指针与链表¶
约 393 个字 77 行代码 5 张图片 预计阅读时间 3 分钟
Error¶
char a[]="axd123";
char **s;
s=&a; //此处a[]为字符串常量 不能取地址 a本身表示该字符串的地址
char *p;
p=a;
// 此时 可以令 s=&p
POINT¶
普通指针¶
- 变量提供访问地址的快捷方式,但是硬件仍然通过地址访问内存位置,名字与内存位置的关联由编译器实现。
*间接访问地址符,只能用于指针类型表达式,对于指针常量不适用,必须强制转换 其访问一个特定的位置 e.g. (int )100 = 25; 即在已知地址 100 的位置存储值 25**NULL**对指针变量进行显式的初始化,在指针解引用之前进行检查,避免非法指针
算术运算与关系运算¶
 在同一个数组内
进行关系运算注意下标
在同一个数组内
进行关系运算注意下标
二级指针¶
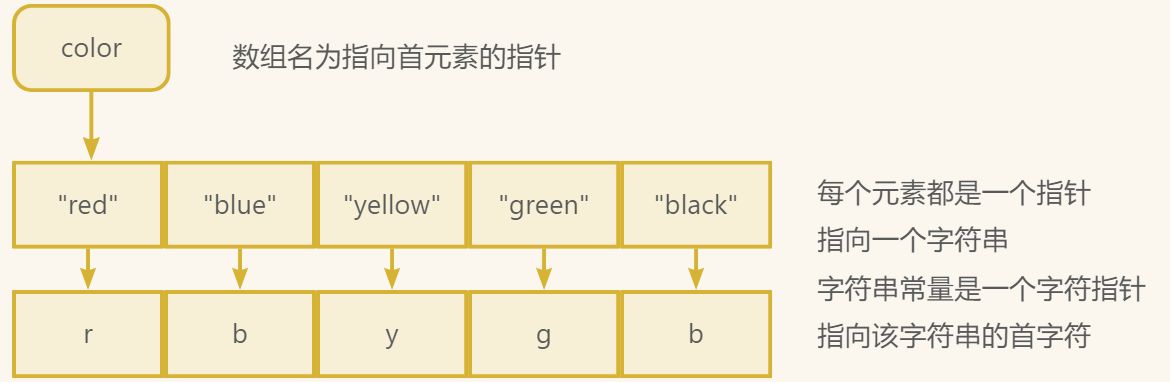
char * color[] = {"red", "blue", "yellow", "green", "black"};
int i, flag = 0; char ch;
char **pc;
pc = color;
printf("Input a character:");
ch = getchar();
for( i =0; i<5; i++ ) {
if( **(pc+i)==ch ) {
flag = 1;
puts(*(pc+i));
}
}
if( flag==0 )
printf("Not Found");
指针数组¶
int * a[]={"asd","dwq"}; a[]中存储的是指针
数组指针¶
int a[10]; &a 数组指针( int (p)[10] ) 指向数组 a a == &a[0] a + 1 == &a[1] a[k] ==(a+k)
函数指针¶
定义 返回值类型(*变量名)(参数类型表)
double (*op) (double);
int _ (_f)();
定义一个函数指针,该函数返回一个整型的指针
int _(_g[])(int,float);
g[ ]为一个数组,其中元素为函数指针;返回整型指针
 函数名也是一个指针
类型:却决于返回值的类型和参数列表的类型以及个数
函数名也是一个指针
类型:却决于返回值的类型和参数列表的类型以及个数
here is an error, the second line of main function, there must be ptr = f1 ;


方便同一个函数内根据实际情况调用不同的子函数
typedef 函数指针类型¶
有利于简化函数指针的使用
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
//typedef 将变量名TFunc替换为函数指针类型名
typedef double (*TFunc)(double);
double calc(TFunc f, double a, double b);
double f1(double);
double f2(double);
int main(void)
{
TFunc ptr = f1;
printf("f1: %.4f\n", calc(ptr,0,1));
printf("f2: %.4f\n", calc(f2,1,2));
return 0;
}
double calc(TFunc f, double a, double b)
{
return (f(a)+f(b))*(b-a)/2;
}
double f1(double x)
{
return x*x;
}
double f2(double x)
{
return sin(x)/x;
}
指针与数组¶
链表¶
单链表¶
插入一个值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct NODE{
int value;
struct Node *next;
}Node;
int value; //supposed that we have get a new value into the link
Node *head,*pre,*p,*new;
pre=NULL;
//引用之前确保p不是null
while(p!=NULL&&p->value<value){
pre=p;
p=p->next;
}
//
new=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(new==NULL) return ;
new->value=value;
new->next=p;
//
if(pre==NULL){
head=new;
}else{
pre->next=new;
}
传入 **Node [&head] 修改头指针 *head=new;