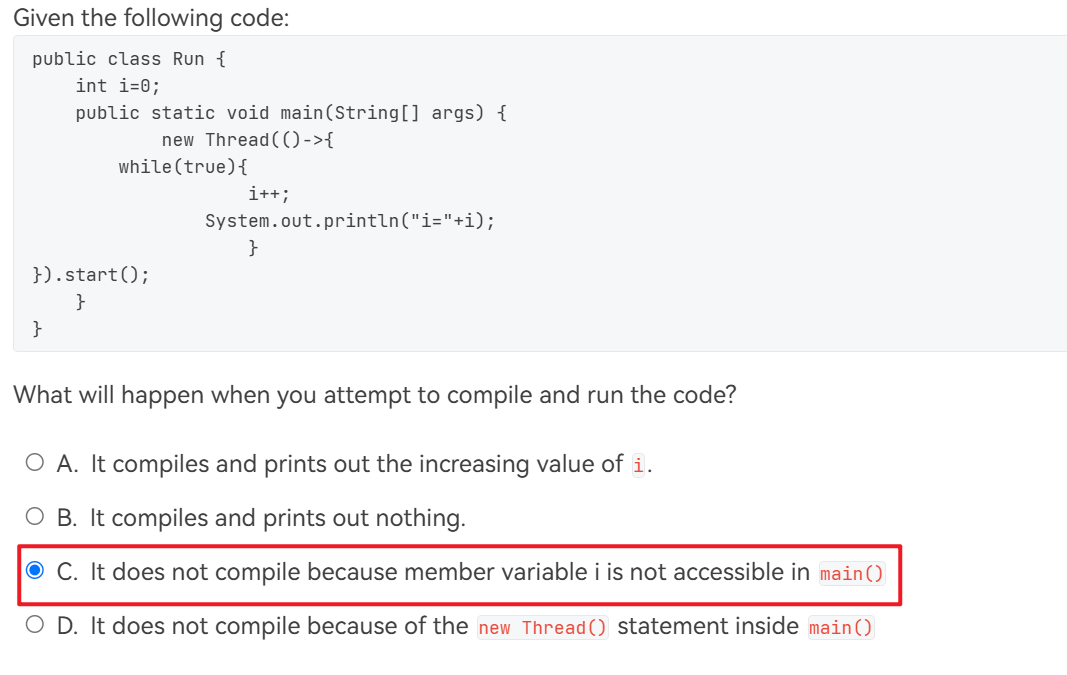
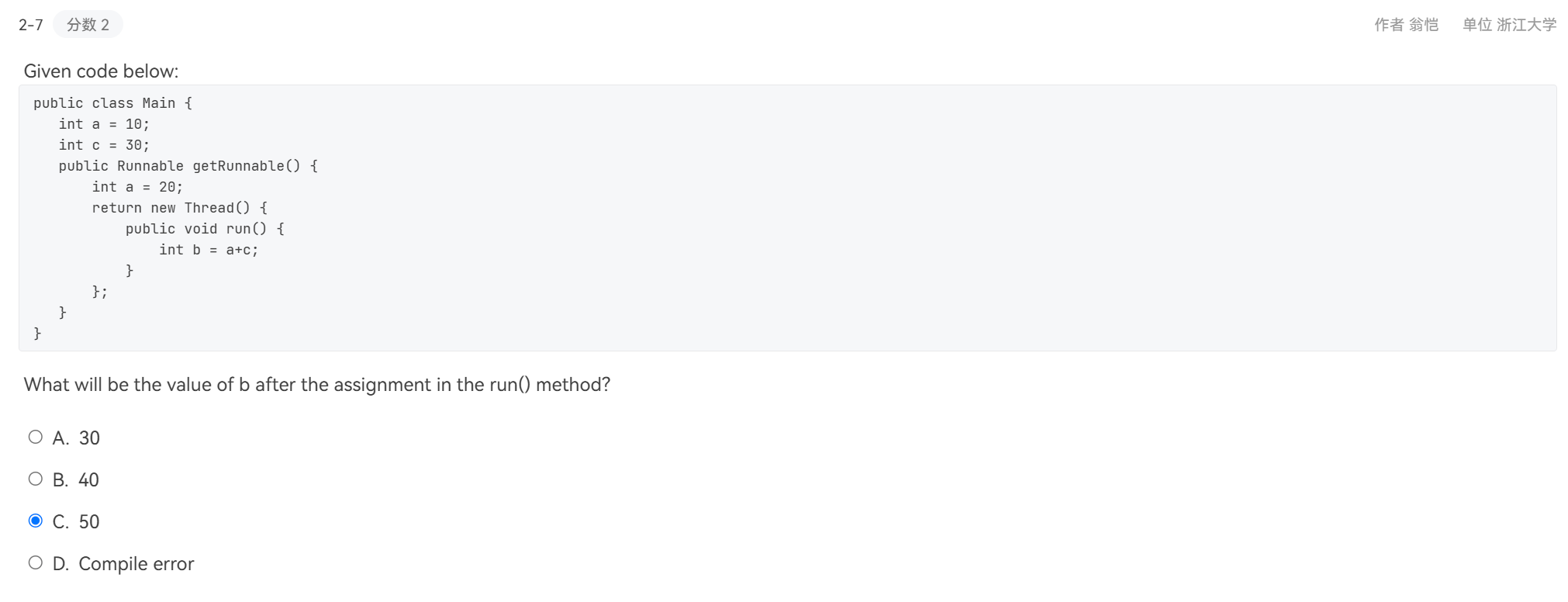
- 广播的实现
- Send 的效率问题
- 消息队列
- 经典的consumer - producer
- 消息队列
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Server {
// 使用CopyOnWriteArrayList保证线程安全,适合读多写少的场景
private final CopyOnWriteArrayList<ClientHandler> clients = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
// 使用线程池处理客户端连接和消息
private final ExecutorService executorService = Executors
.newFixedThreadPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
// 使用NIO的Selector实现非阻塞IO
private Selector selector;
// 消息队列,用于异步处理消息广播
private final BlockingQueue<String> messageQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
class ClientHandler {
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private String clientId;
public ClientHandler(SocketChannel socketChannel) {
this.socketChannel = socketChannel;
this.clientId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
public void sendMessage(String message) {
try {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes());
socketChannel.write(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
removeClient(this);
}
}
}
public void start(int port) {
try {
// 创建ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 创建Selector
selector = Selector.open();
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 启动消息处理线程
startMessageProcessor();
while (true) {
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
handleAccept(serverChannel);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
handleRead(key);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void handleAccept(ServerSocketChannel serverChannel) throws IOException {
SocketChannel clientChannel = serverChannel.accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
ClientHandler client = new ClientHandler(clientChannel);
clients.add(client);
}
private void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int numRead = -1;
try {
numRead = channel.read(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
key.cancel();
channel.close();
return;
}
if (numRead == -1) {
key.cancel();
channel.close();
return;
}
buffer.flip();
byte[] data = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(data);
String message = new String(data);
// 将消息放入队列异步处理
messageQueue.offer(message);
}
private void startMessageProcessor() {
executorService.submit(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
String message = messageQueue.take();
broadcast(message);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
});
}
private void broadcast(String message) {
for (ClientHandler client : clients) {
executorService.submit(() -> client.sendMessage(message));
}
}
private void removeClient(ClientHandler client) {
clients.remove(client);
try {
client.socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Server server = new Server();
server.start(5382);
}
}