基础部分¶
约 1711 个字 392 行代码 12 张图片 预计阅读时间 13 分钟
基础¶
一些注意的地方
- 赋值与初始化其实并不完全相同,初始化是创建变量时赋予一个初始值,赋值是擦除当前值。
- 一般情况下,这一点并没有任何影响
引用¶
引用
这是C++中一种新的特性。我们常说的引用指的是左值引用,还有一种引用是指右值引用
左值引用¶
定义左值引用的使用,一定要赋初始值
warning
- 不允许使用引用的数组C/C++(251)
- 不允许使用引用的引用
int value;
int &refVal = value;
int *PtrValue = &value;
// 指向指针的引用
int *&refPointer = PtrValue;
// 数组引用
int &arr[10]; // 元素为引用类型 ? 不允许使用引用的数组C/C++(251)
int (&arr)[10]; // 整型数组的引用
对一个常量的引用可能是一个非常量,const int &只是对引用的操作有了限制
int i = 10086;
const int m = i;
int &ref_i = i;
const int &Ref_i = i;
ref_i -= 1;
std::cout << "i:" << i << std::endl;
std::cout << "m:" << m << std::endl; // 10086
std::cout << "i:" << ref_i << std::endl; // 10085
std::cout << "I:" << Ref_i << std::endl;
const 引用
double a = 1.12;
const double &ref_a = a;
const int &Ref_a = a;
a = a - 100;
std::cout << "a:" << ref_a << std::endl;
std::cout << "A:" << Ref_a << std::endl;
>> a:-98.88
>> A:1

Warning
引用本身并不是一个对象,它绑定到一个对象上面去,这意味着它并不是复制
不能够形成一个引用的引用
指针¶
Warning
在CPP中,指针的初始化最好使用 nullptr,相当于void *,而NULL在cstdlib中定义,
int * a = nullptr;
const¶
const 分为顶层的和底层的。 顶层的 Top 表示本身不可变,指向的值不一定 底层的 表示本身可变,指向一个不可变的值 而指针既可以是Top-level,也可以是Low-level
const与指针¶
Example
int * const a = &i; // 指针是常量 a顶层的,不能改变
const int * b = &j; // 指向常量的指针
a是一个指针常量,b是一个常量指针;这样侧重后面的一个,可能容易理解一点
距离变量最近的是*或者const可以帮助我们判断变量的类型
const char * a; //指向const对象的指针或者说指向常量的指针。
char const * a; //同上
char * const a; //指向类型对象的const指针。或者说常指针、const指针。 a是不可修改的左值
const char * const a; //指向const对象的const指针。
constexpr和字面值类型¶
constexpr
是一种常量表达式,C11加入作为一种类型 constexpr函数返回值不一定是常量表达式
constexpr函数
定义一个constexpr函数,1. 返回值和形参都必须是字面值类型 2. 函数体内只能存在一句return
constexpr int new_sz() { return 11; }
constexpr size_t scale(size_t cnt){return new_sz()*cnt},在调用这个函数时,必须关注实参的类型。如果不为字面值类型,调用失败
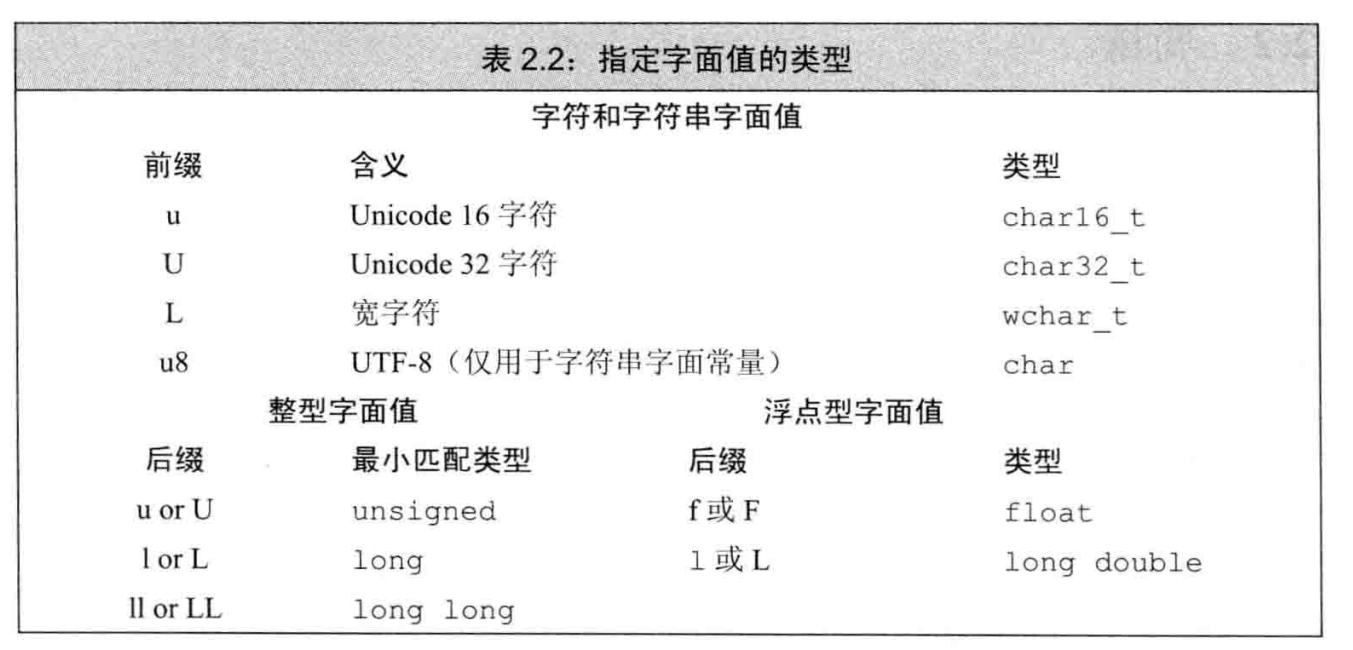
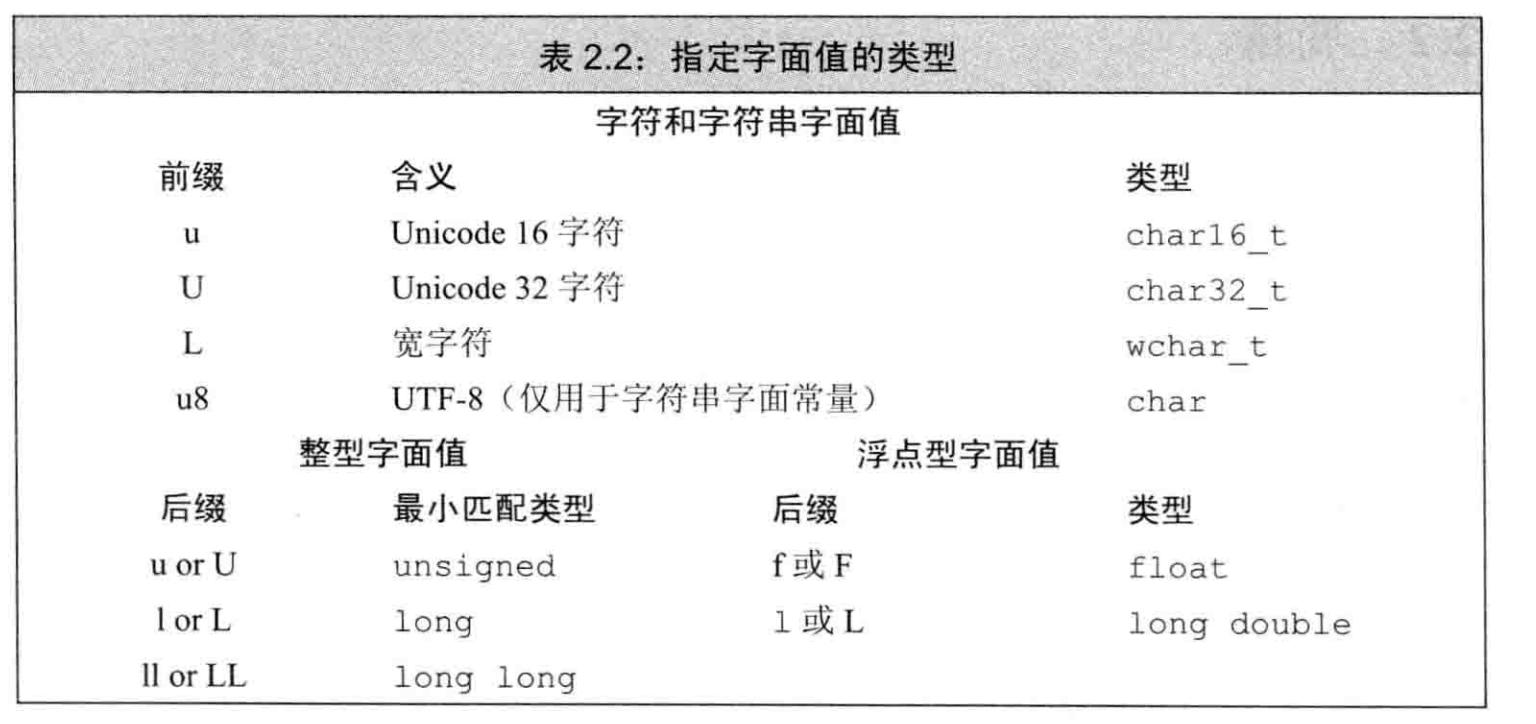
字面值常量 literal
- 整型 浮点型
- 字符串字面值,字符字面值 '' ""
- 指针字面值 nullptr
处理类型¶
类型别名¶
typedef double wage;
using wage = double;
typedef
使用typedef时,以下两种用法可能带来不同的影响
typedef char *prtChar;
const char*A = &ch;
const prtChar B = &ch;
// 这种情况下,B是一个指针;A是一个常量
typedef char (*prtChar);
const char *A = &ch;
const prtChar B = &const_ch;
// 这种情况下,A、B相同,都是一个指针类型的常量
为什么是这样定义的
Todo Typedef的实际作用 是如何发生的
auto¶
C11
auto的自动推断,会使得顶层的const失效,保留底层的const
int i = 0;
const int ci = i,&cr = ci;
auto b = ci; // b is int
auto c = cr;
decltype¶
C11
有时候,我们只希望获得一个
Function的最终运算类型,而不希望由它来赋予初始值
int i;
decltype(f()) sum;
const int ci = 0, &cj = ci;
decltype(ci) a = 0; // const int
decltype(cj) b = a; // const int &
decltype((i)) c; //Error!! 引用必须赋予初始值
Note
decltype(())的结果永远是引用
decltype()则不然
字符串¶
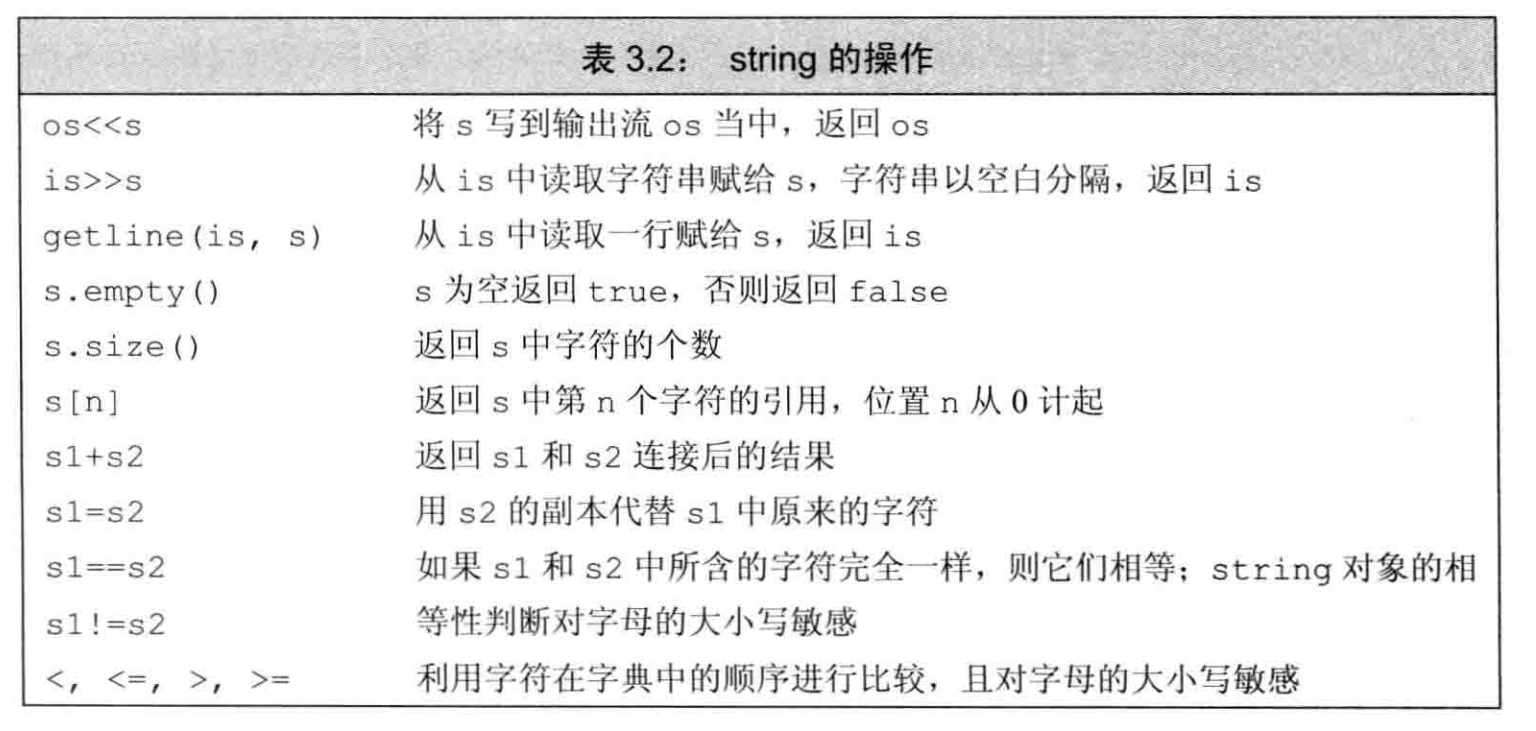
基本操作¶
// Initailize
string s;
string _10c(10,'c');
string _hi("hi");
string s = "value";
// Input
getline(input,receive);
// Method
s.size(); // unsigned int
s.empty();
//
string str1 = "World";
string str2 = "Hello";
string str3 = str2 + ", " + str1;
string str4 = "Hello" + " , " + str1; //false
Warning
C++中的字符串的字面值类型并不是标准库string的对象。也就是说,字符串的字面值类型和string不是同一类型。
cctype¶

for (auto c : str)
cout << c << endl;
for (auto &c : str)
c = toupper(c);
Vector¶
Warning
尽量减少使用数组和指针,尽量使用 Vector 和 iterator或者const_iterator
尽量使用String而不是C风格的基于数组的字符串
string str = "ab"; char str[] = {'a','b','\0'}
// Initailize
vector<int> v1(n, val);
vector<vector<int>> v2;
vector<string> v3;
string word;
# 可以使用数组来初始化Vector
int int_array[] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6};
vector<int> vec(begin(int_array),end(int_array));
// Method
while (cin >> word)
v3.push_back(word);
v3.pop_back();
// 返回的是 引用类型
v3.back(); v3.front();
// 返回迭代器
v3.begin(); v3.end();
v3.empty();
v3.size();
# 必须要指定清楚type
vector<int>::size_type;
# 在函数中返回一个Vector
vector<string> process()
{
if(...)
return {};
else
return {"Yes","No","CPP"};
}
// 遍历
vector<string> a;
a.push_back("begin");
a.push_back("NO.1");
*a.begin() = "change";
for (auto ch : a[0])
cout << ch;
cout << endl;
cout << "2 : " << a[1];
// Insert
position = vector.begin(); // 是一个iterator类型
vector.insert(position,number,val);
// Erase
vector.erase(position);
vector.erase(position_begin,position_end);
迭代器¶
Note
begin end
返回值类型可能是 iterator或者const_iterator
cbegin cend
一定是const_iterator
-
迭代器类型
-
迭代器运算
string vector支持 获取任意位置的iterator
数组¶
size_t cnt = 0;
constexpr size_t rowCnt = 3, colCnt = 4;
int Arr[rowCnt][colCnt];
for(auto &Row : Arr) // note!
for(auto Col : Row)
{
}
enum¶
-
沿用C中的表达
enum Color{red,green,blue}; -
使用C++的类
enum class Color{red,green,blue};
表达式¶
类型转换¶
Info
- 隐式类型转换
- 显式类型转换
- 整型提升
- 无符号类型转换

强制类型转换¶
cast-name<type>(expression)
static_cast¶
只要不包含底层的const就可以使用
double m;
void *p = &m;
double *dp = static_cast<double *>(p);
const_cast¶
只能改变底层const
reinterpret_cast¶
为转换对象的位模式提供更低层次的重新解释
运算符¶
概念
- 重载运算符
- 左值和右值
优先级的问题¶
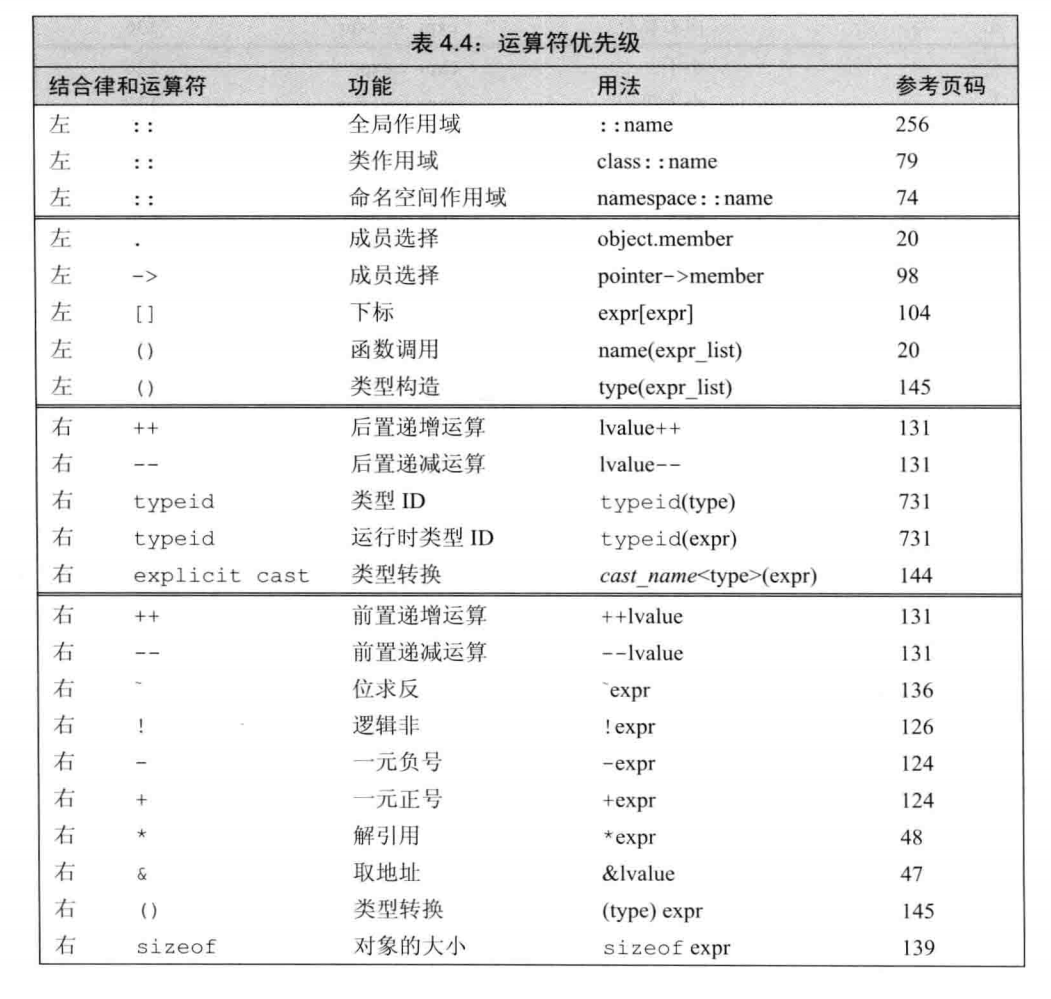
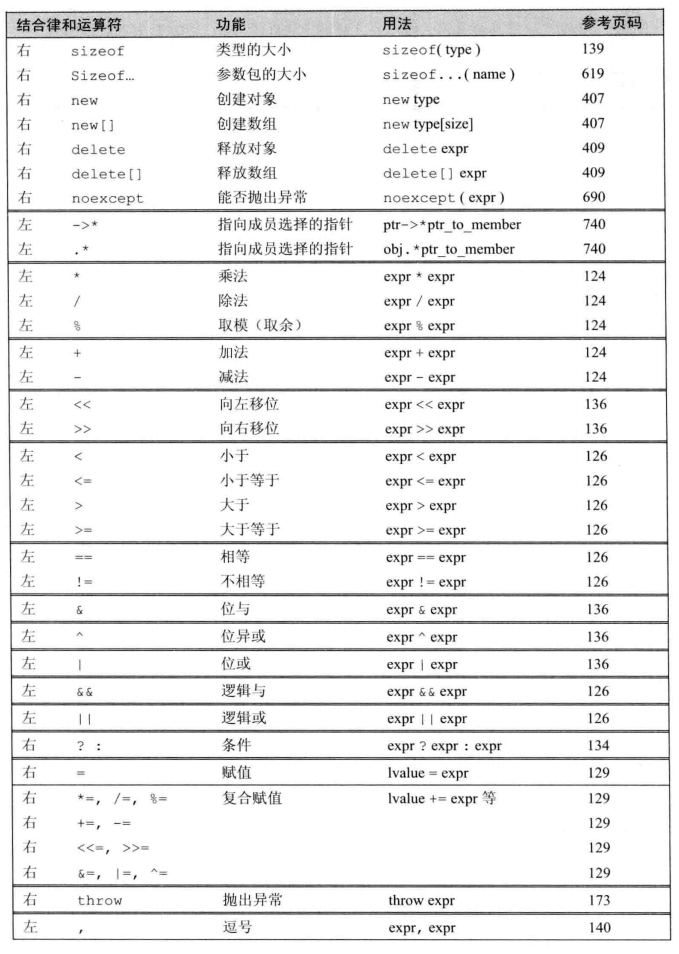
异常处理¶
Info
- 异常检测
throw 表达式
- 异常处理
try block异常类
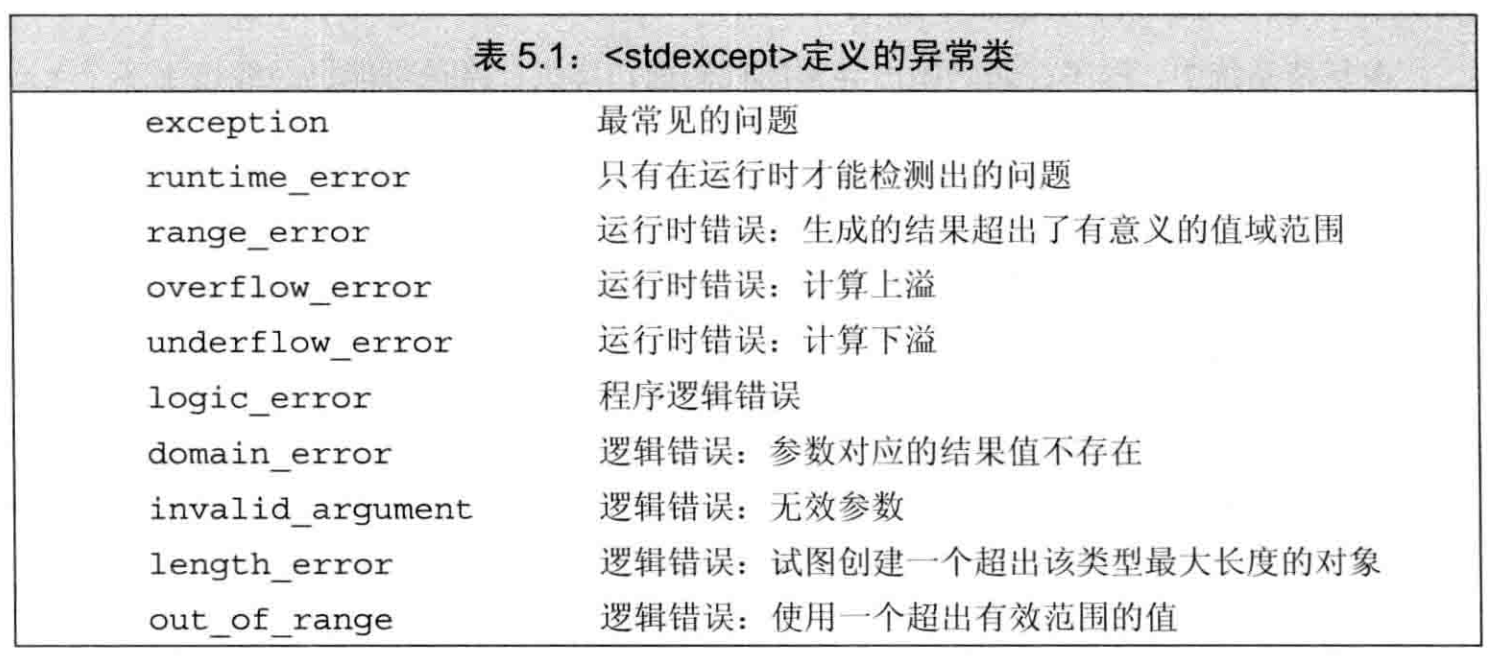
// throw
if(ISBN1 != ISBN2)
throw runtime_error("Data ...");
// try
try {
// if throw one exception
// then, go for the related catch to deal with it
} catch(runtime_error err){
cout << err.what();
} catch(){
}
list bubu
函数¶
可变参数传递¶
形参数量未知,但类型相同
initializer_list<int> lst{1, 2, 3};
lst.size();
lst.begin();
lst.end();
void error_msg(int type, initializer_list<string> il)
{
for (auto j : il)
cout << j;
cout << endl;
}
string a = "NO";
error_msg(0, {"Yes", " or ", a});
便于C++访问部分特殊的C代码设置的。特别的是,大多数类类型的对象在传递给省略符形参时都无法正常拷贝。
void func(int a,...); void func(...);
返回值¶
尾置返回类型
auto func(int i) -> int (*)[10]
a
函数重载¶
不允许
- 两个除了返回类型之外完全相同的函数
- 参数中,顶层const无法区分,底层可以(比如区分指针或者引用指向的是常量对象或者非常量对象)
// 无法区分 int lookup(int); int lookup(const int); // 可以区分 int lookup(int *); int lookup(const int *); int lookup(int &); int lookup(const int &);
默认实参¶
Tips
注意,对同一函数的声明可以多次进行。
但是,在给定的作用域内,一个形参只能有一个默认参数;后续的声明只能给之前没有默认实参的参数添加默认实参,而且该实参右侧的形参必须具有默认实参。
typedef string::size_type sz;
string sreen(sz ht,sz wid,char = '');
string sreen(sz = 100,sz = 80,char );
Example
void testFunc(int a = 10086)
{
cout << a << endl;
return;
}
int m = 0;
int main()
{
testFunc();
// 用于初始化默认实参的如果是变量,不能是局部变量
void testFunc(int = m);
testFunc();
return 0;
}
函数匹配¶

函数指针¶
using PF = int(*)(int *, int );
using F = int(int *, int );
PF m;
// 声明指向函数的指针
// f1 返回
PF f1(int);
P * f2(int);
// 由内向外读 f3是一个函数,返回值为指针,这个指针是一个函数指针
int (* f3(int))(int * , int);
auto f4(int) -> int (*)(int * ,int);
函数指针
int ReturnNum(int *array, int index)
{
return array[index];
}
auto f4(int) -> int (*)(int *, int)
{
return ReturnNum;
};
int main()
{
int array[10] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
cout << f4(4)(array, 5);
return 0;
}
类¶
概述
- 基本介绍
- 构造函数
- friend private public mutable
- 静态成员
介绍¶
this相当于一个常量指针,它是隐式定义的 !!! question "Question" 如下图,this默认情况下不是一个指针常量吗?感觉前后说法有些矛盾
- ``
e.g.
// 常量成员函数,关键在理解const
std::string isbn() const{return bookNo;}
// 在类外部定义,必须加上所属的类名
double Sales_data::avg_price() const{
if(units_sold)
return revenue;
}
//
std::string bookNo;
构造函数¶
// 类的内部
Sales_data( ) = default;
Sales_data(const std::string &s) : bookNo(s) { }
// 类的外部
Sales_data::Sales_data(std::istream &is)
{
// read will read a transaction from is into this object
read(is, *this);
}
访问控制与封装¶
abstract
- 我们使用private、public、protected访问说明符加强类的封装
- class 和 struct的唯一区别在于默认的访问权限: 类可以在第一个访问说明符之前定义成员,struct则默认为public,class默认为private
- friend 允许其他类或者函数访问 private 成员(在类外定义一些接口)
example
#include <iostream>
using std::istream;
using std::ostream;
#include "Sales_data.h"
Sales_data::Sales_data(std::istream &is)
{
// read will read a transaction from is into this object
read(is, *this);
}
double
Sales_data::avg_price() const
{
if (units_sold)
return revenue / units_sold;
else
return 0;
}
// add the value of the given Sales_data into this object
Sales_data &
Sales_data::combine(const Sales_data &rhs)
{
units_sold += rhs.units_sold; // add the members of rhs into
revenue += rhs.revenue; // the members of ``this'' object
return *this; // return the object on which the function was called
}
Sales_data
add(const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs)
{
Sales_data sum = lhs; // copy data members from lhs into sum
sum.combine(rhs); // add data members from rhs into sum
return sum;
}
// transactions contain ISBN, number of copies sold, and sales price
istream &
read(istream &is, Sales_data &item)
{
double price = 0;
is >> item.bookNo >> item.units_sold >> price;
item.revenue = price * item.units_sold;
return is;
}
ostream &
print(ostream &os, const Sales_data &item)
{
os << item.isbn() << " " << item.units_sold << " "
<< item.revenue << " " << item.avg_price();
return os;
}
#ifndef SALES_DATA_H
#define SALES_DATA_H
#include "Version_test.h"
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
class Sales_data {
friend Sales_data add(const Sales_data&, const Sales_data&);
friend std::ostream &print(std::ostream&, const Sales_data&);
friend std::istream &read(std::istream&, Sales_data&);
public:
// constructors
// using the synthesized version is safe only
// if we can also use in-class initializers
#if defined(IN_CLASS_INITS) && defined(DEFAULT_FCNS)
Sales_data() = default;
#else
Sales_data(): units_sold(0), revenue(0.0) { }
#endif
#ifdef IN_CLASS_INITS
Sales_data(const std::string &s): bookNo(s) { }
#else
Sales_data(const std::string &s):
bookNo(s), units_sold(0), revenue(0.0) { }
#endif
Sales_data(const std::string &s, unsigned n, double p):
bookNo(s), units_sold(n), revenue(p*n) { }
Sales_data(std::istream &);
// operations on Sales_data objects
std::string isbn() const { return bookNo; }
Sales_data& combine(const Sales_data&);
double avg_price() const;
private:
std::string bookNo;
#ifdef IN_CLASS_INITS // using the synthesized version is safe only
unsigned units_sold = 0;
double revenue = 0.0;
#else
unsigned units_sold;
double revenue;
#endif
};
// nonmember Sales_data interface functions
Sales_data add(const Sales_data&, const Sales_data&);
std::ostream &print(std::ostream&, const Sales_data&);
std::istream &read(std::istream&, Sales_data&);
// used in future chapters
inline
bool compareIsbn(const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs)
{
return lhs.isbn() < rhs.isbn();
}
#endif
其他特性¶
可变数据成员¶
mutable 使得const func也能够改变其值
public:
//
private:
mutable size_t count;
class Window_mgr{
private:
std::vector<Screen> sreens{Screen(24,80,'')};
};
// 如果函数为const类型,返回的引用为const type &;
inline Screen &Screen::Display const(){}
inline Screen &Screen::set(char c)
{
contents[cursor] = c;
return *this;
}
Friend
- 可以将另外一个类指定为本类的friend 友元关系不存在传递性
我的奴隶的奴隶不是我的奴隶
- 令成员函数为friend,而不是令另外一整个类变成友元
class Screen{ friend void Window_mgr::clear(ScreenIndex); }
隐式转换¶
通过一个实参调用的构造函数定义一条从构造函数的参数类型向类类型转换的规则
限制
隐式转换只允许最多一步
可以使用explicit(只允许在类内出现 explicit Sales_data(std::istream &))来限制隐式转换(但是仍然可以进行显式的转换)

静态成员¶
与类相关,而不是与类的成员相关;一旦发生改变,所有的成员对象都能使用改变后的值
note
- 通常情况下,静态成员在类的外部进行初始化;但常量表达式情况是一个例外,
static constexpr int period = 30; double daily[period];,一般情况下,我们还需要在类的外部对常量静态数据成员进行定义,constexpr int Account::period; - 与非静态成员的区别
class Bar{ public: 1. 可以作为默认实参 Screen &clear(char = bkground) private: 2. 可以使用不完全类型定义 static Bar mem1; Bar Wrong; // × static const char bkground; }
// 声明
class Account {
public:
static double rate() {return interestRate;}
static void rate(double);
private:
std::string owner;
double amount;
static double interestRate;
static double initRate() { return .0225; }
static const std::string accountType;
}
// 使用
double r = Account::rate();
Account ac1;
Account &ac2;
ac1.rate();
ac2->rate();
// 定义
void Account::rate(double newRate) # (1)
{
interestRate = newRate;
}