Chapter 1 | Computer Abstraction¶
约 360 个字 20 张图片 预计阅读时间 2 分钟
info
这一章是总览性质的,没有特别的知识点,很多都是性质、概述。 要注意Time的计算
- Instruction set architecture(ISA,指令集系统结构) ---- the interface between hardware and lowest-level software
组成¶
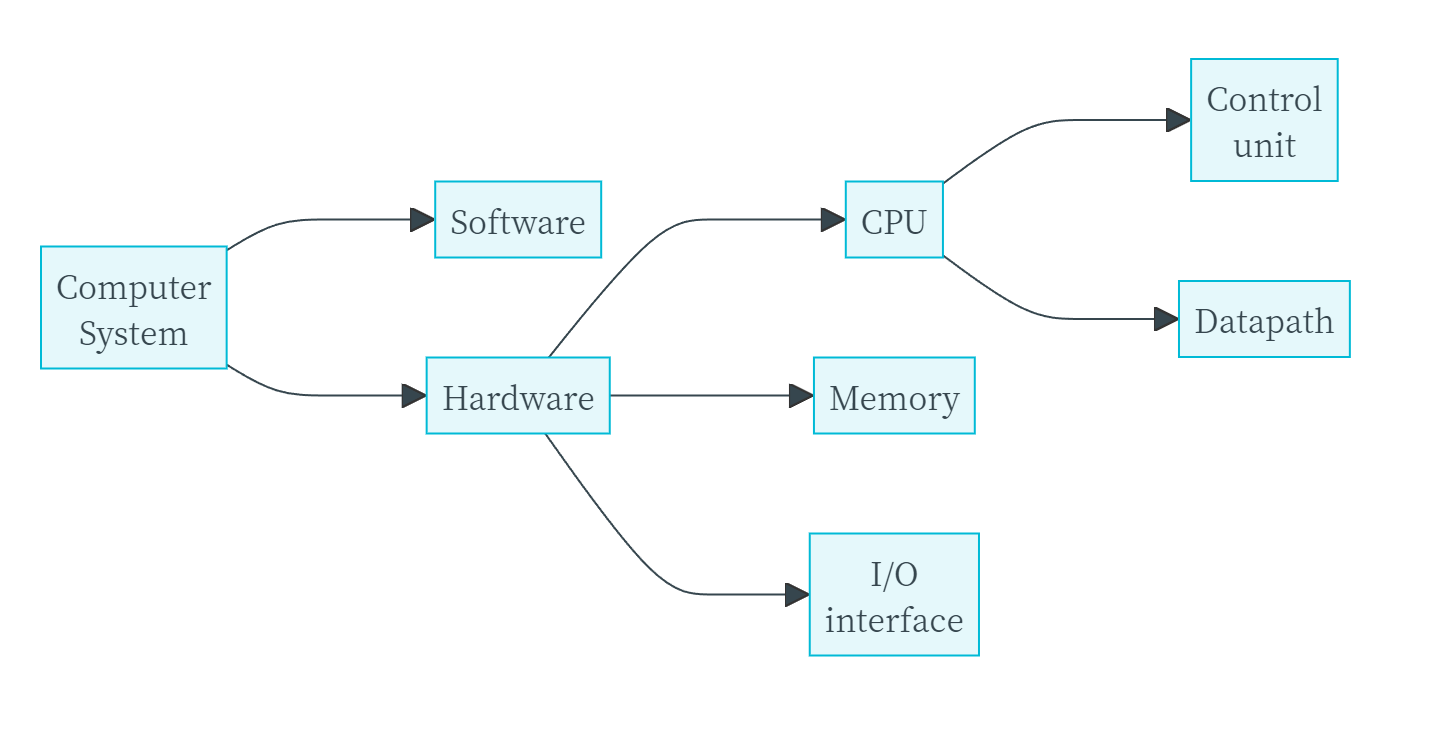
Graph From https://xuan-insr.github.io/
graph LR
1[Computer System]
2[Software]
3[Hardware]
2.1[Application Software]
2.2[System Software]
2.2.1[Operation System]
2.2.2[GCC]
2.2.3[Firmware/Driver Software]
1 --> 2
1-->3
2-->2.1
2-->2.2
2.2-->2.2.1
2.2-->2.2.2
2.2-->2.2.3
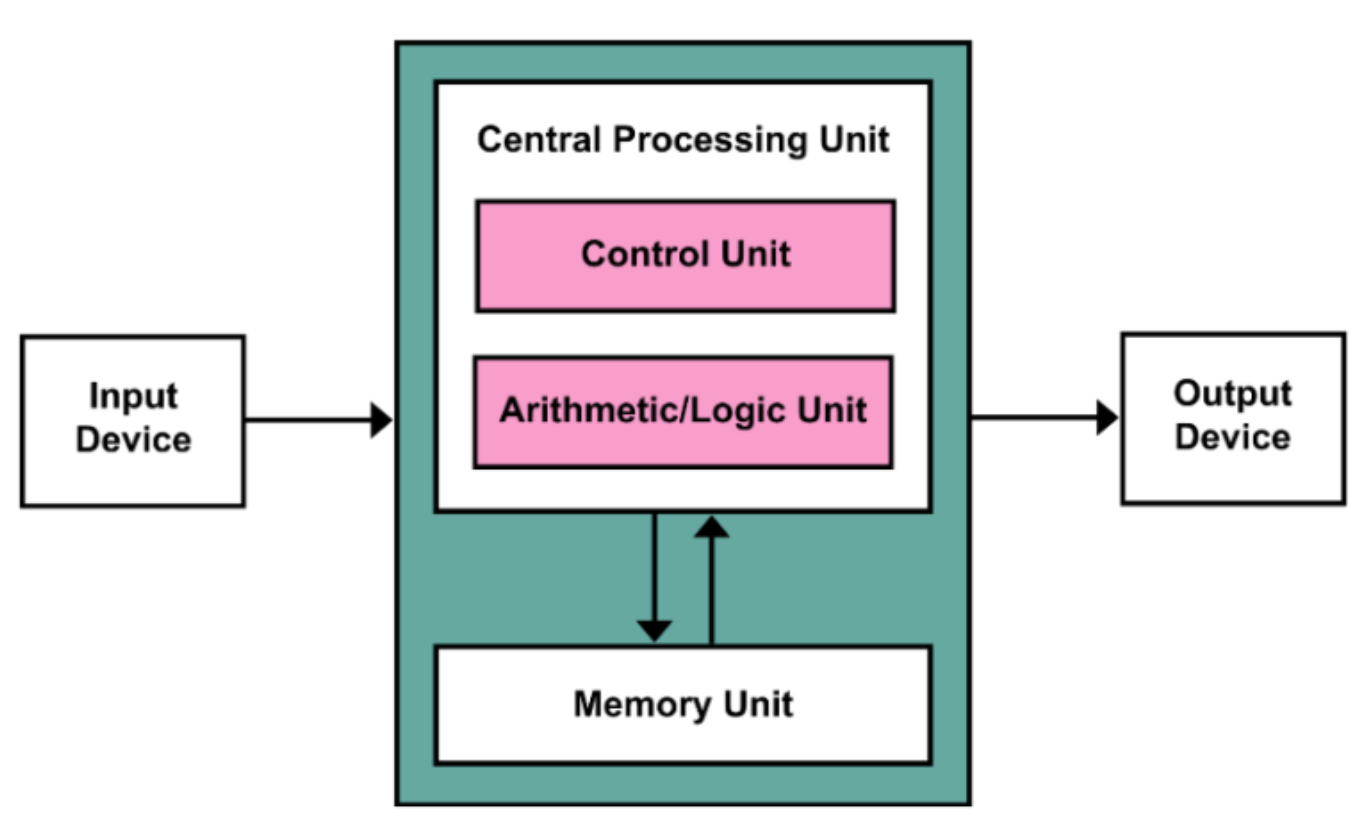
3.1[CPU]
3.2[Memory]
3.3[I/O interface]
3.1.1[Control unit]
3.1.2[DataPath]
3-->3.1
3-->3.2
3-->3.3
3.1-->3.1.1
3.1-->3.1.2
3.3.1[Input: keyboard]
3.3.2[Bidirectional: RS-232,USB]
3.3.3[Output: VGA,LCD]
3.3-->3.3.1
3.3-->3.3.2
3.3-->3.3.3没想到期中考试竟然考了Software部分的框图
SoftWare
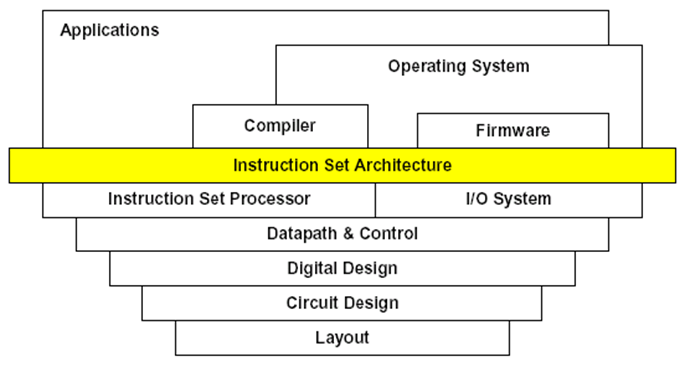
I/O Interface¶
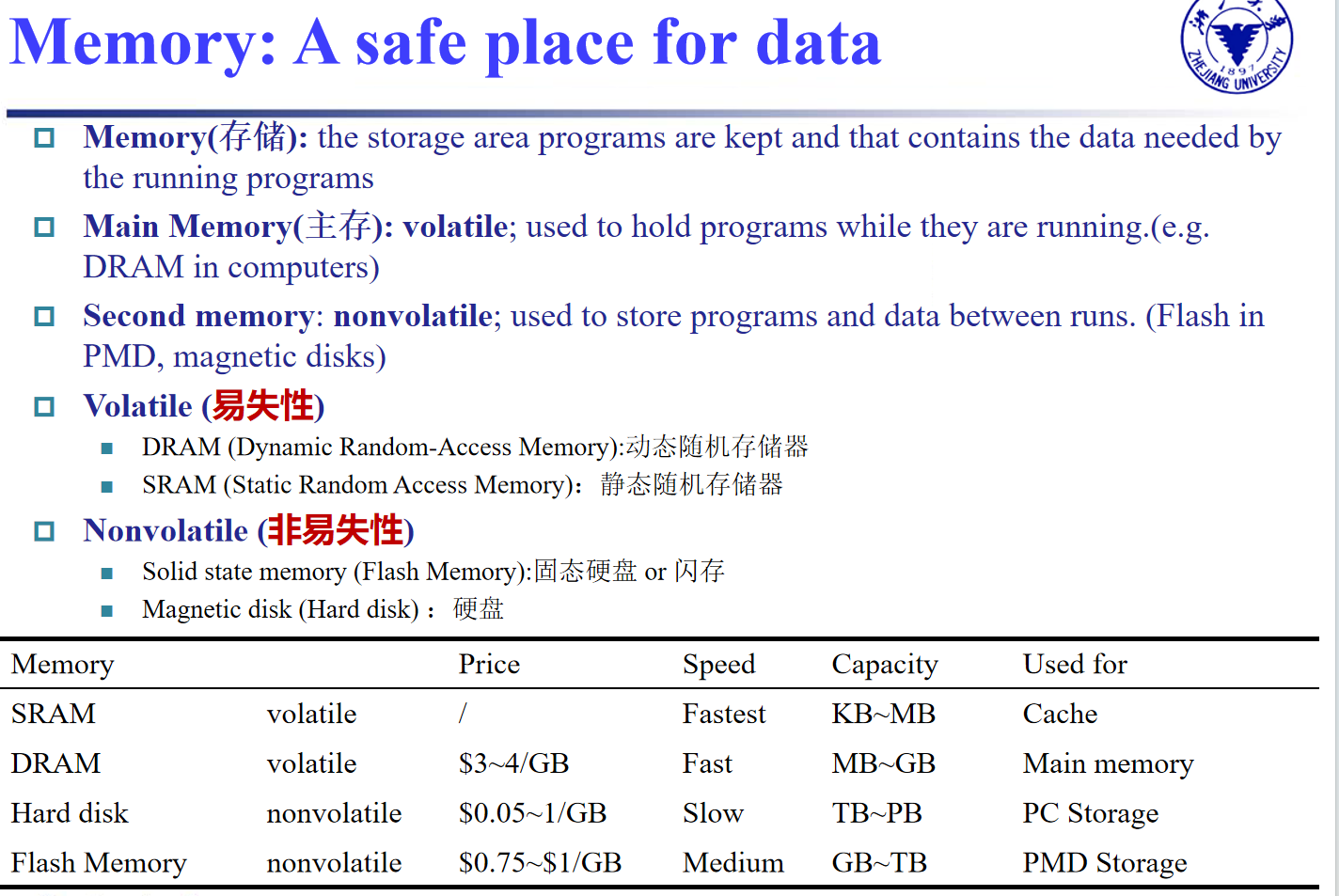
Memory¶
语言转换¶
graph
高级编程语言--Compiler-->汇编--ASsembler-->3[Machine Code]* Time的计算¶
处理器执行时间由处理频率, 程序执行的指令数目和每条指令的性能决定; 而每条指令的性能,由每条指令所需时钟数决定
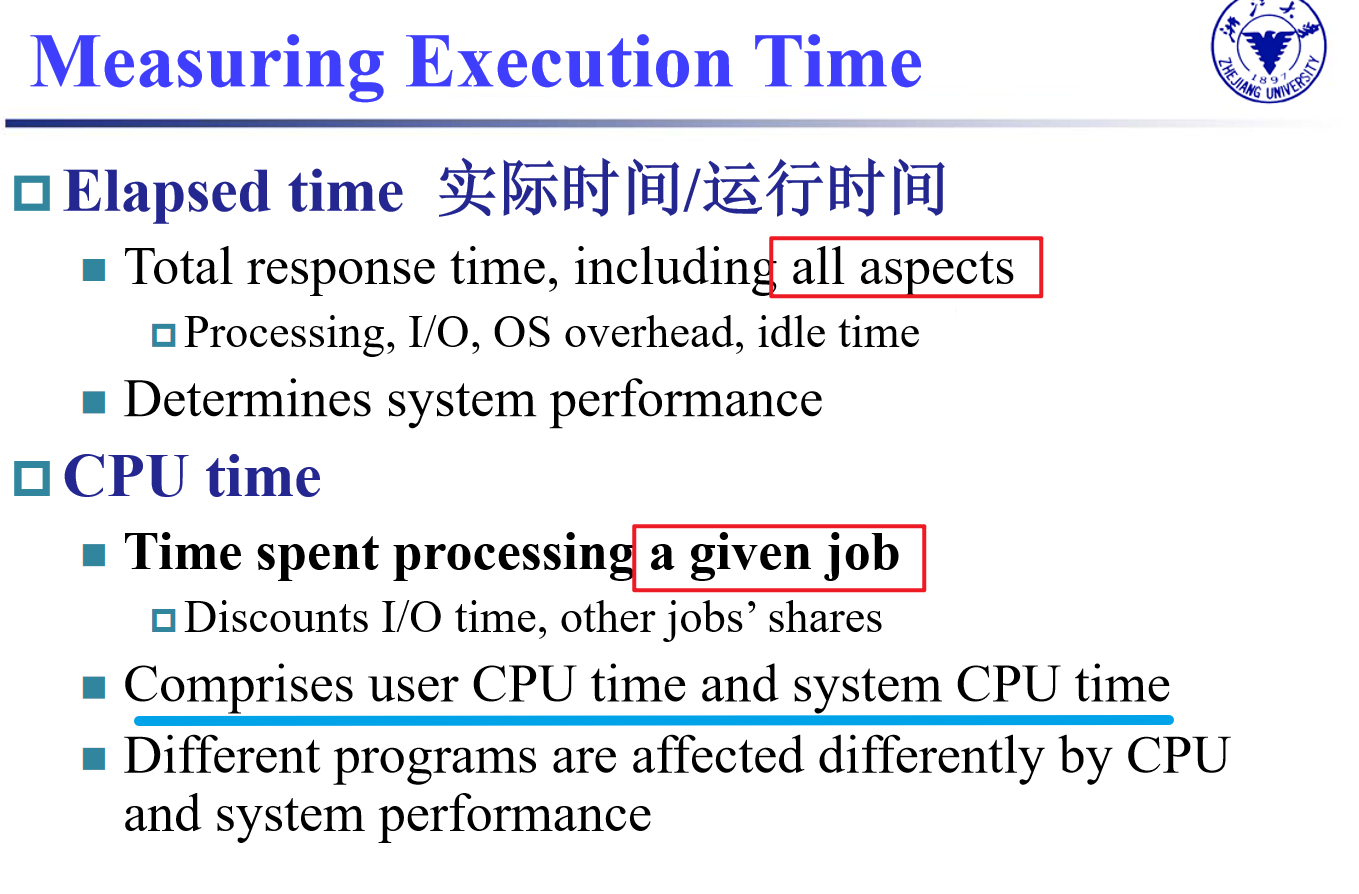
Response time/execution time 响应时间/执行时间
- How long it takes to do a task
Throughput (bandwidth) 吞吐率
- Total work done per unit time
- e.g., tasks/transactions/… per hour
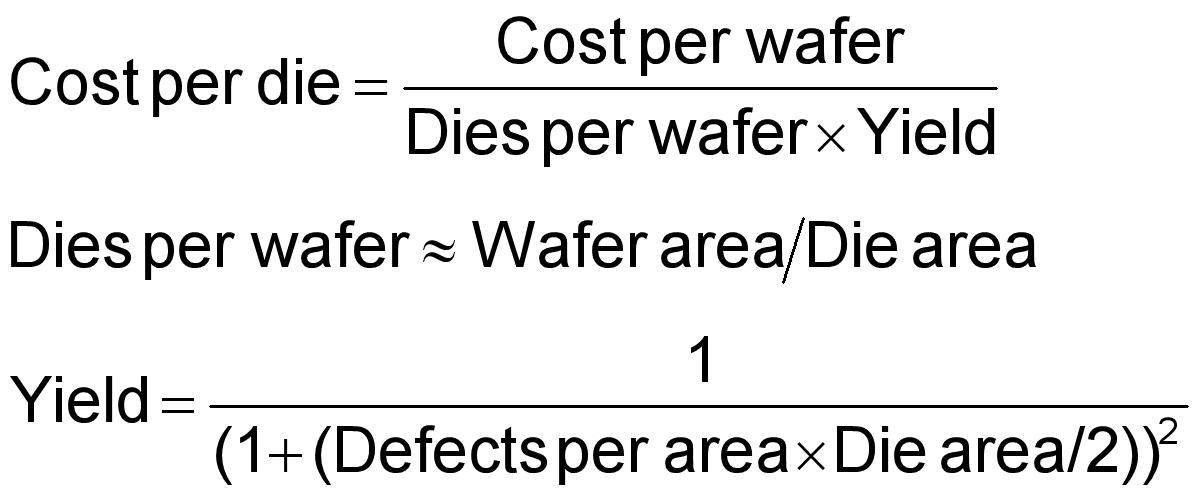
了解cost
Performance = 1/Execution Time

一个指令周期,包含多个 CPU 周期,而一个 CPU 周期包含多个时钟周期。
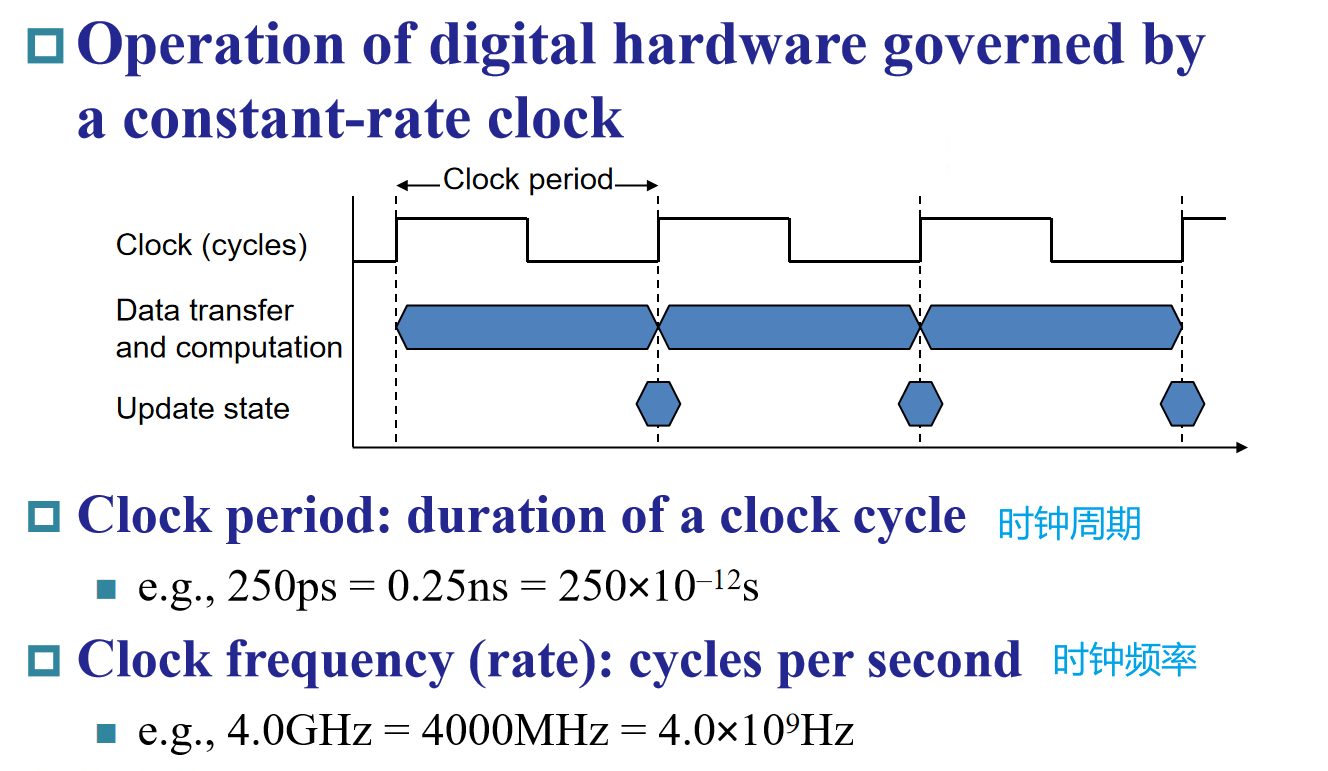


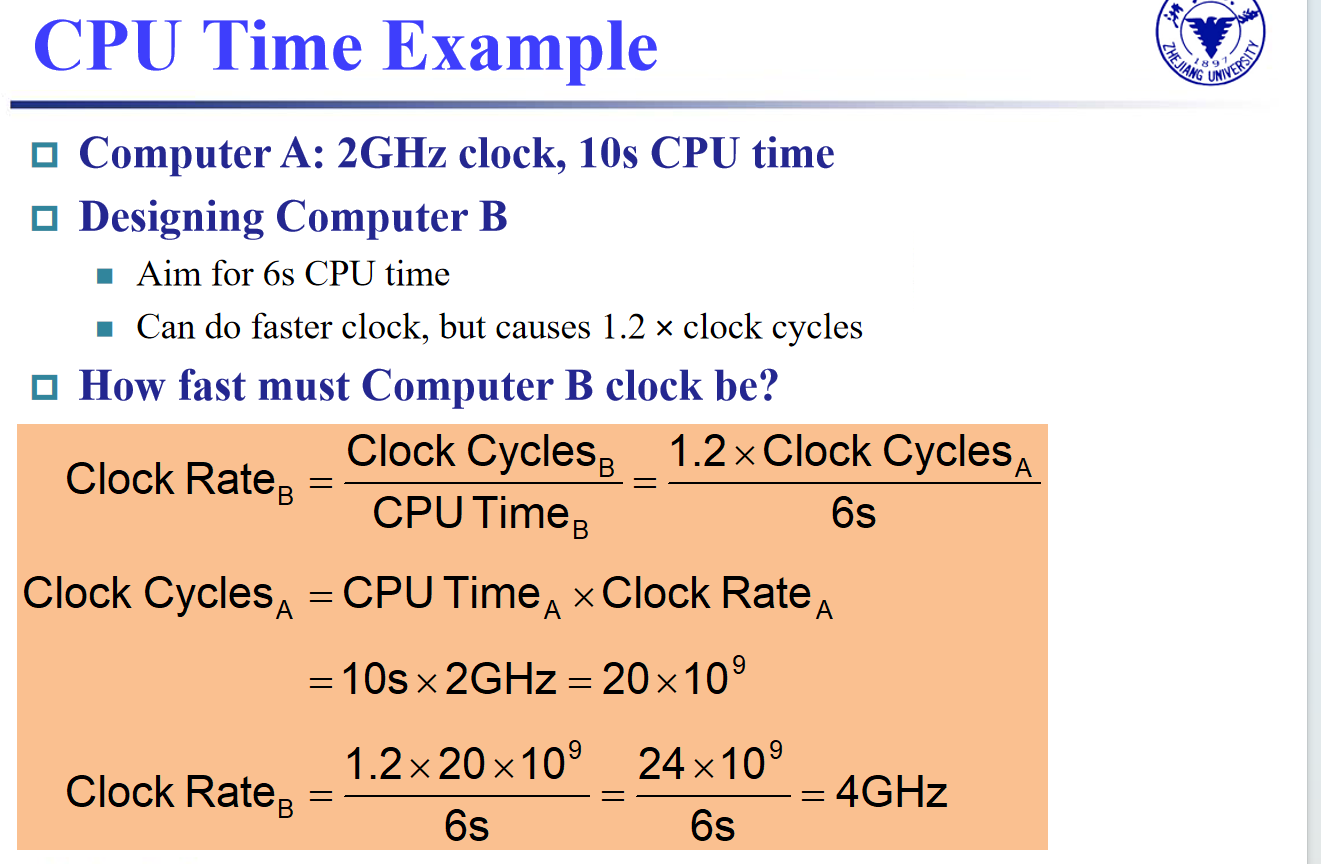
example
- CPI : 每条指令的平均周期数(Average cycles per instruction) → CPU 周期
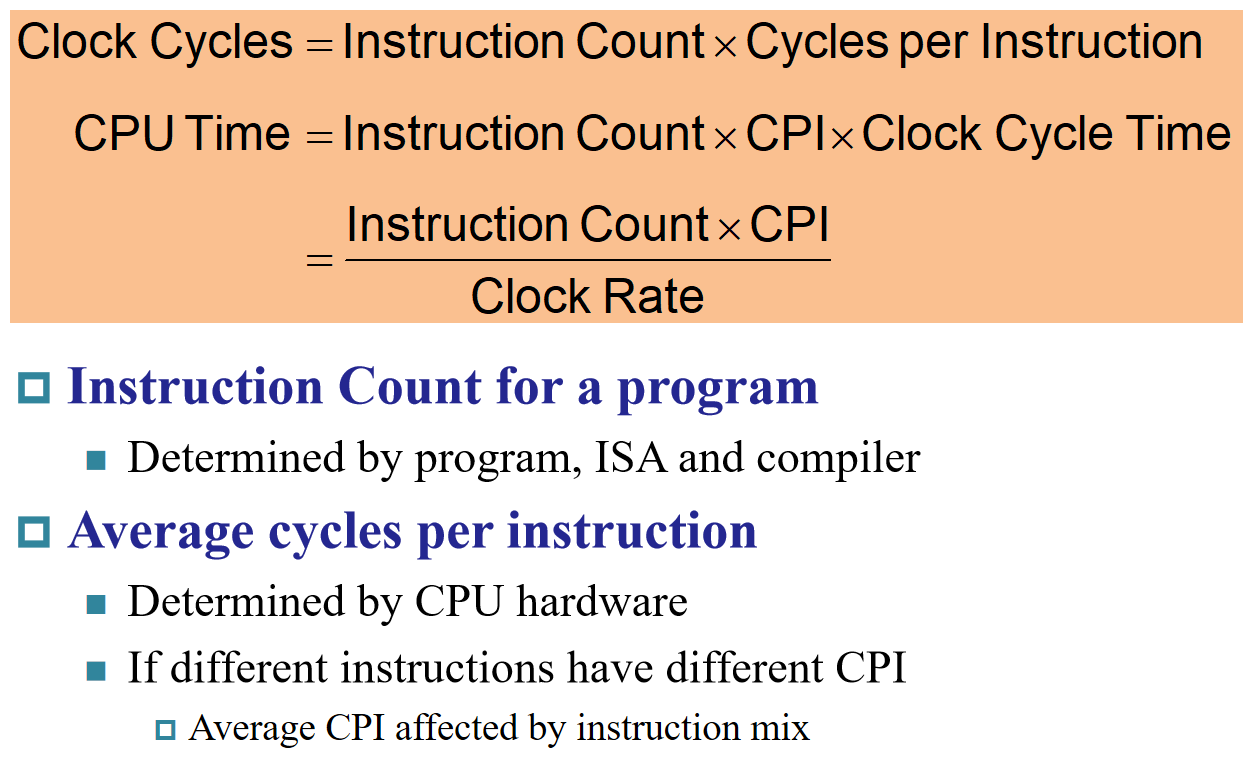
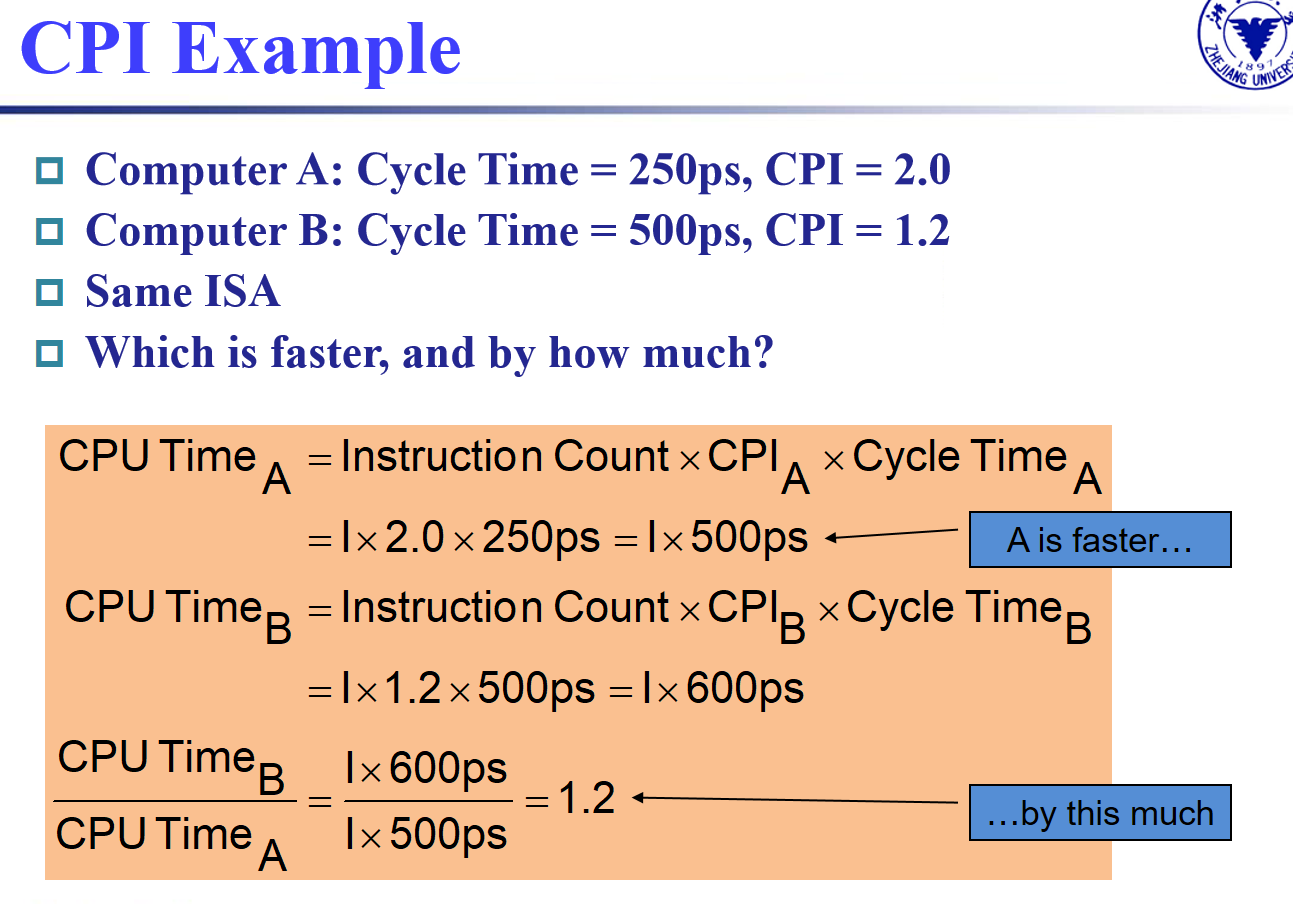
example
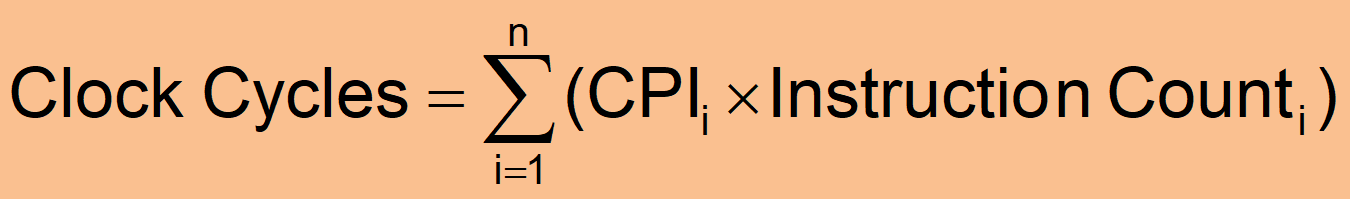
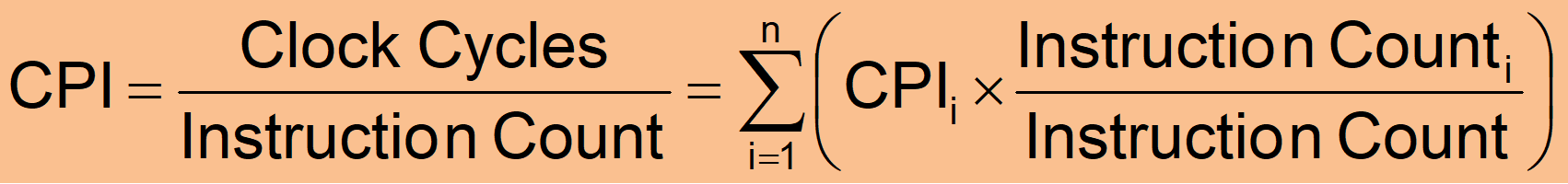
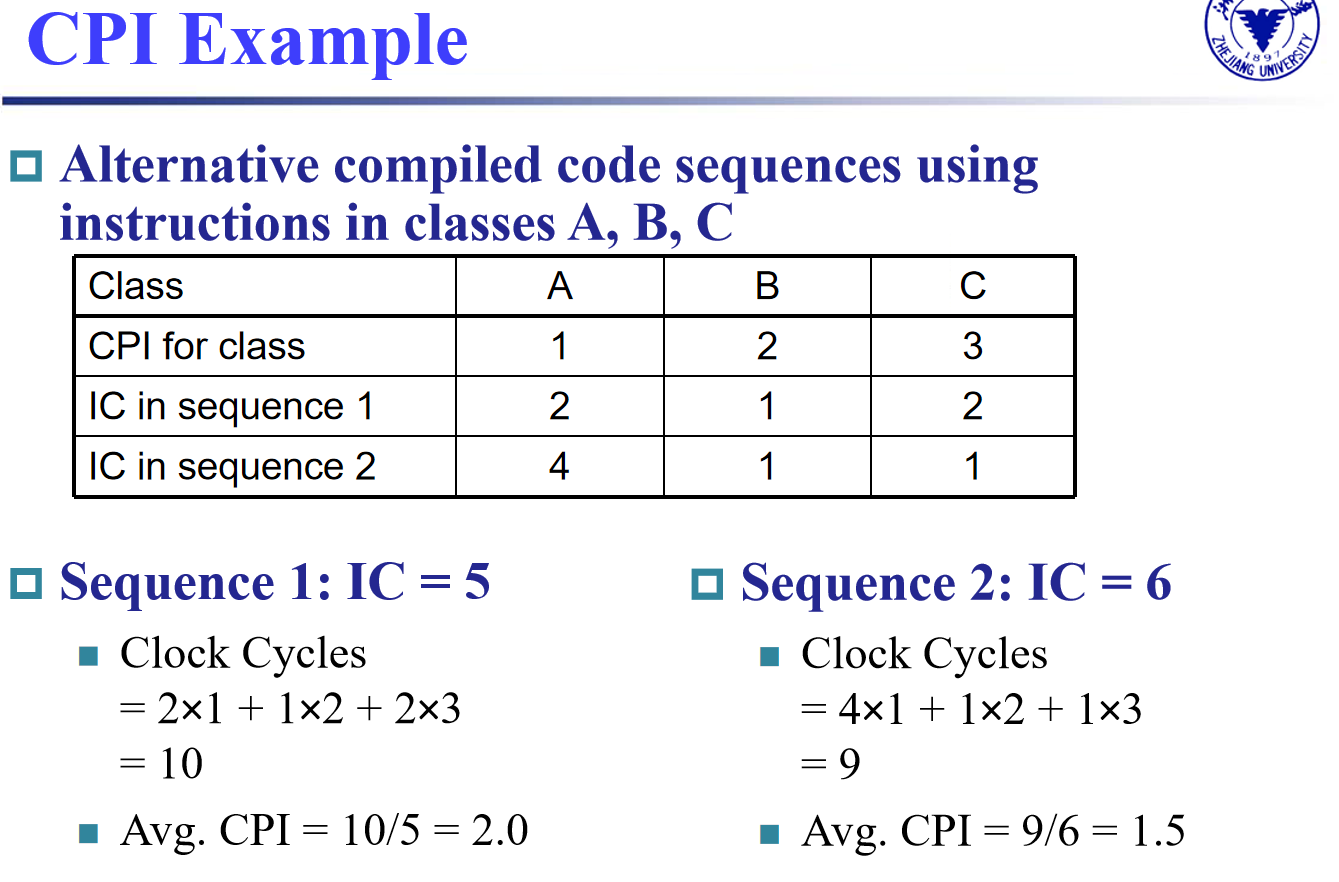
example
- MIPS: Millions of Instructions Per Second

Eight Great Ideas¶
-
Design for Moore’s Law (设计紧跟摩尔定律)
-
Use Abstraction to Simplify Design ( 采用抽象简化设计 )
-
Make the Common Case Fast ( 加速大概率事件 )
-
Performance via Parallelism ( 通过并行提高性能 )
-
Performance via Pipelining ( 通过流水线提高性能 )
-
Performance via Prediction ( 通过预测提高性能 )
-
Hierarchy of Memories ( 存储器层次 )
-
Dependability via Redundancy ( 通过冗余提高可靠性)
补充¶
Power Trend¶
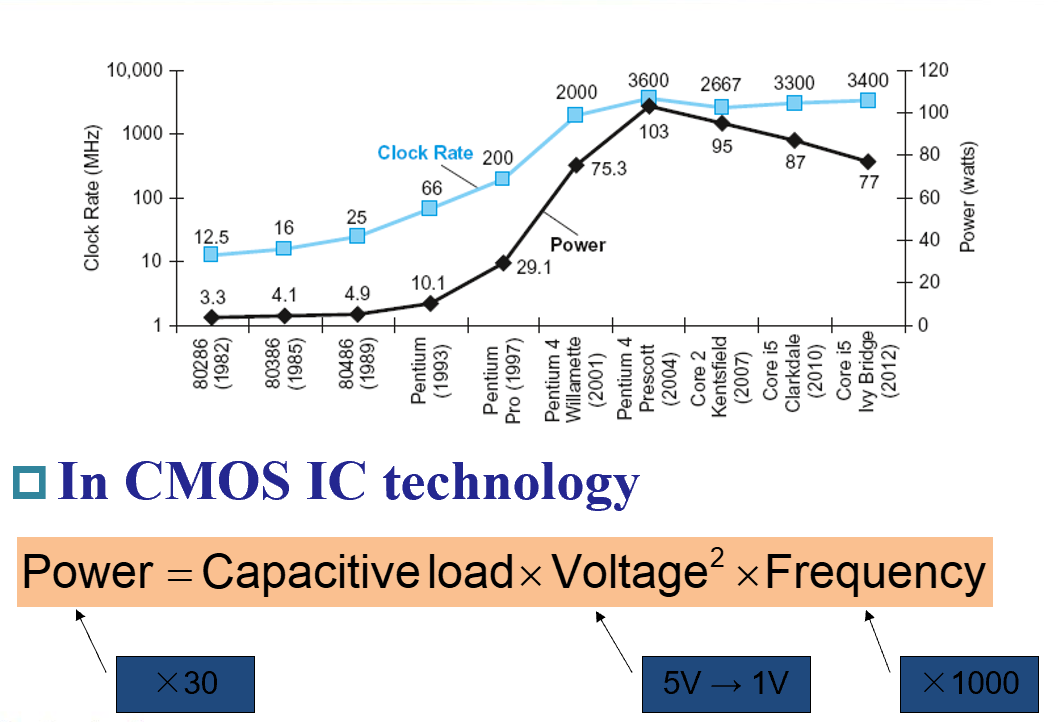
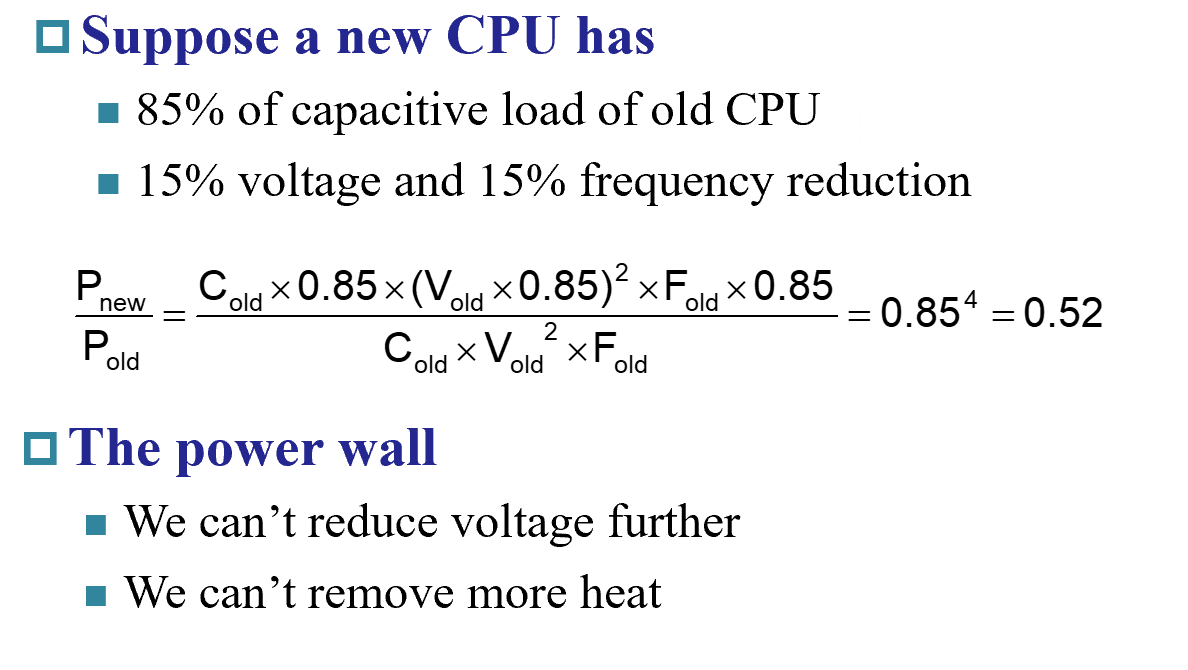
期中考到了, 题目大意跟上图一致,计算$\frac{P_{new}}{P_{old}}$
题目¶
Eight Idea¶