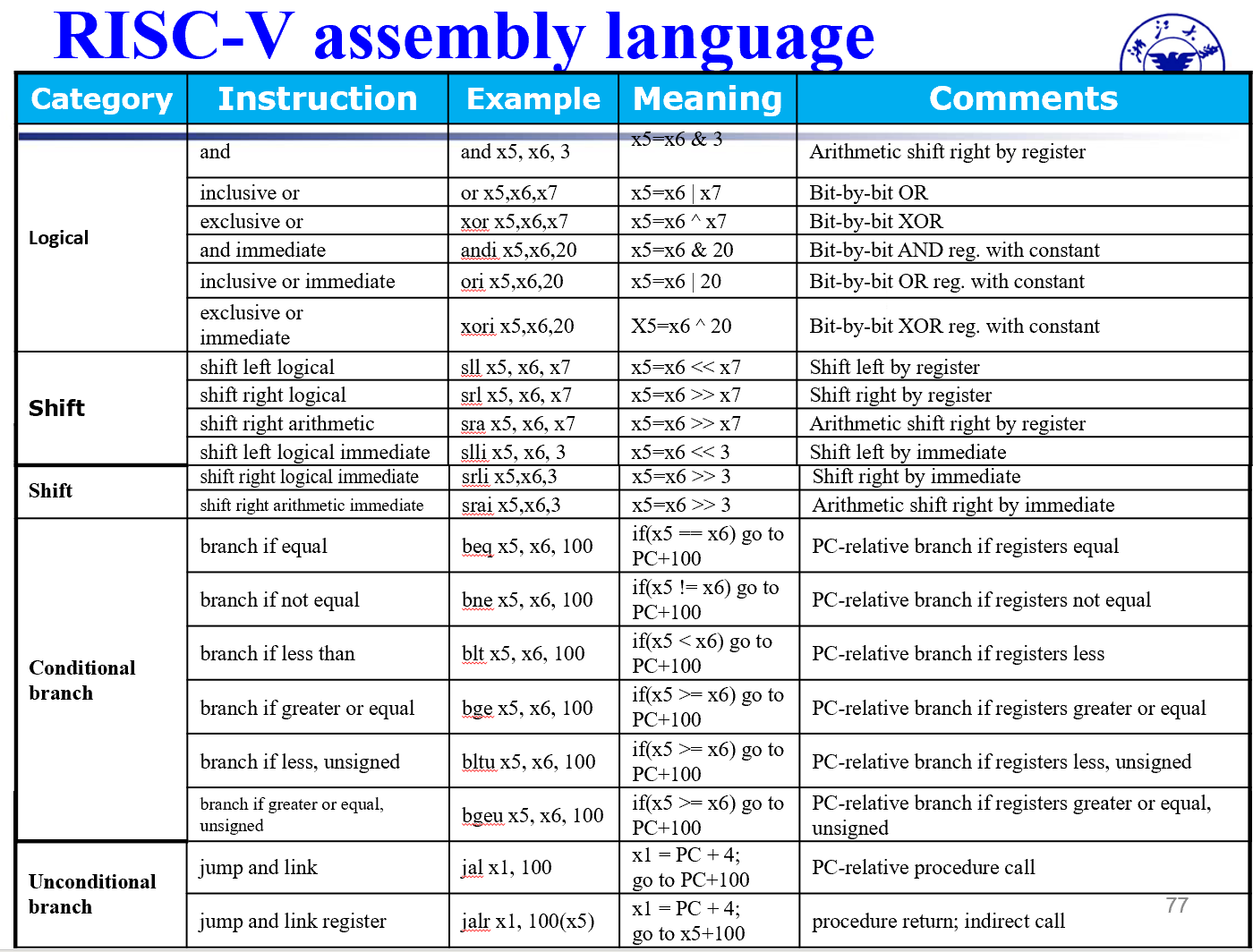
Chapter 2 | Instruction¶
约 866 个字 50 行代码 48 张图片 预计阅读时间 5 分钟
概述
- Introduction
- Operations of the computer hardware (计算机硬件的操作)
- Operands of the computer hardware(计算机硬件的操作数)
- Signed and unsigned numbers (有符号和无符号数)
- Representing instructions in the computer(计算机中指令的表示)
- Logical operations(逻辑操作)
- Instructions for making decision(决策指令)
- Supporting procedures in computer hardware(计算机对过程的支持)
- Instruction addressing (指令的寻址)
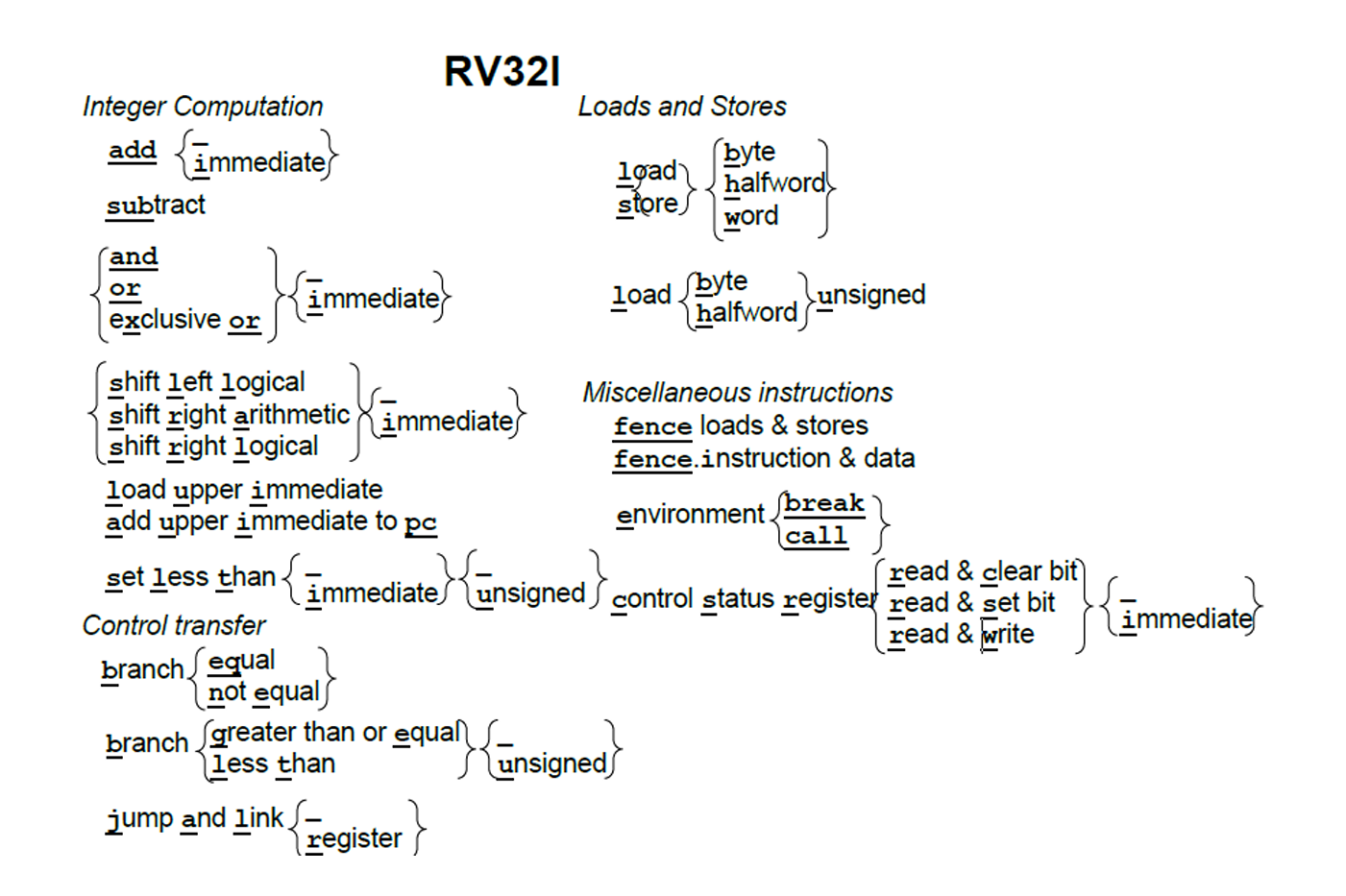
信息量 Op > Func 3 > Func 6/7
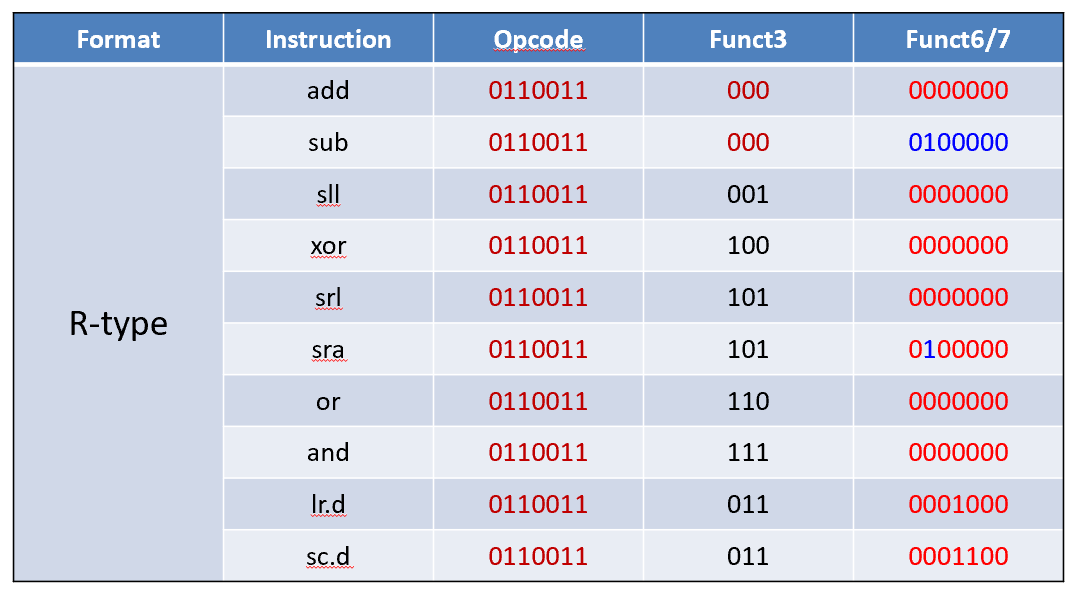
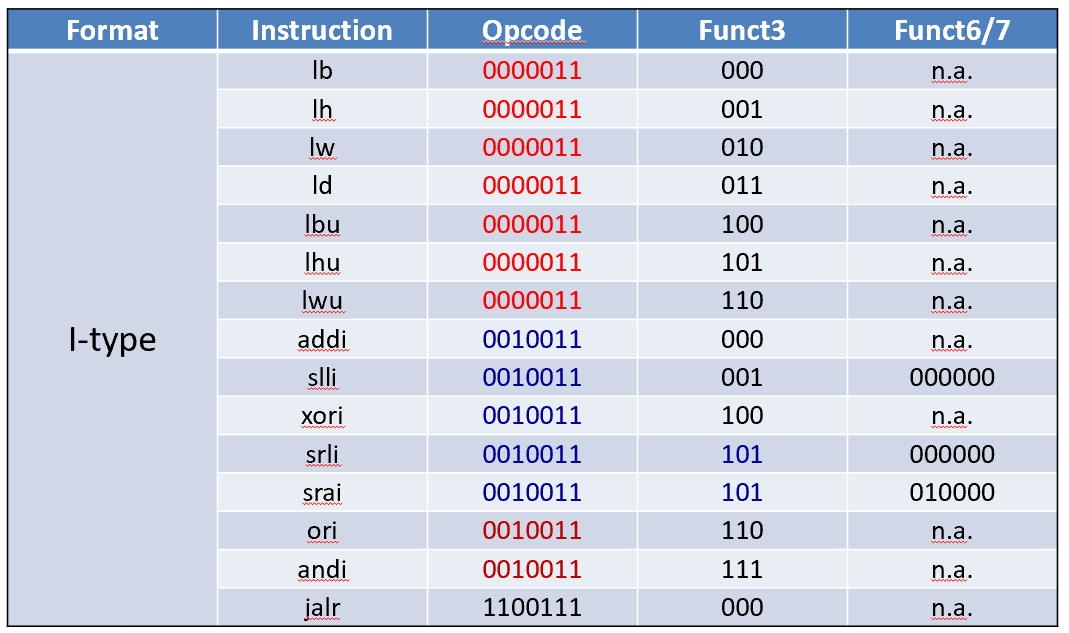
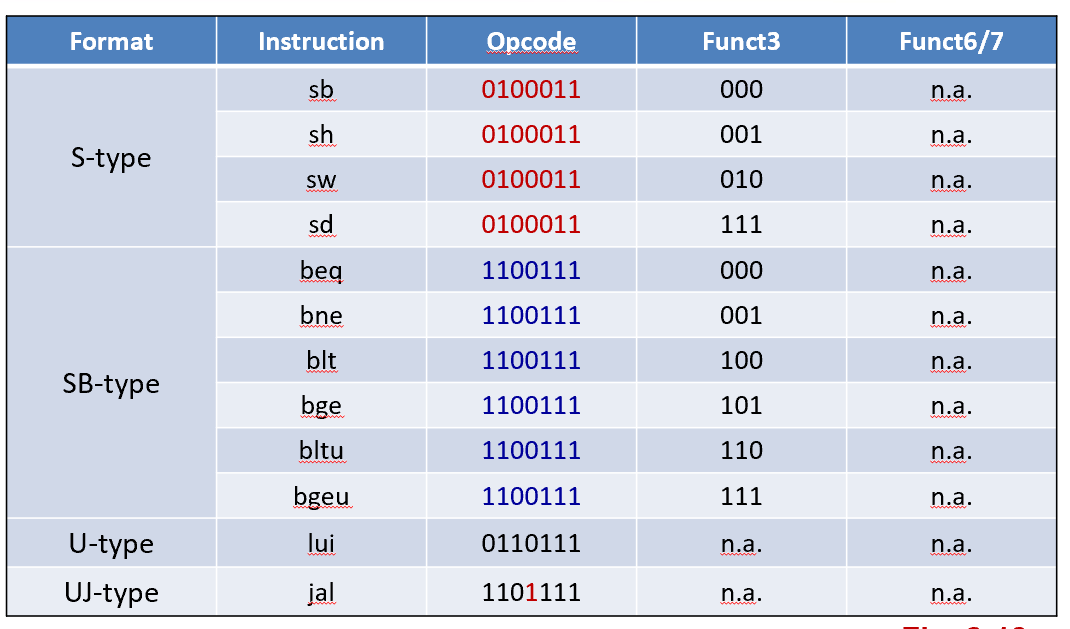
Mention¶
重点理解
- Branch指令进行循环等操作
- Procdure尤其是栈的写法
- 递归,斐波那契
- 区分jal jalr
jal 跳转是基于PC的跳转 UJ type
jalr 相当于jal的寄存器版本 跳转范围更加广 I type
PC + 4 都要存回去
- 立即数的种类
- 转换code的时候注意rs1,rs2的位置
Introduction¶
存储程序概念: 指令和多种类型的数据不加区分地存储在存储器中并因此易于更改,因为产生了存储程序计算机
Operation¶
- 一条指令一个操作

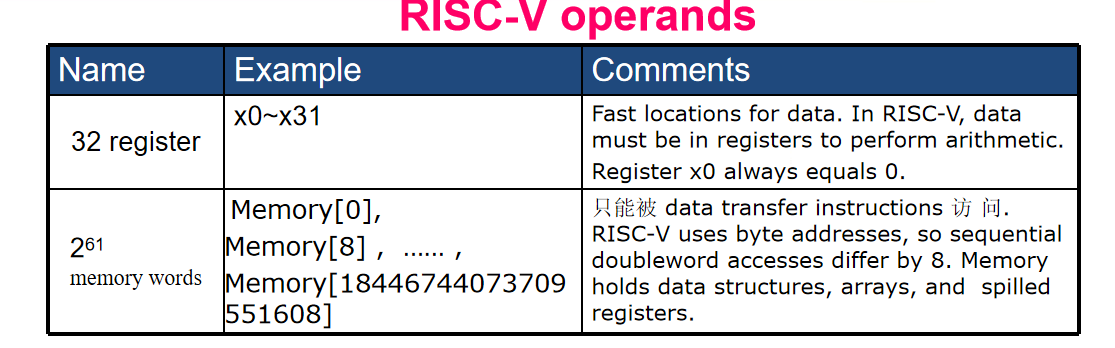
Operands¶
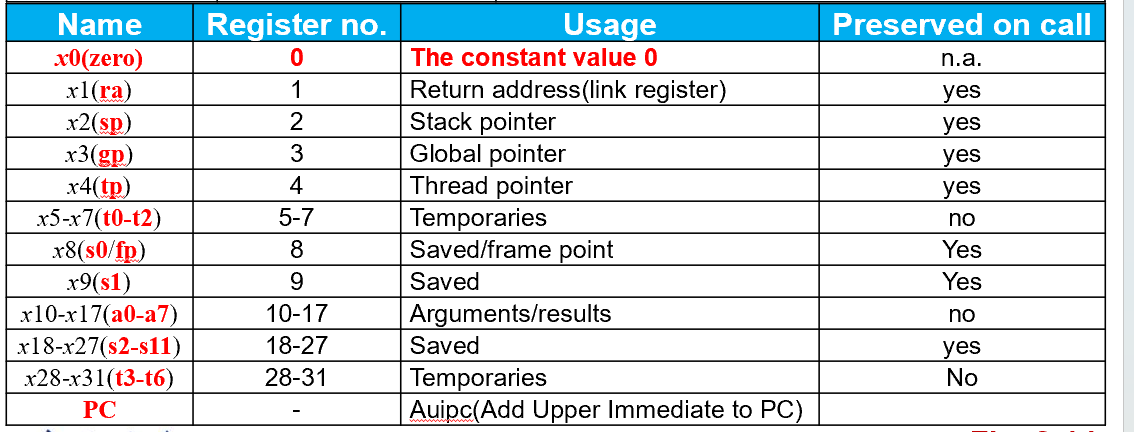
RISC - V 32 × 64-bit register file
word: 32 bits
double word : 64 bits
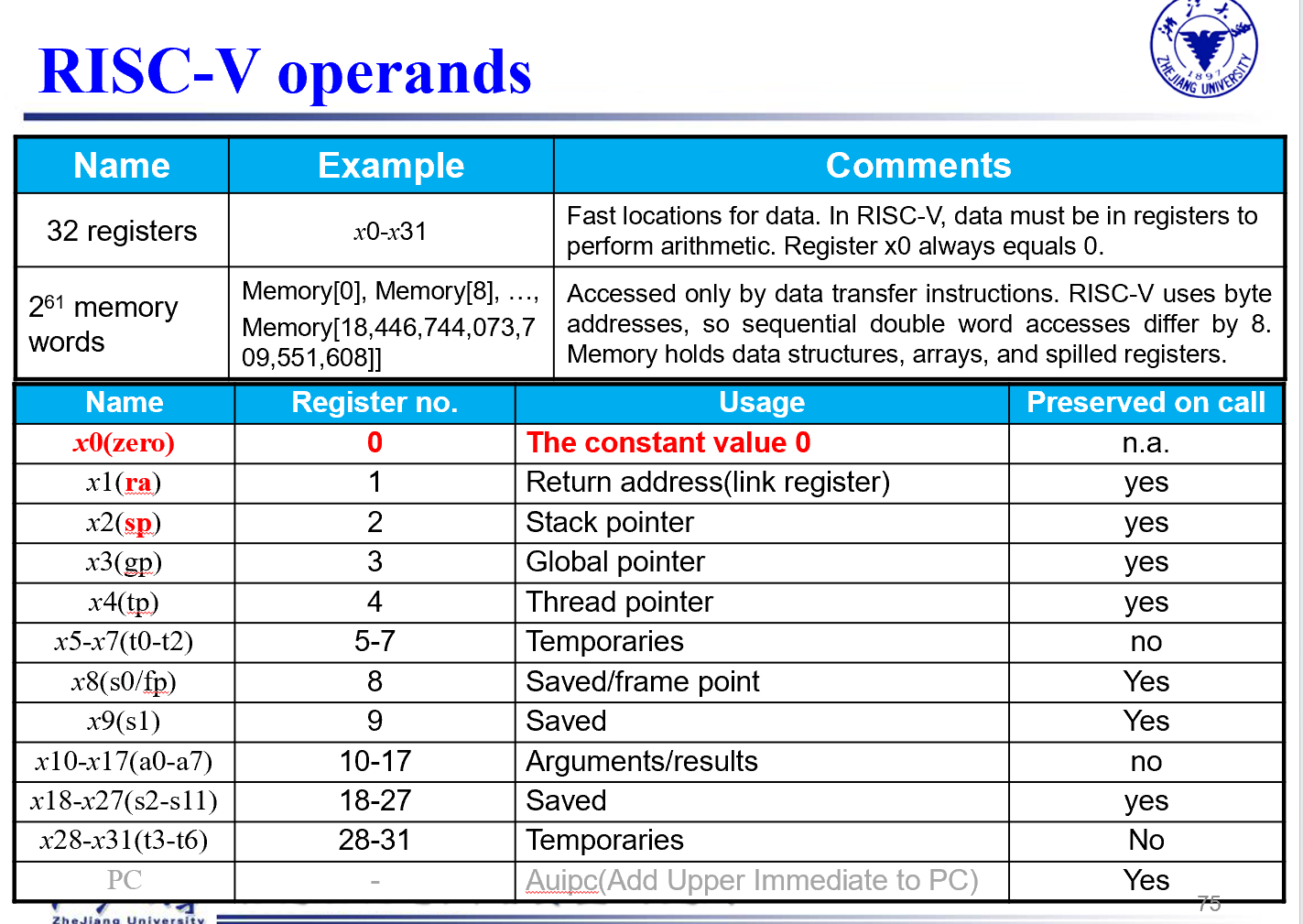
- Arithmetic instructions use register operands 必须在寄存器
- 以64bits的想法理解后续的所有操作
Register¶
C code: f = (g + h) - (i + j); f, …, j in x19, x20, …, x23 Compiled
RISC-V code:
add x5, x20, x21 add x6, x22, x23 sub x19, x5, x6
Memory Operands¶
byte addressed¶
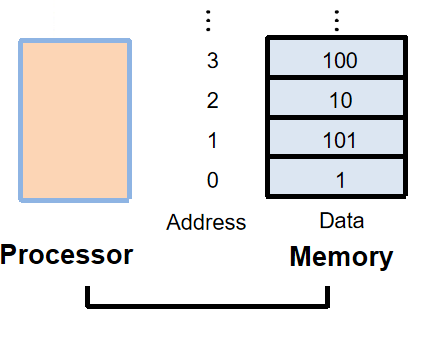
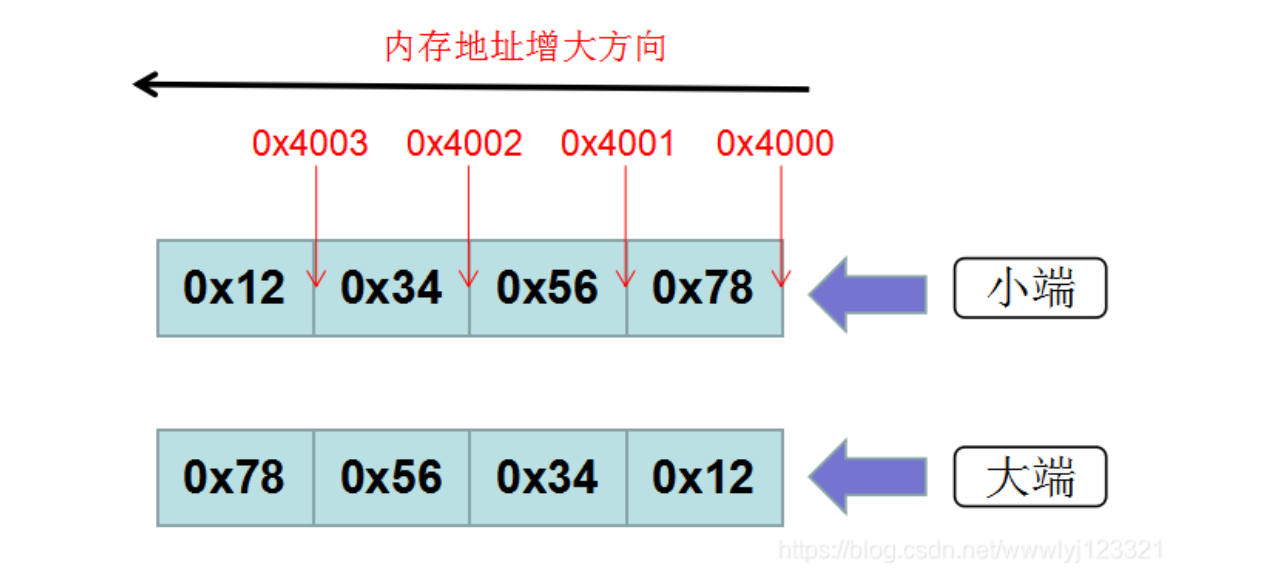
little endian¶
-
大端小端针对的是一个word, 在内存中有影响
-
Least-significant byte at least address of a word
-
c.f. Big Endian: most-significant byte at least address
0x 12345678 word index : 3210
32bits,4bytes
==> 78 is the lsb, 这个byte位于3
word 对齐 Alignment¶
RISV - V不强制要求word aligned
struct {
int a;
char b;
char c[2];
char d[3]
float e;
}
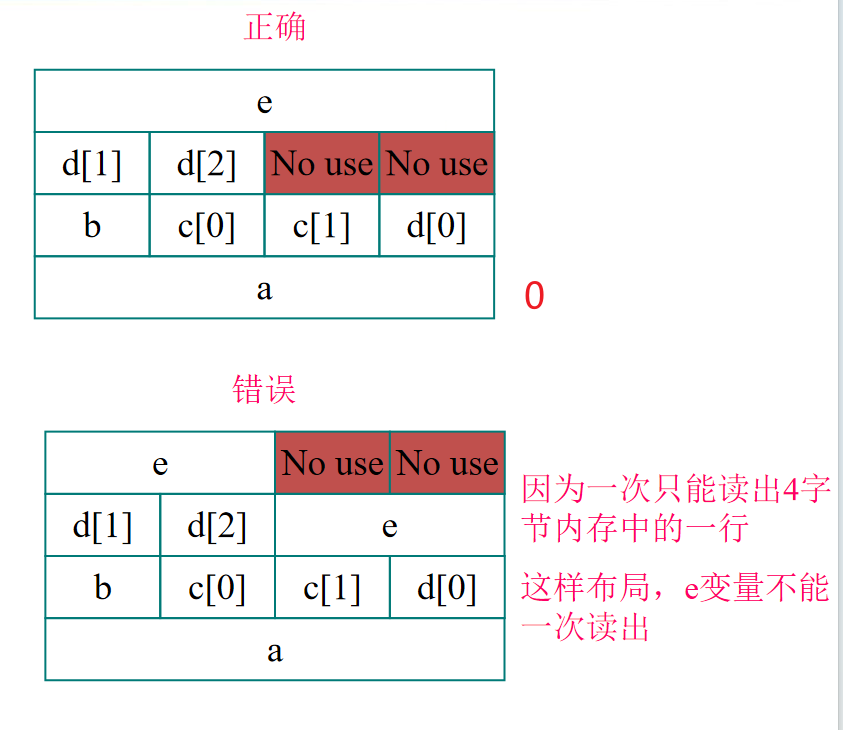
example¶
- 能访问寄存器的只有
loadstore - 这里展示的是
字节寻址(8 bits)
Constant or immediate operands¶
避免常数操作时load store 浪费时间
Offer versions of the instruction
addi x22, x22, 4 // x22= x22+ 4
Constant zero: a register x0
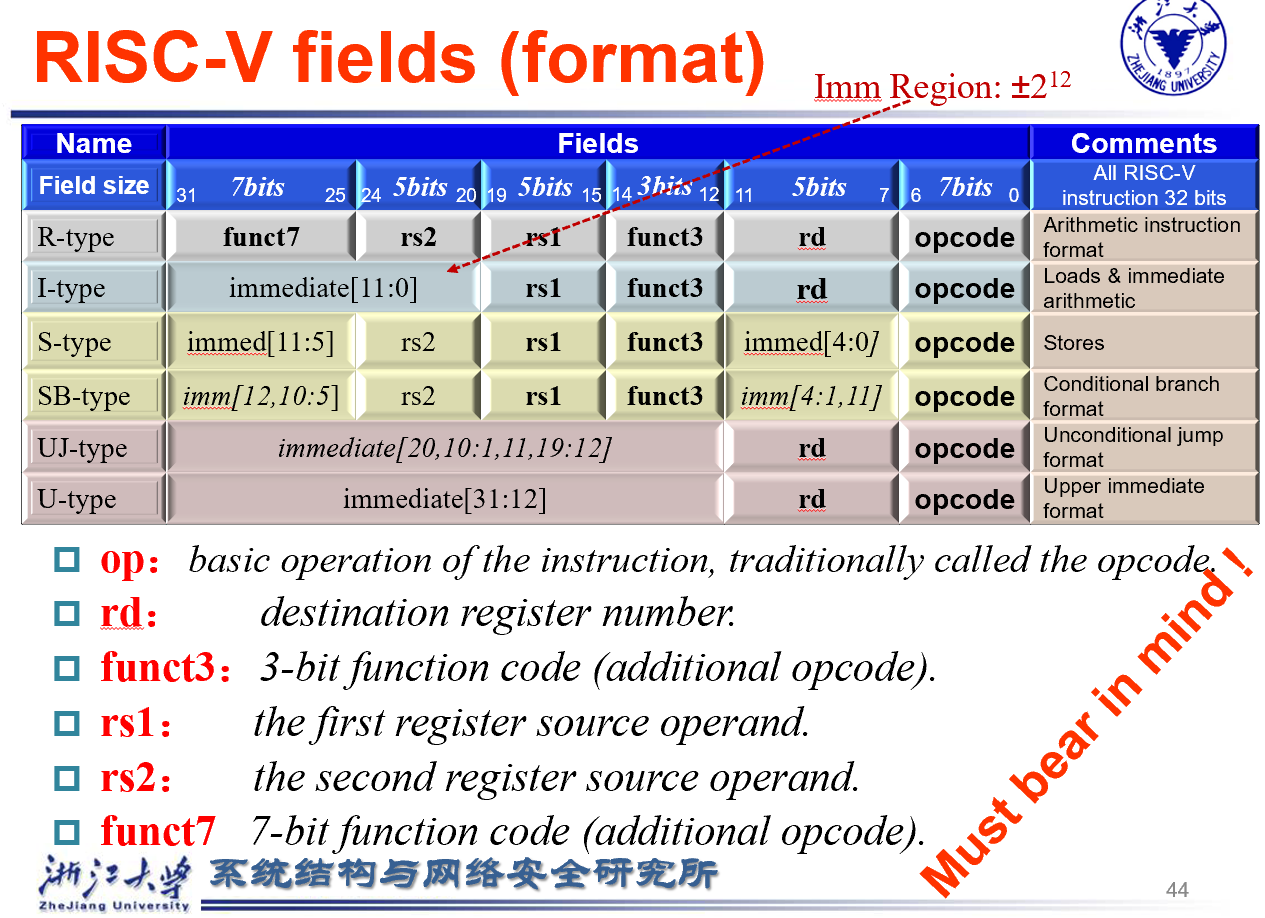
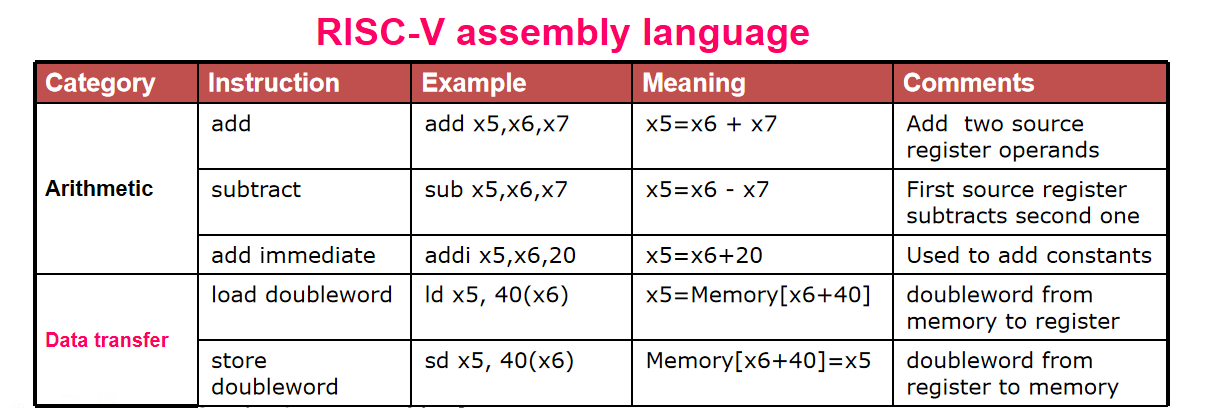
Representing Instructions¶
Mapping registers into numbers map registers x0 to x31 onto registers 0 to 31
RISC-V instructions
- Encoded as 32-bit instruction words 每条指令一个word
- Small number of formats encoding operation code (opcode), register numbers, …Regularity
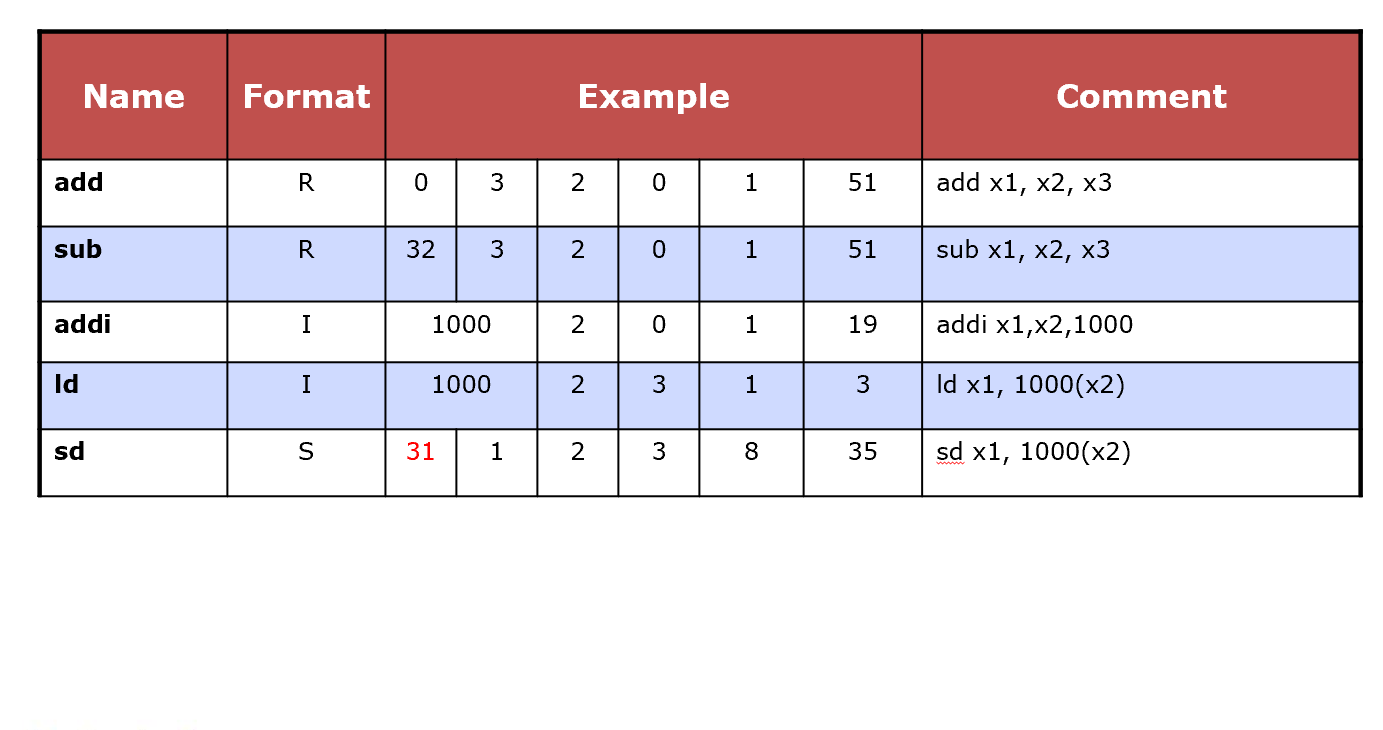
sd A,Bld
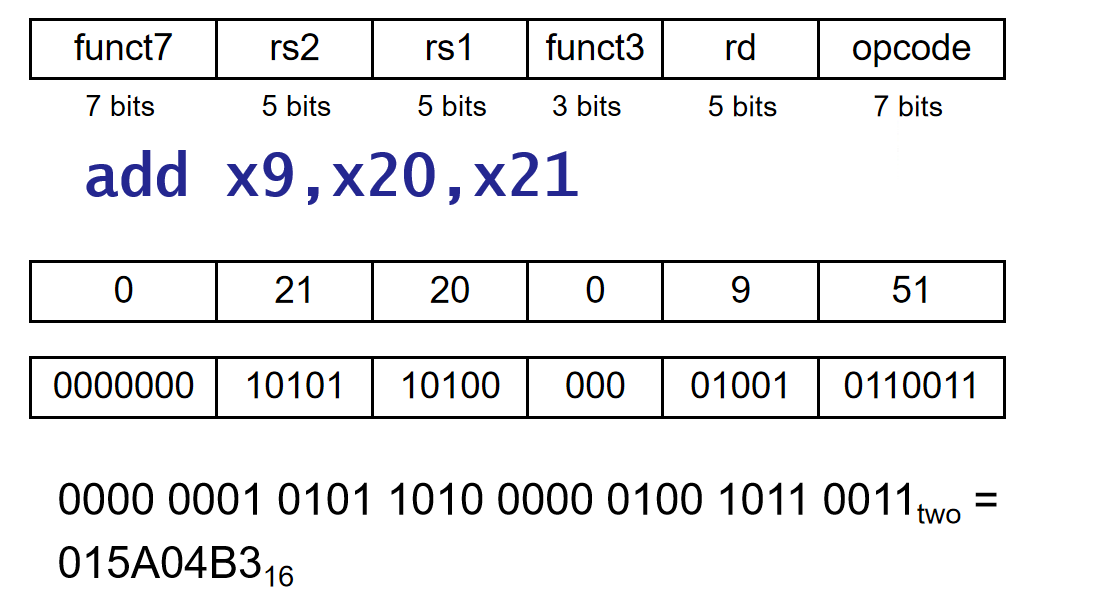
R-Format instructions¶
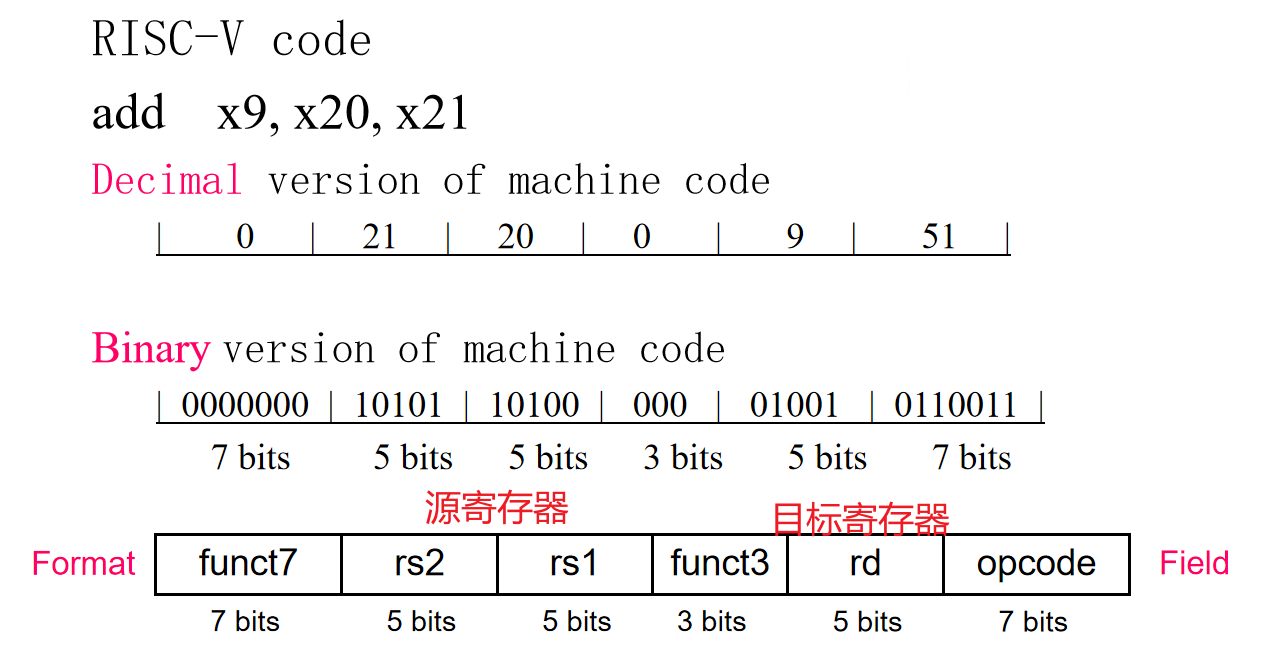
opcode: operation coderd: destination register numberfunct3: 3-bit function code (additional opcode) 例如区分加减法rs1: the first source register numberrs2: the second source register numberfunct7: 7-bit function code (additional opcode)
example
I-Format Instructions¶
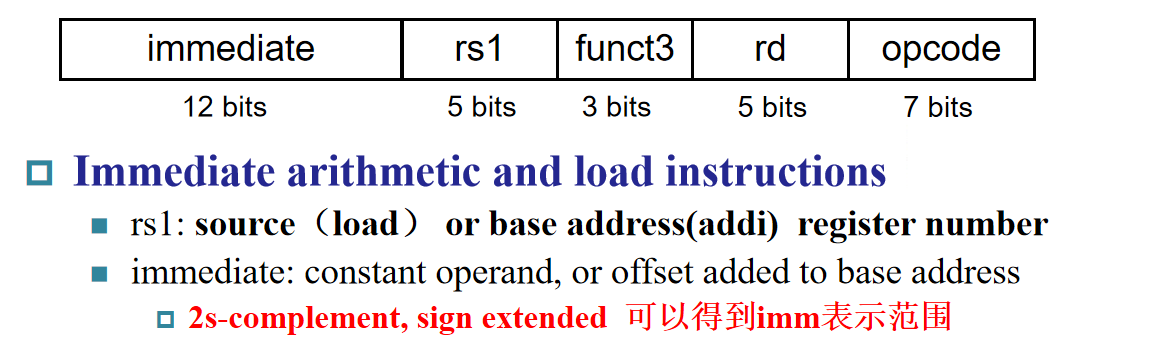
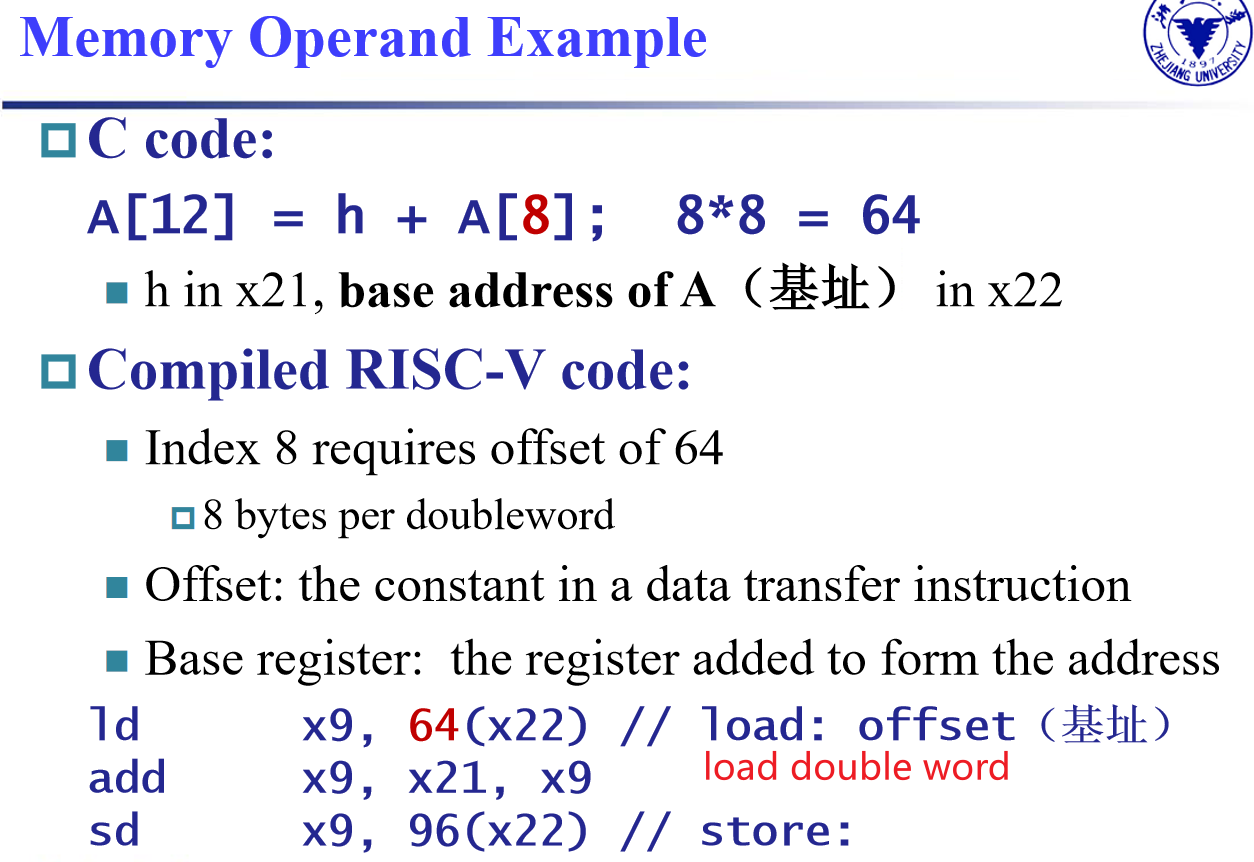
loadaddi
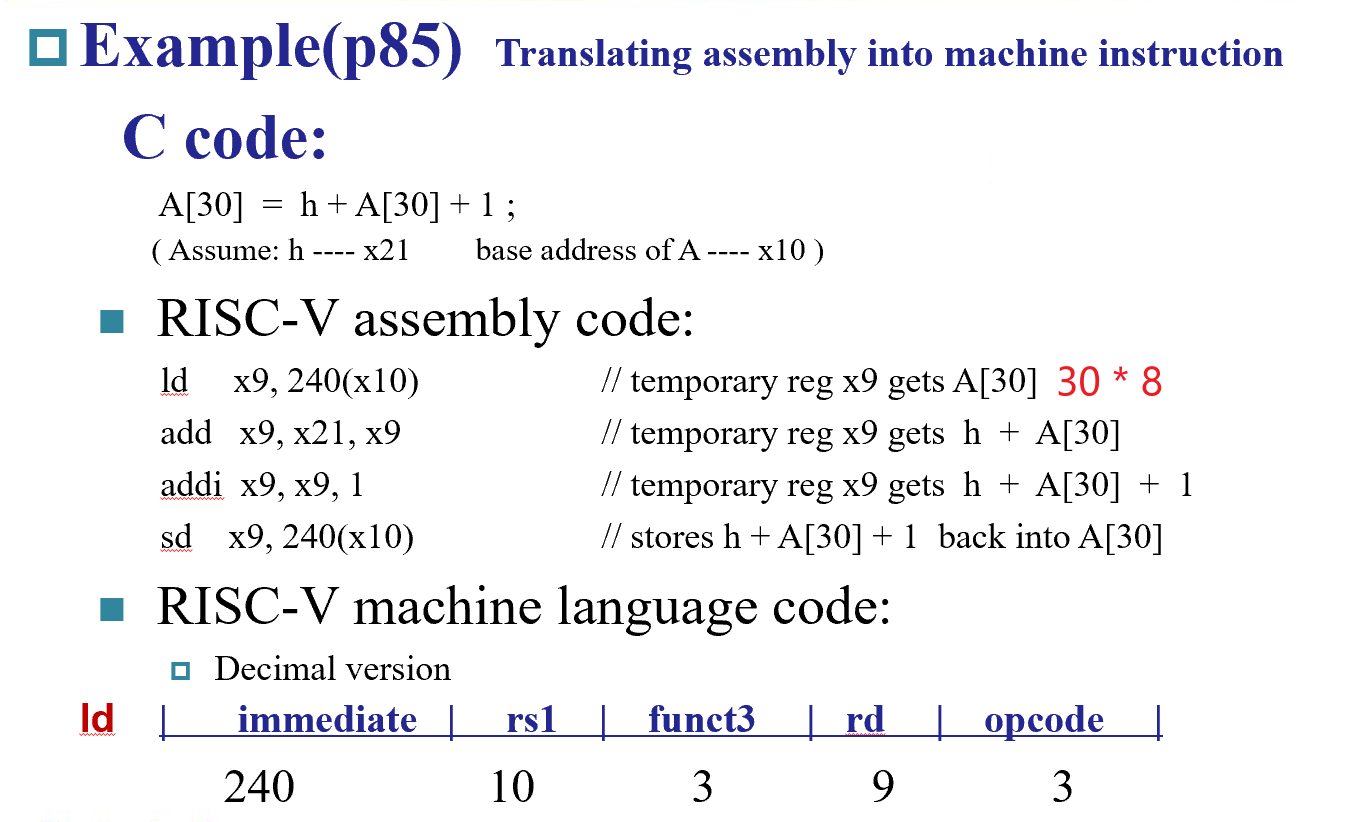
Example:ld x9, 64(x22)
22 (x22) is placed rs1;
64 is placed immediate
9 (x9) is placed rd
S-Format Instructions¶
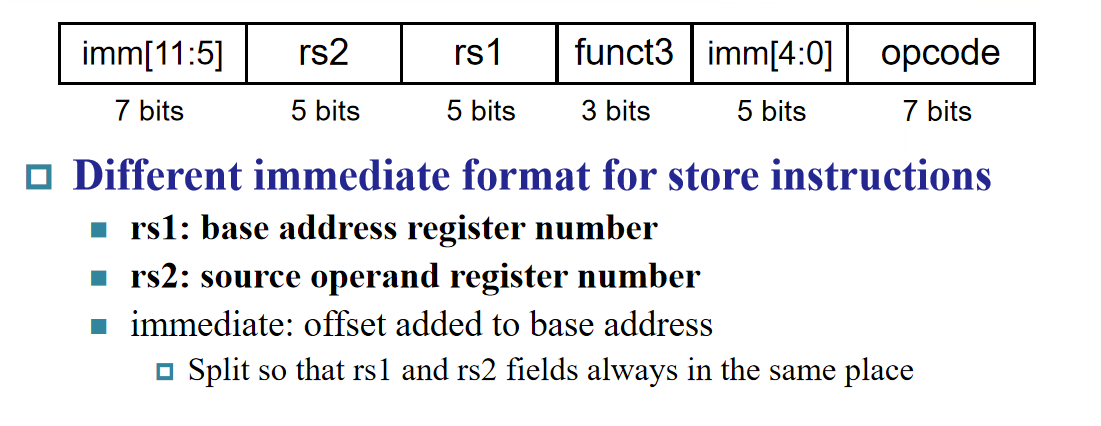
Example:sd x9, 64(x22)
22 (x22) is placed rs1;
64 is placed immediate
9 (x9) is placed rs2
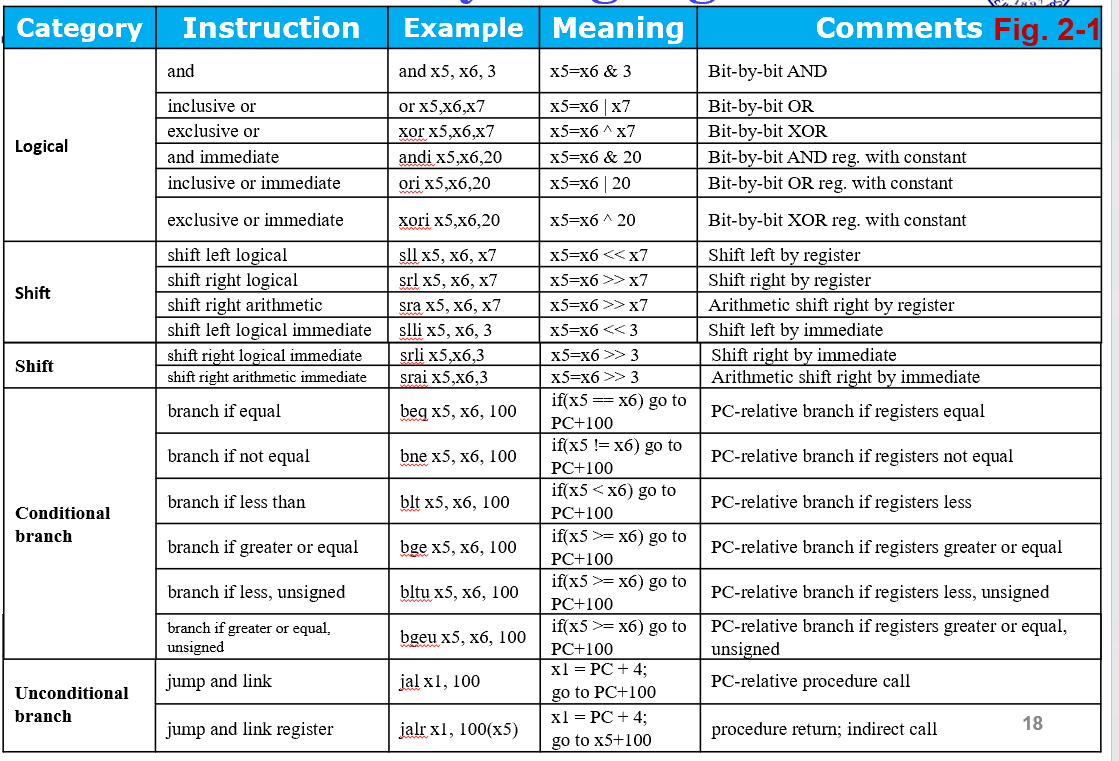
Logical¶
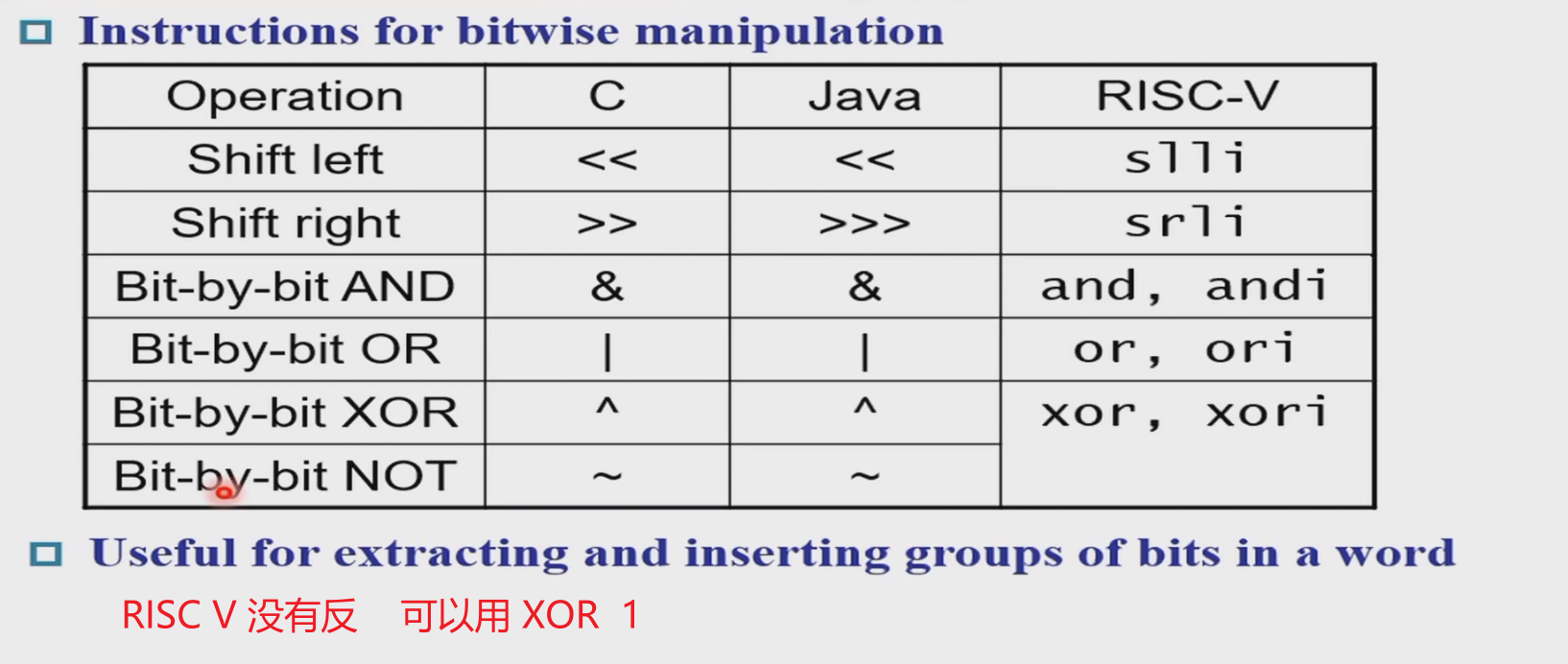

slli、ori...使用的仍然是I type Instruction,只是imm只用了低6位
Instructions for making decisions¶
Branch 指令¶
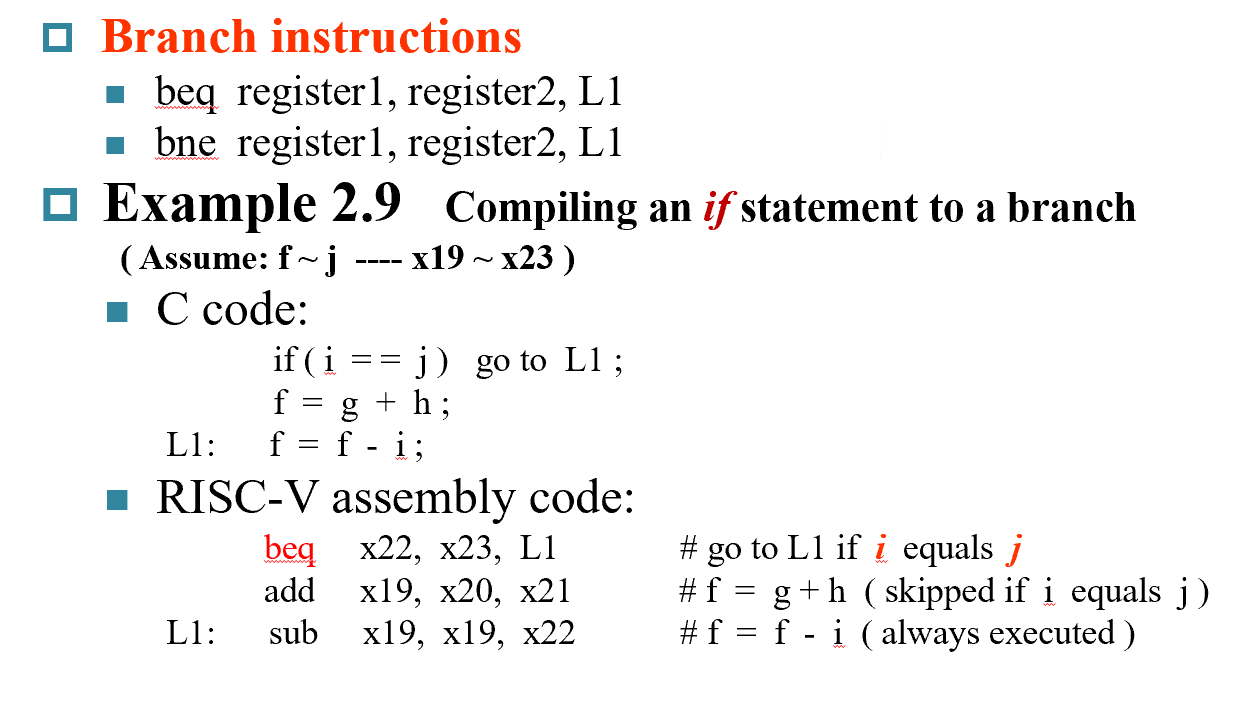
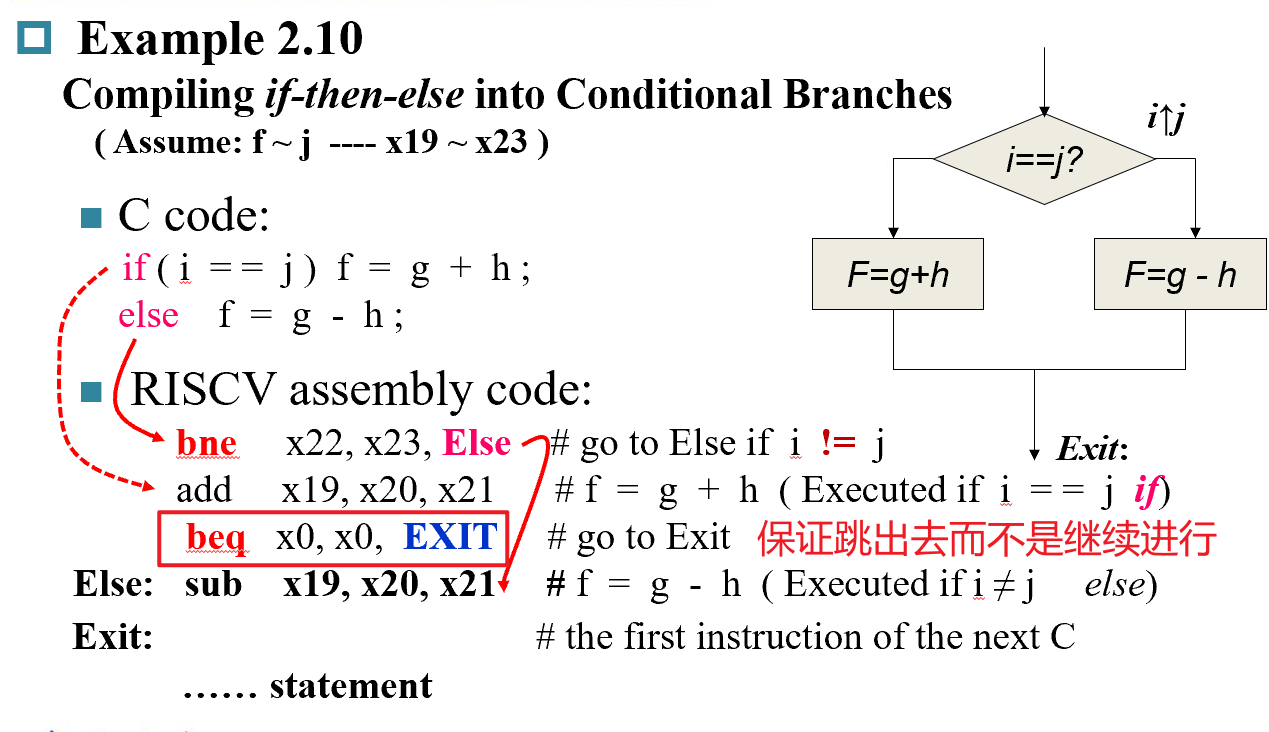
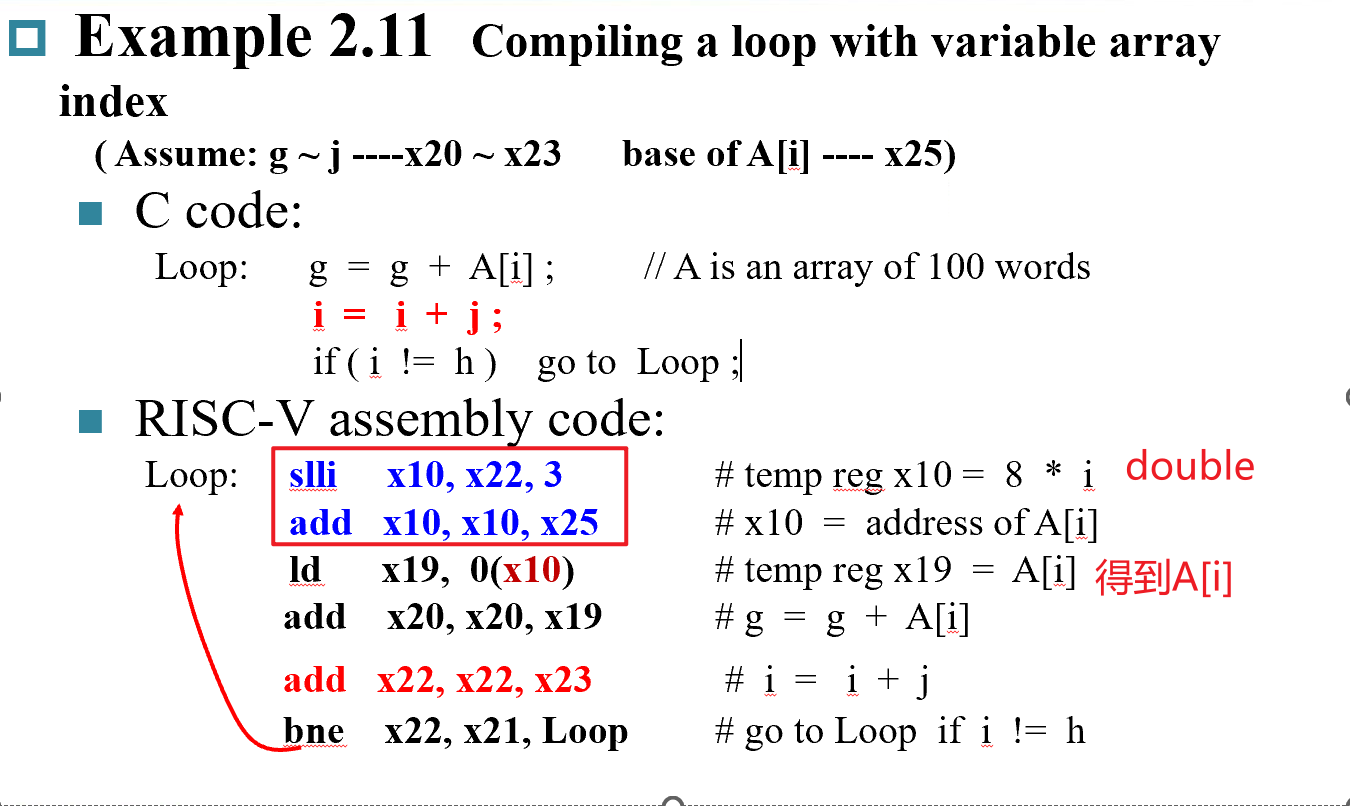
- 通过
slli x10,x22,3将 i 左移3位得到地址偏移量
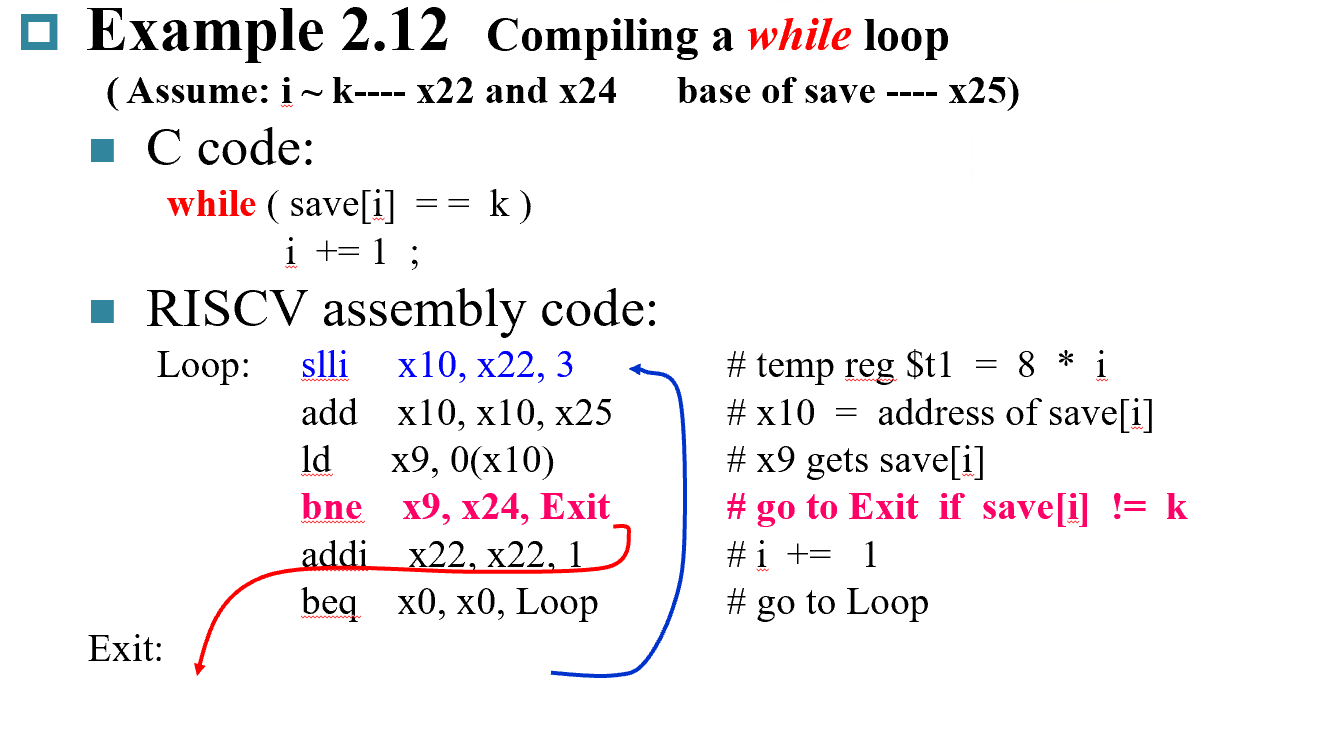
SLT¶

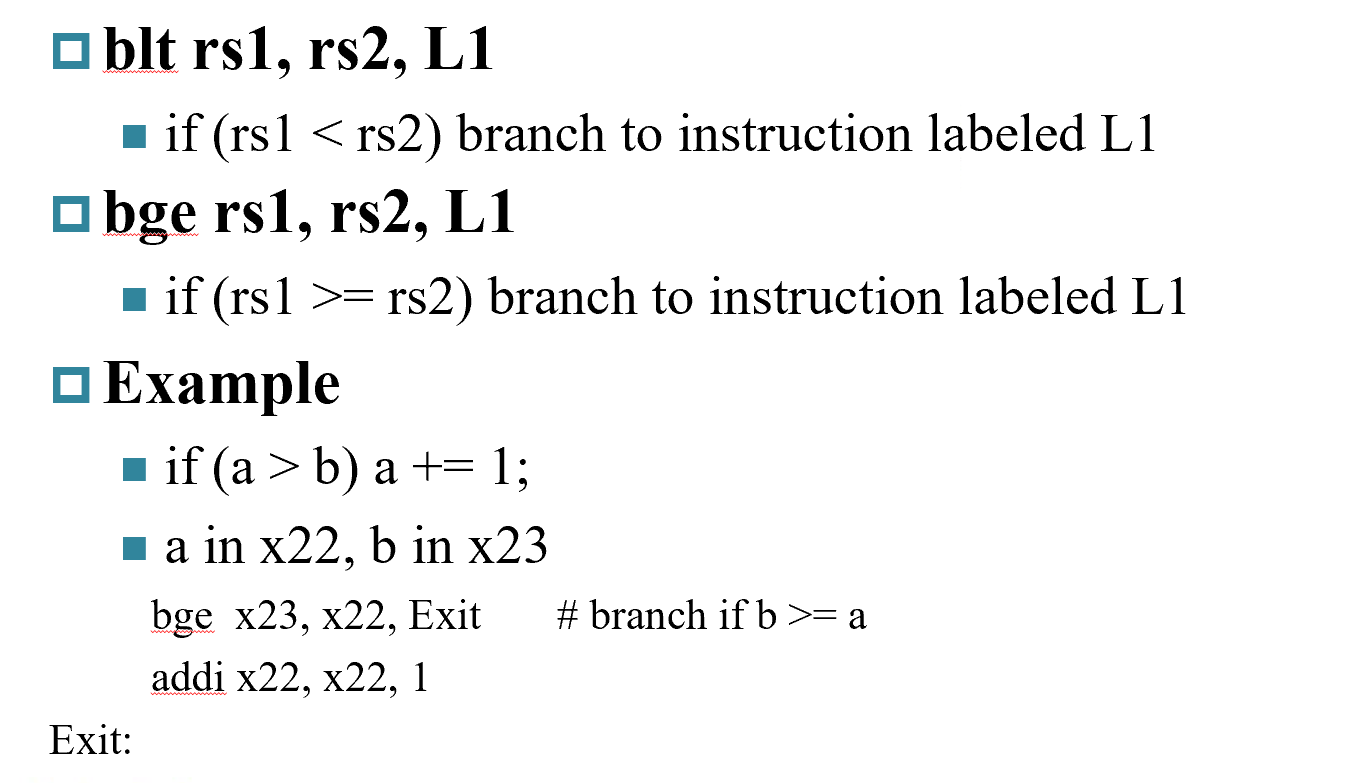
- 注意这里的大于表示方法,
bge>= beq== bne!=A>B B>=A
有符号数比较
blt: less thanbge: greater equal
无符号数 bltu bgeu
Switch/Case¶
jalr :jump and load register
JumpTable中存储的是目标程序的地址,这个Table的起始地址假设在X6
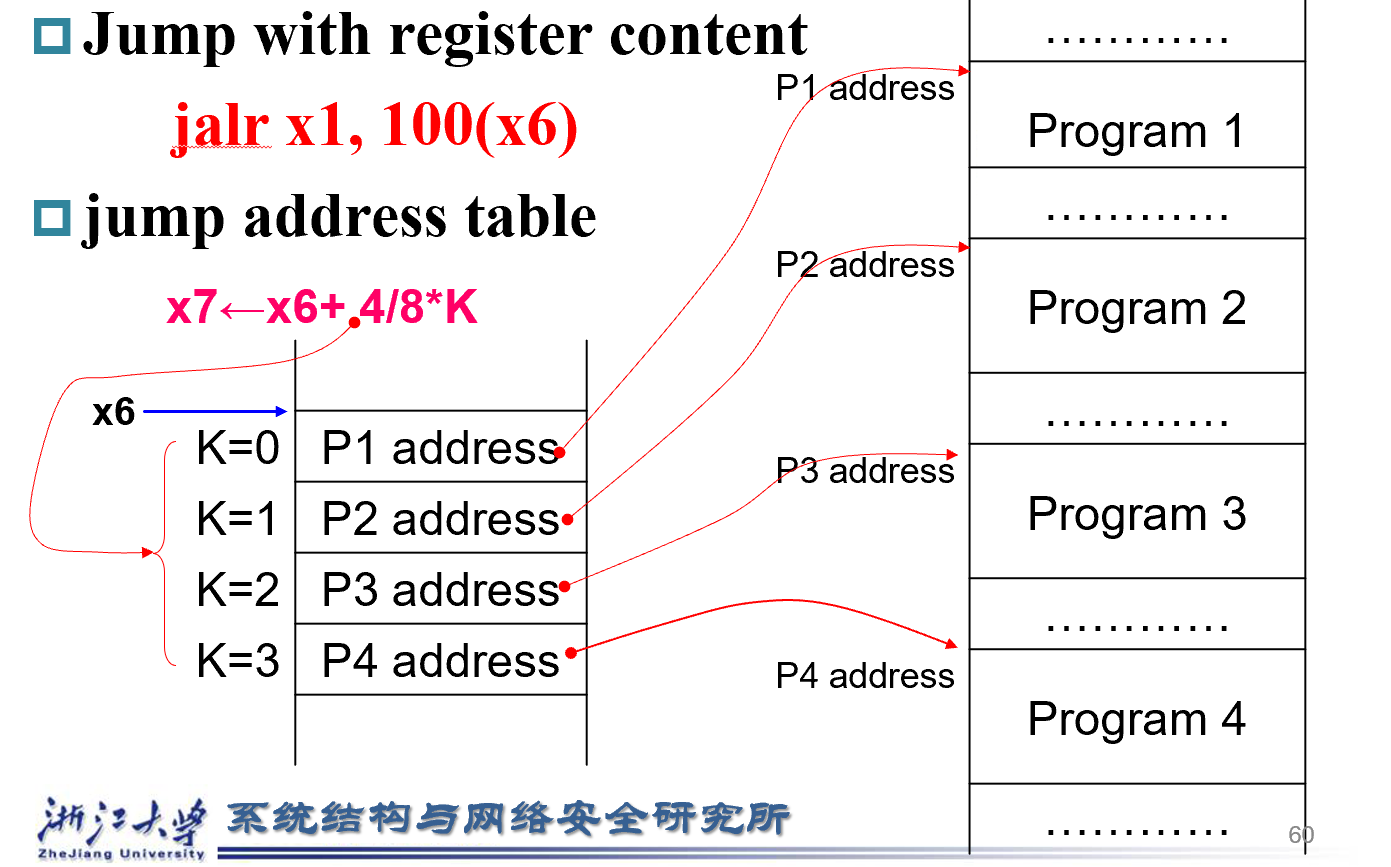
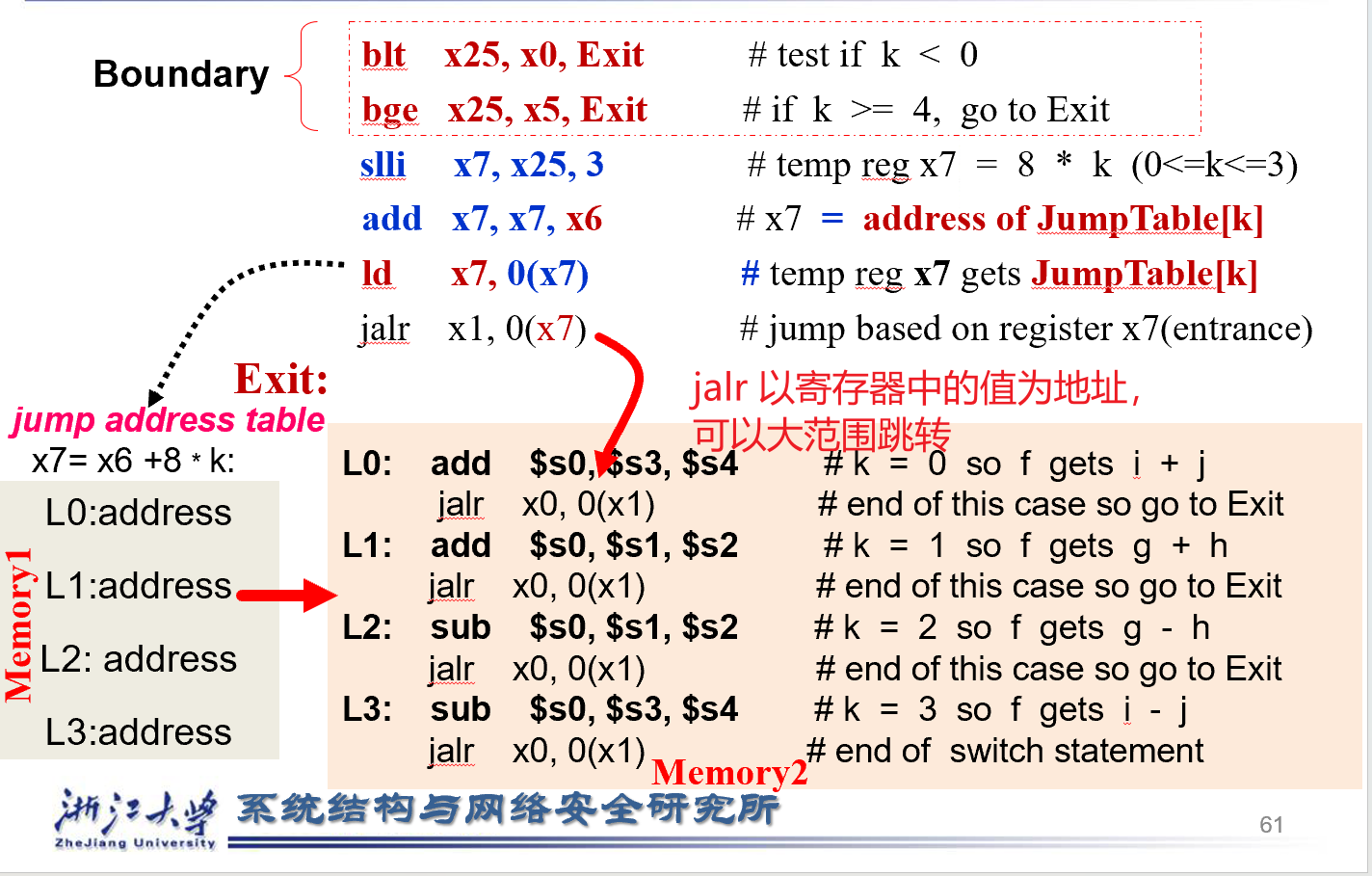
- 边界控制
- 计算Table中的地址
- 取出Table中的值(一个跳转的地址)
- 跳转
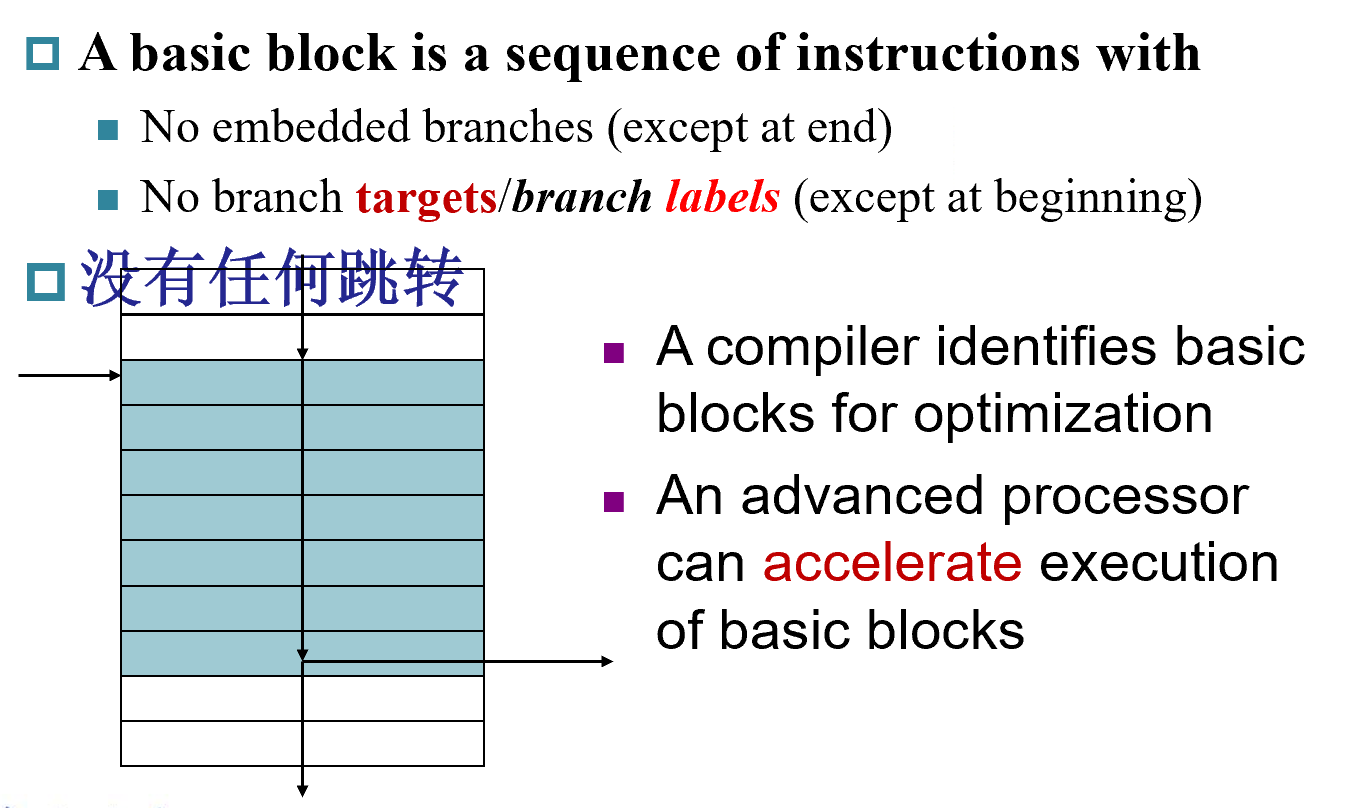
Basic Blocks¶
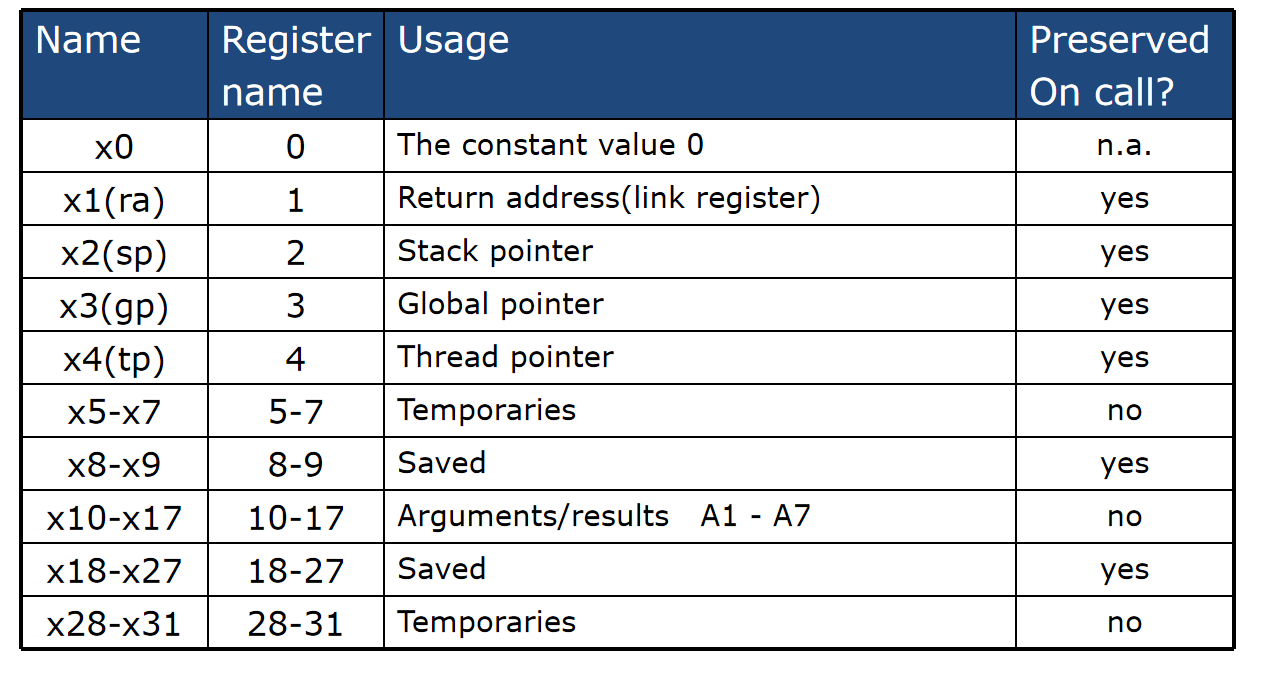
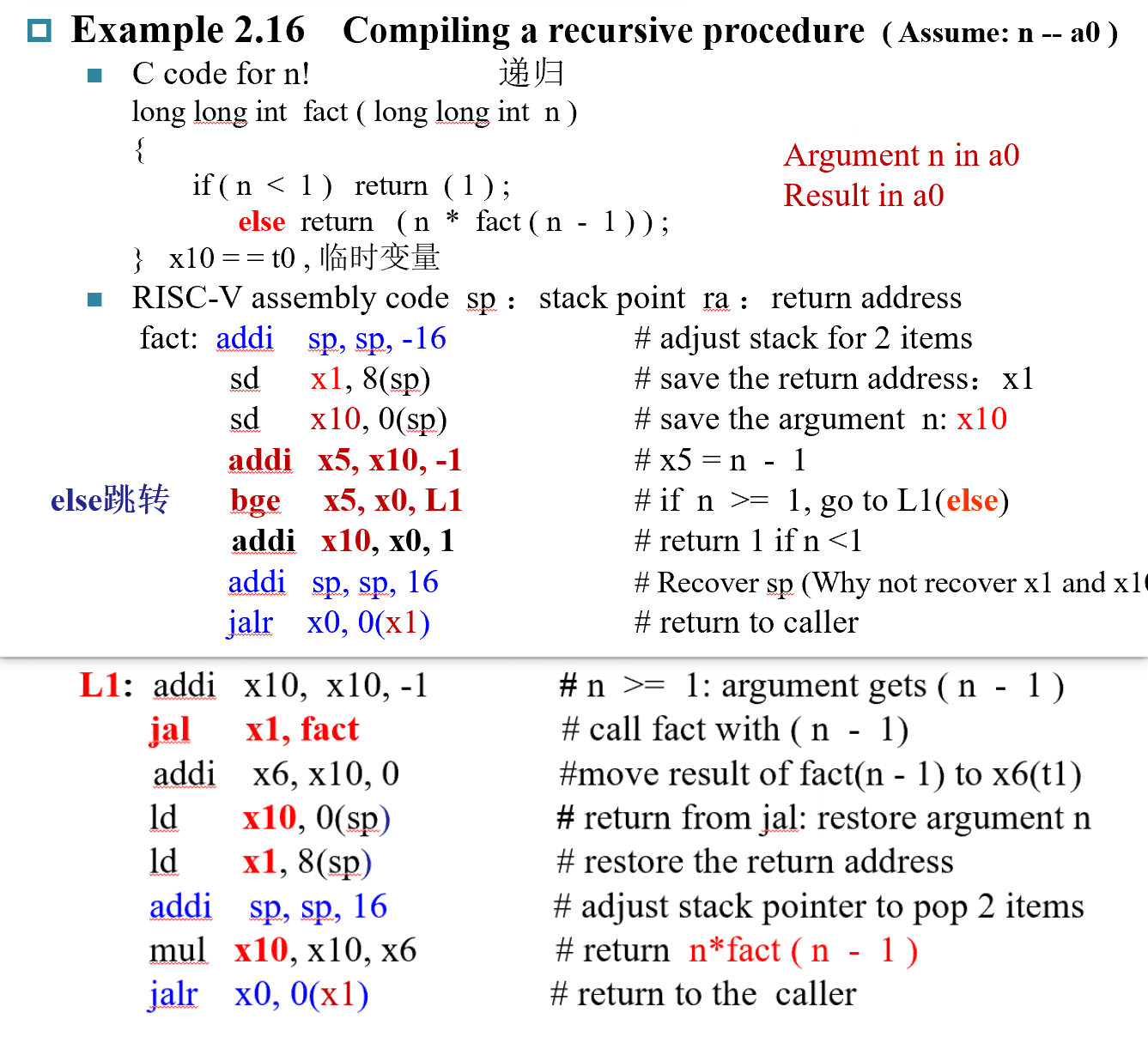
Procedure/function¶
jal : jump and link
jal x1,100 跳到 PC + 100 的位置
jarl x1,100(x5) 几乎相同,只是跳转的基址是reg中的值
基本流程
// Caller !push to stack!
Place Parameters in a place where the procedure can access them
Transfer control to the procedure:jump to
Acquire the storage resources needed for the procedure
Perform the desired task
Place the result value in a place where the calling program can access it
// Callee jalr x0,0(x1)
// !pull from stack and recover!
// !注意函数return的值要给某个另外的寄存器,而不是temporary寄存器!
Return control to the point of origin
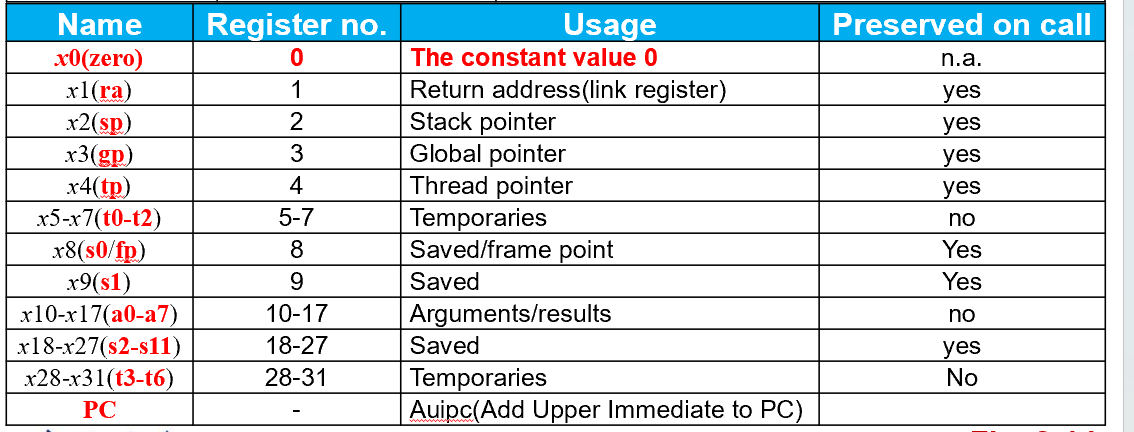
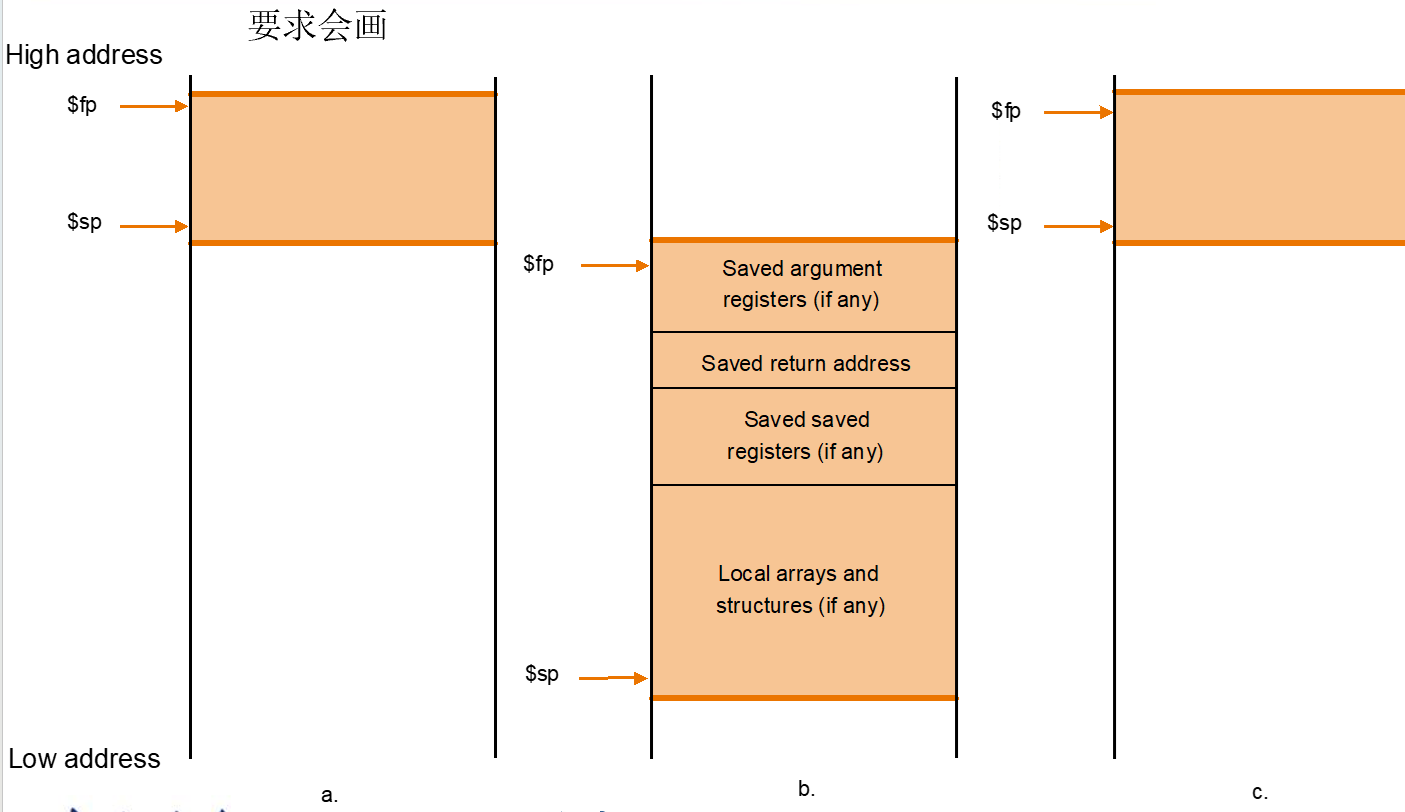
Stack
 - 当参数多于临时寄存器的个数
- 恢复原来的参数 针对
- 当参数多于临时寄存器的个数
- 恢复原来的参数 针对Saved value
- 注意方向,可以看到下面是低位,所以push要sp - 8*bits
Communicating with People¶
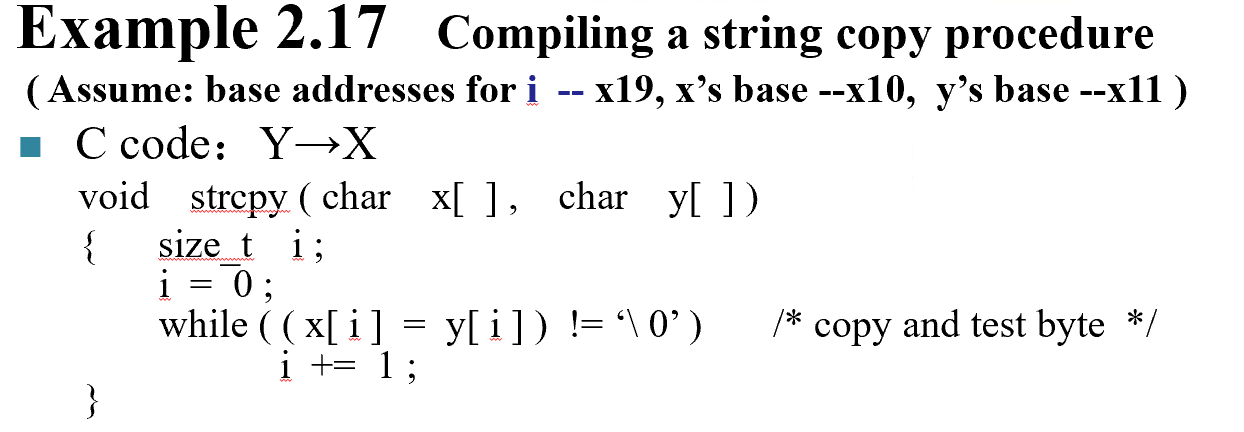
strcpy: addi sp, sp, -8 # adjust stack for 1 doubleword
sd x19, 0(sp) # save x19
add x19, x0, x0 # i = 0
L1:
add x5, x19, x11 # x5 = address of y[ i ]
lbu x6, 0(x5) # x6 = y [ i ]
add x7, x19, x10 # x7 = address of x[ i ]
sb x6, 0(x7) # x[ i ] = y[ i ]
beq x6, x0, L2 # if y[i] == 0 then exit
addi x19, x19, 1 # i = i + 1
jal x0, L1 # next iteration of loop
L2: ld x19, 0(sp) # restore saved old s3
addi sp, sp, 8 # pop 1 double word from stack
jalr x0 0(x1) # return
注意这里计算address的时候是char类型的
32-Bit Immediate and Addresses¶
lui

寻址¶
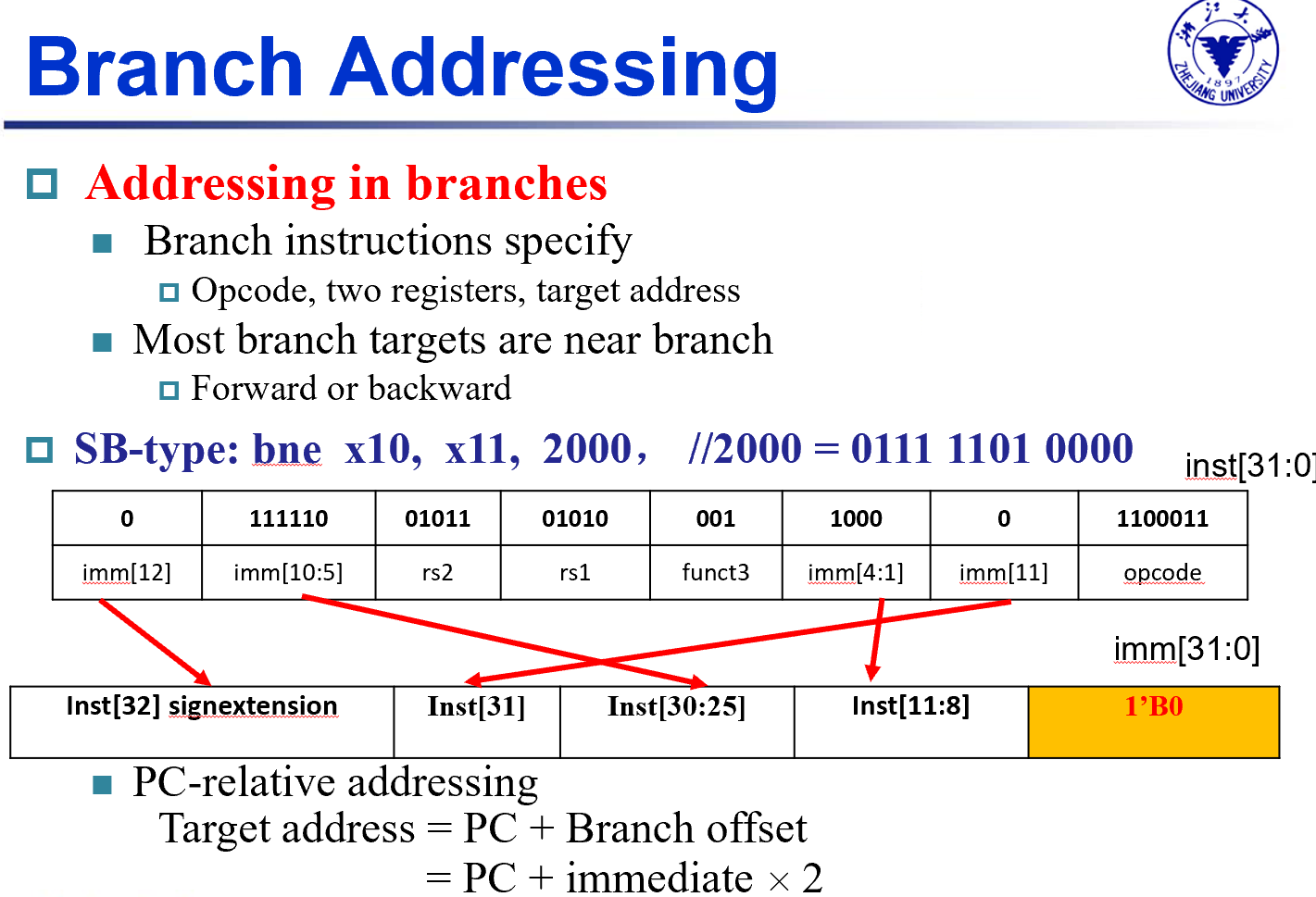
- PC相对寻址方式
下面两种imm的最低为恒为1
Branches
Jump
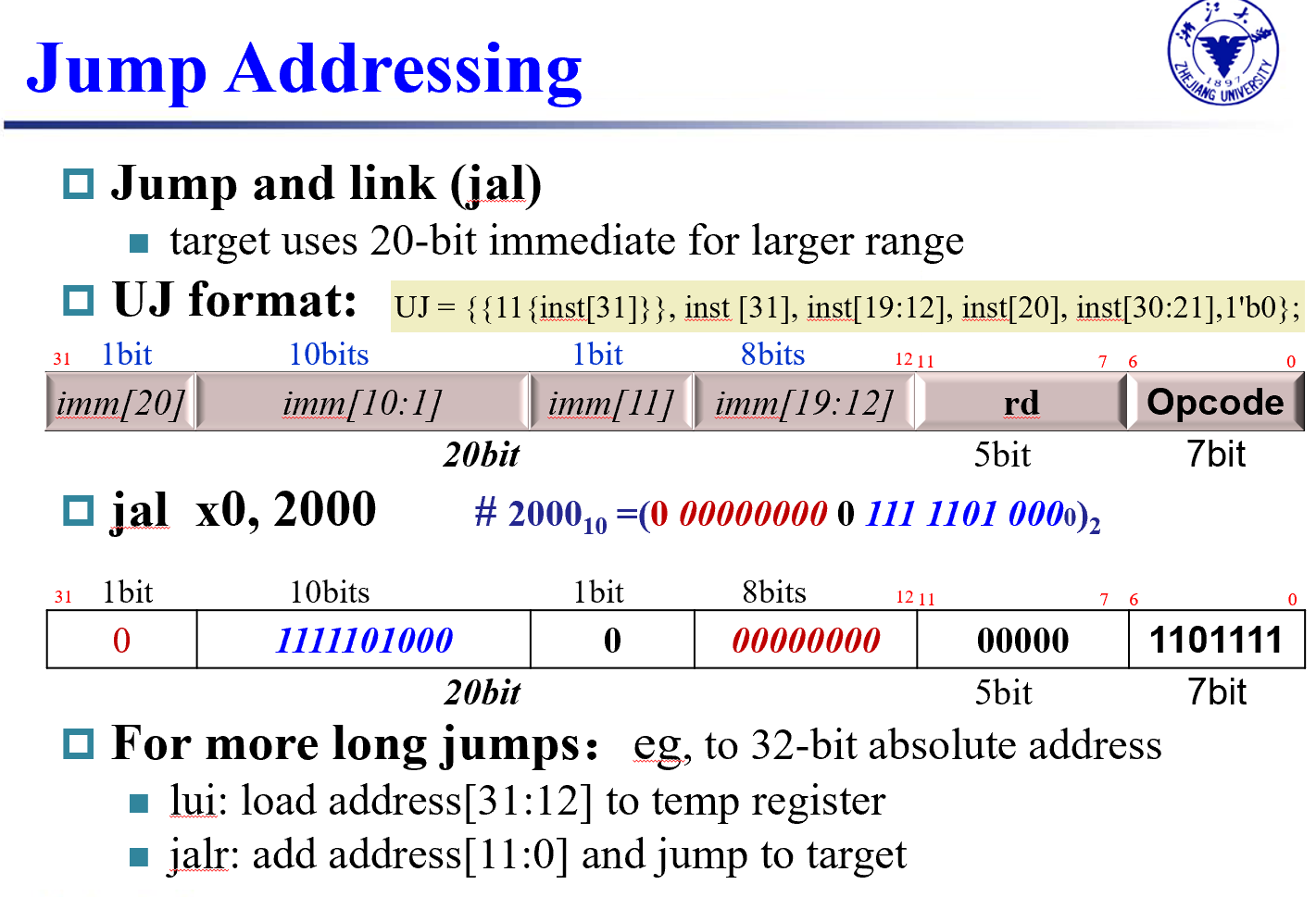
这里的jump指的是jal
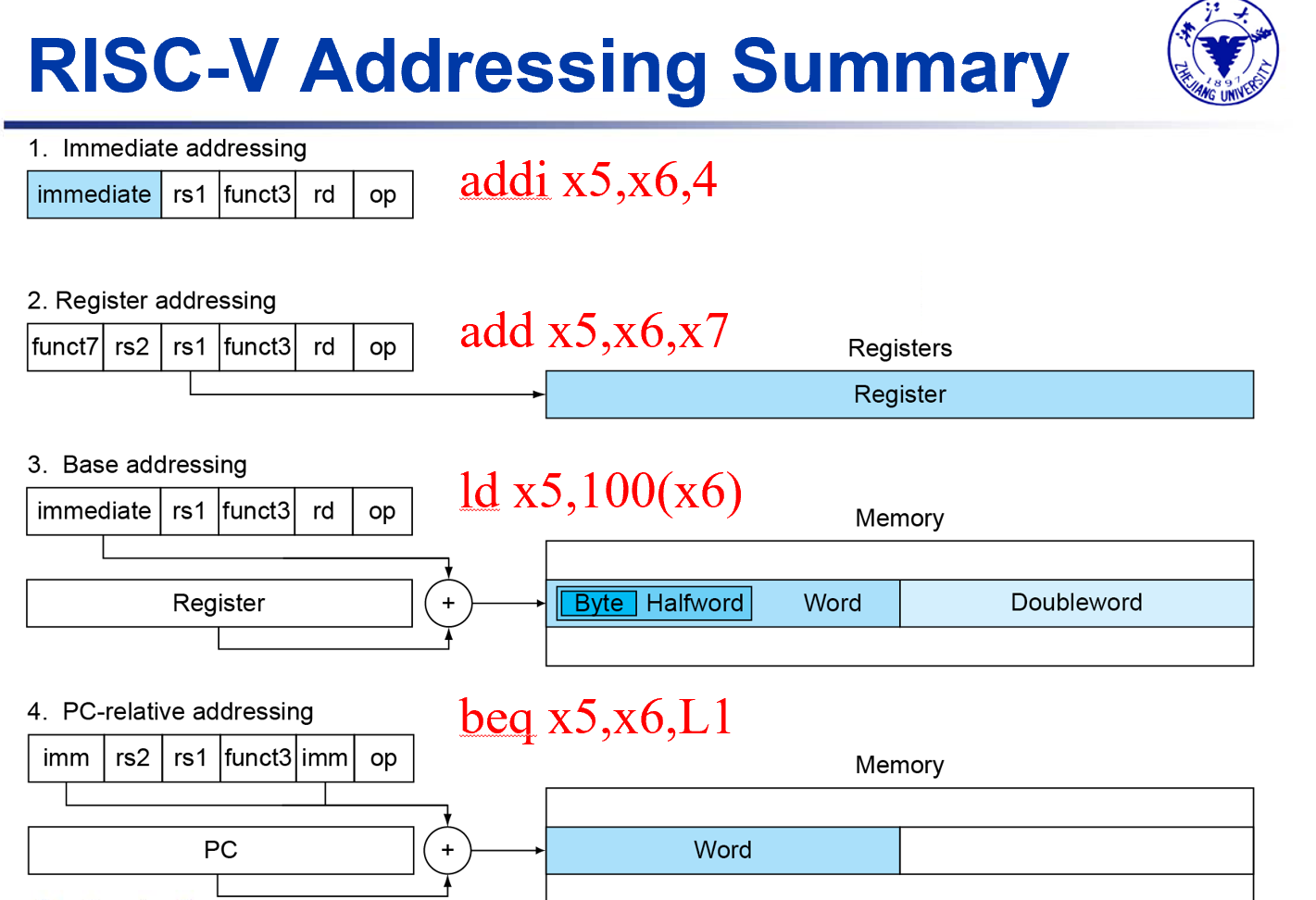
Synchronization in RISC-V | 同步¶
不想学了
A C Sort Example To Put it All Together¶
主要要理解一下loop
题目¶
大小端对齐¶
这里一个byte存储两个16进制数
answer
-
0x11
-
0x88
汇编¶
斐波那契数¶
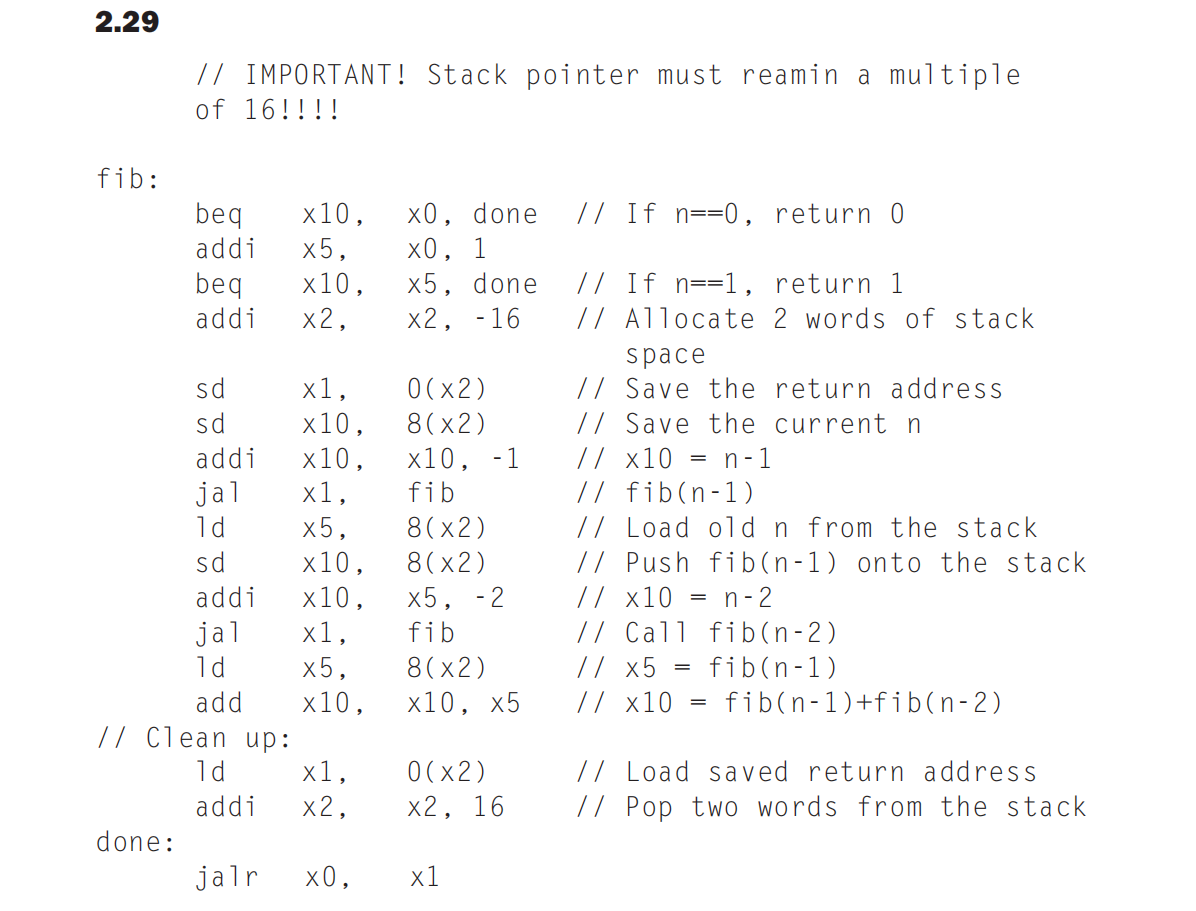
尾递归的优化、¶


